Abstract
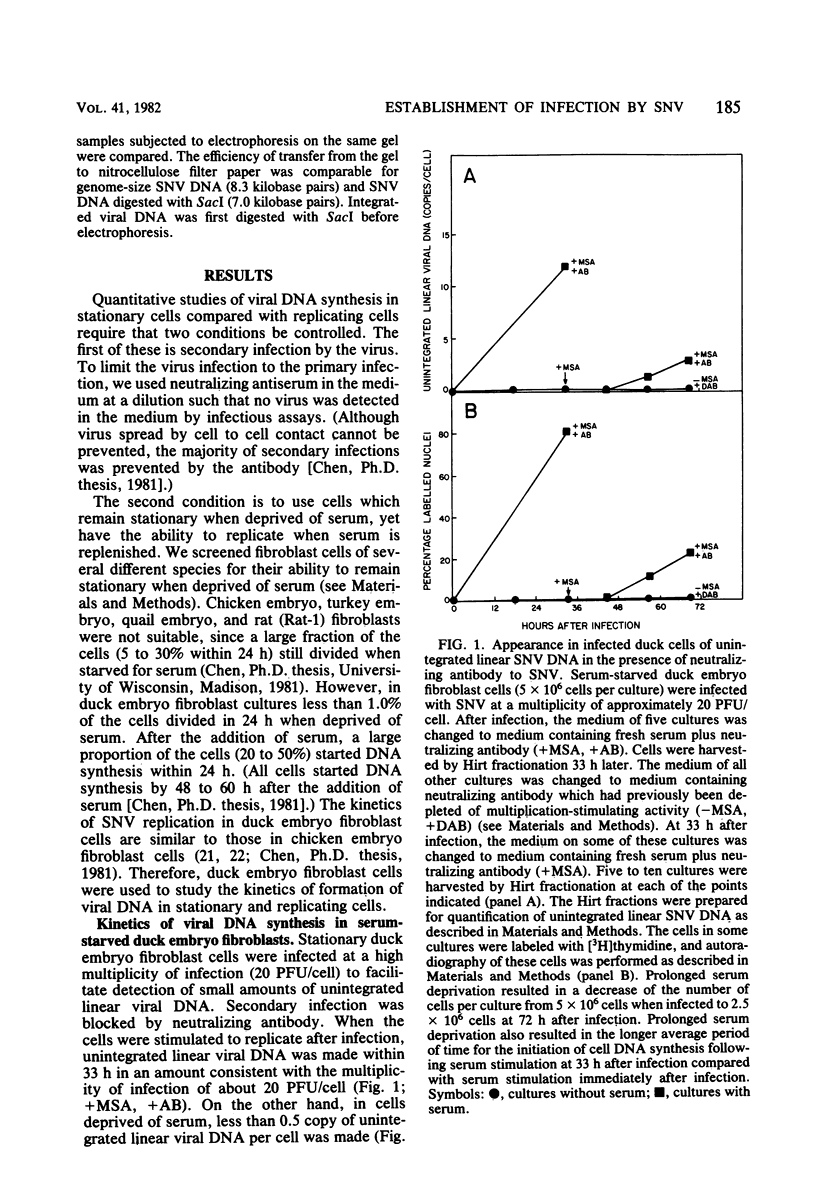
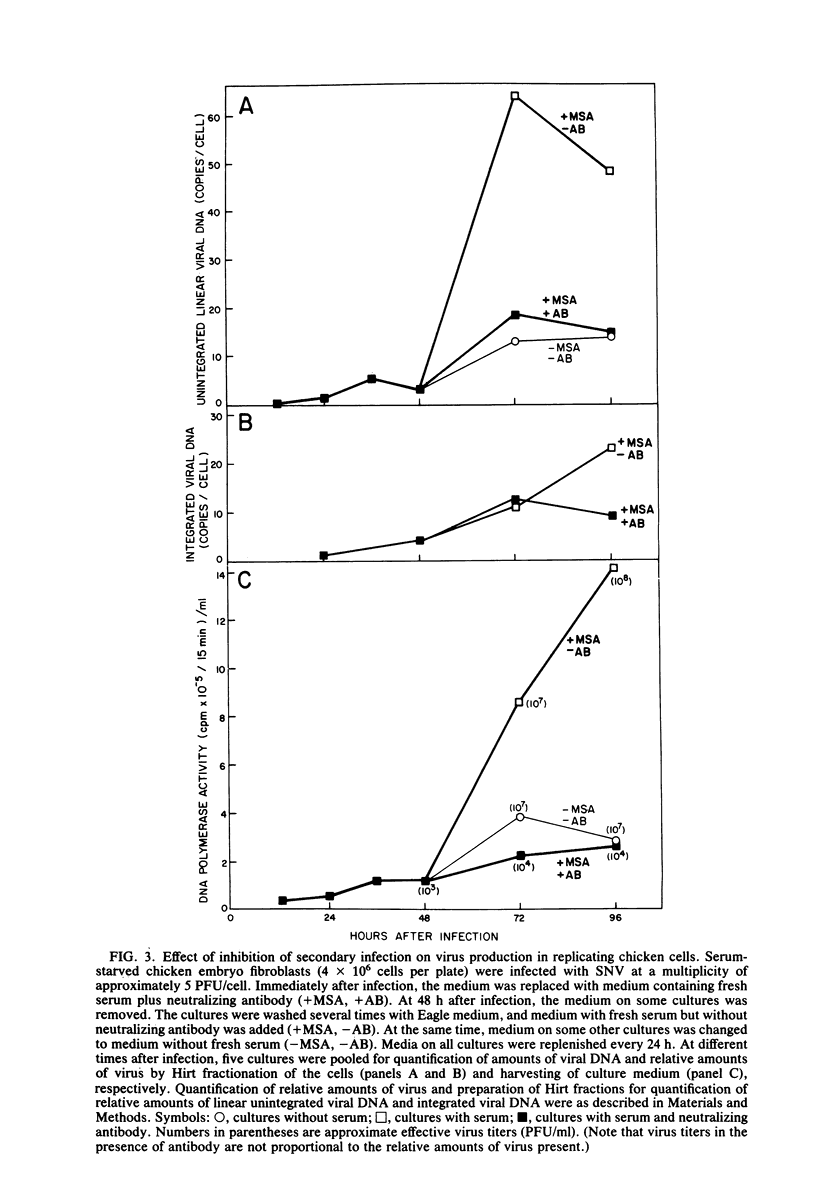
The relationship of two early events in the establishment of infection by avian retroviruses, the inhibition of viral DNA synthesis in stationary avian cells and the secondary infection which occurs after infection of replicating cells, was investigated. When neutralizing antibody to spleen necrosis virus was used to prevent secondary infection, the amount of unintegrated linear spleen necrosis virus DNA detected was much lower in infected stationary cells than in infected replicating cells. The amount of unintegrated linear spleen necrosis virus DNA in stationary cells was less than one copy per cell even at high multiplicities of infection. Viral DNA synthesis resumed after stimulation of the cells to replicate. The time of this viral DNA synthesis was closely correlated with renewed cellular DNA synthesis. In addition, blocking secondary infection of replicating cells prevented the rate of virus production from reaching the high levels usually associated with a normal productive infection by SNV. Virus production increased if secondary infection was allowed. However, this rise in virus production was not proportional to the amounts of viral DNA integrated after secondary infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avery R. J., Norton J. D., Jones J. S., Burke D. C., Morris A. G. Interferon inhibits transformation by murine sarcoma viruses before integration of provirus. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):93–95. doi: 10.1038/288093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boettiger D., Temin H. M. Light inactivation of focus formation by chicken embryo fibroblasts infected with avian sarcoma virus in the presence of 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):622–624. doi: 10.1038/228622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Temin H. M. Ribonucleotides in unintegrated linear spleen necrosis virus DNA. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1058–1073. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1058-1073.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E. F., Temin H. M. Inhibition of viral DNA synthesis in stationary chicken embryo fibroblasts infected with avian retroviruses. