Abstract
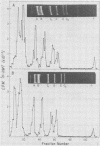
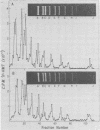
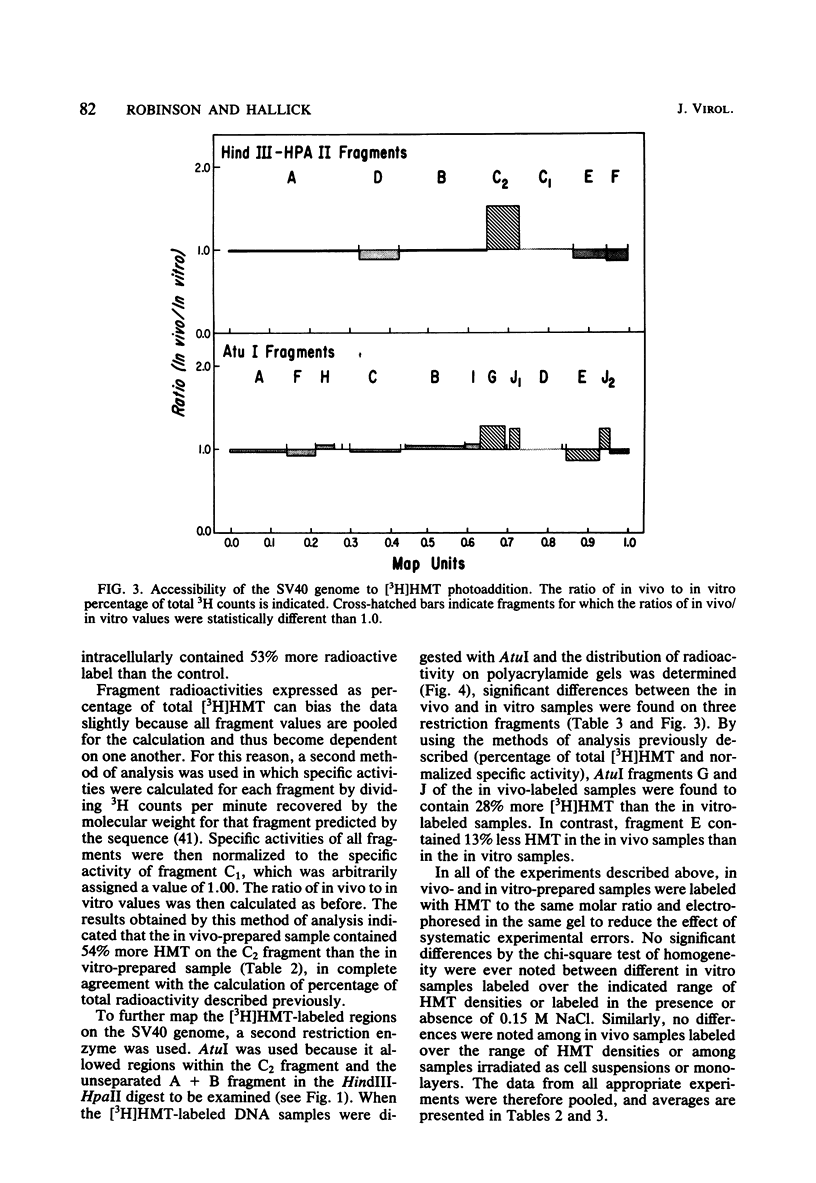
Intracellular simian virus 40 (SV40) chromatin was photoreacted with a 3H-labeled psoralen derivative, hydroxymethyltrimethylpsoralen (HMT), at 48 h postinfection. Psoralen compounds have been shown to readily penetrate intact cells and, in the presence of long-wavelength UV light, form covalent adducts to DNA, preferentially at regions unprotected by nucleosomes. The average distribution pattern of [3H]HMT on the SV40 genome was determined by specific activity measurements of the DNA fragments generated by HindIII plus HpaII or by AtuI restriction enzyme digestion. At levels of 1 to 10 [3H]HMT photoadducts per SV40 molecule, the radiolabel was found to be distributed nonrandomly. Comparison of the labeling pattern in vivo with that of purified SV40 DNA labeled in vitro revealed one major difference. A region of approximately 400 base pairs, located between 0.65 and 0.73 on the physical map, was preferentially labeled under in vivo conditions. This finding strongly suggests that the highly accessible region near the origin of replication, previously observed on isolated SV40 "minichromosomes," exists on SV40 chromatin in vivo during a lytic infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beard P., Kaneko M., Cerutti P. N-Acetoxy-acetylaminofluorene reacts preferentially with a control region of intracellular SV40 chromosome. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):84–85. doi: 10.1038/291084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Potter D., Pardue M. L. Chromatin structure in living cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):191–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T., Pardue M. L. Cross-linking of DNA with trimethylpsoralen is a probe for chromatin structure. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):631–640. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. S. Light-induced cross-linking of DNA in the presence of a furocoumarin (psoralen). Studies with phage lambda, Escherichia coli, and mouse leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 17;217(1):30–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K., Tegtmeyer P., Anthony D. D. Relationship of replication and transcription of Simian Virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1927–1930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crémisi C., Pignatti P. F., Yaniv M. Random location and absence of movement of the nucleosomes on SV 40 nucleoprotein complex isolated from infected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):548–554. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90845-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K. J., Sack G. H., Jr, Nathans D. Studies of simian virus 40 DNA. VII. A cleavage map of the SV40 genome. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G. C., Allison D. P., Niyogi S. K. Sites including those of origin and termination of replication are not freely available to single-cut restriction endonucleases in the supercompact form of simian virus 40 minichromosome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90937-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):115–122. doi: 10.1038/271115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Seidman M. M., Levine A. J. The detection and characterization of multiple forms of SV40 nucleoprotein complexes. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariglio P., Llopis R., Oudet P., Chambon P. The template of the isolated native simian virus 40 transcriptional complexes is a minichromosome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 15;131(1):75–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90302-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. H., Brooks T. L. Isolation of two forms of SV40 nucleoprotein containing RNA polymerase from infected monkey cells. Virology. 1976 Jul 1;72(1):110–120. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutai M. W., Nathans D. Evolutionary variants of simian virus 40: Nucleotide sequence of a conserved SV40 DNA segment containing the origin of viral DNA replication as an inverted repetition. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90362-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick L. M., Yokota H. A., Bartholomew J. C., Hearst J. E. Photochemical addition of the cross-linking reagent 4,5', 8-trimethylpsoralen (trioxaslen) to intracellular and viral simian virus 40 DNA-histone complexes. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):127–135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.127-135.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson C. V., Shen C. K., Hearst J. E. Cross-linking of DNA in situ as a probe for chromatin structure. Science. 1976 Jul 2;193(4247):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.935855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J. P., Scott W. A. Distribution of DNase I-sensitive sites in simian virus 40 nucleoprotein complexes from disrupted virus particles. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):908–915. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.908-915.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. E., Hearst J. E. Binding of psoralen derivatives to DNA and chromatin: influence of the ionic environment on dark binding and photoreactivity. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1251–1257. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs S. T., Shen C. K., Hearst J. E., Rapoport H. Synthesis and characterization of new psoralen derivatives with superior photoreactivity with DNA and RNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1058–1064. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessel D., Landau T., Hudson J., Lalor T., Tenen D., Livingston D. M. Identification of regions of the SV40 genome which contain preferred SV40 T antigen-binding sites. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauch C. H., Krämer D. M., Wacker A. Zum Wirkungsmechanismus photodynamischer Furocumarine Photoreaktion von Psoralen-(4-14C) mit DNS, RNS, Homopolynucleotiden und Nucleosiden. Photochem Photobiol. 1967 May;6(5):341–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1967.tb08882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Nathans D. A map of temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):70–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBon J. M., Kado C. I., Rosenthal L. J., Chirikjian J. G. DNA modifying enzymes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: effect of DNA topoisomerase, restriction endonuclease, and unique DNA endonuclease on plasmid and plant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4097–4101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggins G. L., English M., Goldstein D. A. Structural changes in simian virus 40 chromatin as probed by restriction endonucleases. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):718–732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.718-732.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Precise location of DNase I cutting sites in the nucleosome core determined by high resolution gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):41–56. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K., Hunter T. Association of simian virus 40 T antigen with simian virus 40 nucleoprotein complexes. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):232–241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.232-241.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musajo L., Rodighiero G., Breccia A., Dall'Acqua F., Malesani G. Skin-photosensitizing furocoumarins: photochemical interaction between DNA and -O14CH3 bergapten (5-methoxy-psoralen). Photochem Photobiol. 1966 Sep;5(9):739–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1966.tb05823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans D., Danna K. J. Specific origin in SV40 DNA replication. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 19;236(68):200–202. doi: 10.1038/newbio236200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak M. A., Krämer D. M. Photosensitization of skin in vivo by furocoumarins (psoralens). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 19;195(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B., McCarthy B. Location of histones on simian virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2895–2899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. A., Crawford L. V. The arrangement of nucleosomes in nucleoprotein complexes from polyoma virus and SV40. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):35–49. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Shure M., Vinograd J. The quantitation of fluorescence by photography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1409–1418. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Piatak M., Weissman S. M. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's. I. Genomic localization of 3' and 5' termini and two major splices in mRNA from transformed and lytically infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):279–296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.279-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Ferguson J., Davis R. W., Stark G. R. T antigen binds to simian virus 40 DNA at the origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1605–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser J., Renart J., Crawford L. V., Stark G. R. Specific association of simian virus 40 tumor antigen with simian virus 40 chromatin. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):78–87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.78-87.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D., Robbins A., Myers R., Tjian R. Regulation of simian virus 40 early transcription in vitro by a purified tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5706–5710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Brockman W. W., Nathans D. Biological activities of deletion mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1976 Dec;75(2):319–334. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Wigmore D. J. Sites in simian virus 40 chromatin which are preferentially cleaved by endonucleases. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa M., Sugano S., Yamaguchi N. Association of simian virus 40 T antigen with replicating nucleoprotein complexes of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):320–330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.320-330.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M., Garber E., Levine A. J. Parameters affecting the stability of SV40 virions during the extraction of nucleoprotein complexes. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):256–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton E. R., Wassarman P. M., DePamphilis M. L. Structure, spacing, and phasing of nucleosomes on isolated forms of mature simian virus 40 chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):771–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D. R., Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of the simian virus 40 replicon: pseudorevertants of mutants with a defective replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Shenk T. Definition of the boundaries of the origin of DNA replication in simian virus 40. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3635–3642. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Staphylococcal nuclease makes a single non-random cut in the simian virus 40 viral minichromosome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):535–546. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Radonovich M. F., Salzman N. P. Characterization of the 5'-terminal structure of simian virus 40 early mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):437–446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.437-446.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Holde K. E., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Shaw B. R. A model for particulate structure in chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1579–1586. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Chumackov P. M., Georgiev G. P. Minichromosome of simian virus 40: presence of histone HI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):2101–2113. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.2101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Georgiev G. P. Heterogeneity of chromatin subunits in vitro and location of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):477–492. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O. H., Bohn M. J. SV40 viral minichromosome: preferential exposure of the origin of replication as probed by restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3469–3477. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Föhring B., Chowdhury K., Gruss P., Sauer G. Origin of DNA replication in papovavirus chromatin is recognized by endogenous endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5964–5968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Removal of histone H1 exposes a fifty base pair DNA segment between nucleosomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3307–3314. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieshahn G. P., Hyde J. E., Hearst J. E. The photoaddition of trimethylpsoralen to Drosophila melanogaster nuclei: a probe for chromatin substructure. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):925–932. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]