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.461-469.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E., Temin H. M. Formation and structure of infectious DNA of spleen necrosis virus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):119–130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.119-130.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries E. H., Glover C., Reichmann M. E. Rous sarcoma virus infection of synchronized cells establishes provirus integration during S-phase DNA synthesis prior to cellular division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2601–2605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries E. H., Temin H. M. Cell cycle-dependent activation of rous sarcoma virus-infected stationary chicken cells: avian leukosis virus group-specific antigens and ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.82-87.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries E. H., Temin H. M. Requirement for cell division for initiation of transcription of Rous sarcoma virus RNA. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):531–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.531-546.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Temin H. M. Reticuloendotheliosis virus nucleic acid sequences in cellular DNA. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1179–1188. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1179-1188.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., O'Rear J. J., Temin H. M. DNA of noninfectious and infectious integrated spleen necrosis virus (SNV) is colinear with unintegrated SNV DNA and not grossly abnormal. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., Temin H. M. Cell killing by spleen necrosis virus is correlated with a transient accumulation of spleen necrosis virus DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):376–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.376-388.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. K., Temin H. M. Carcinogenesis by RNA sarcoma viruses. XIV. Infection of stationary cultures with murine sarcoma virus (Harvey). Int J Cancer. 1970 May 15;5(3):320–326. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910050304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rear J. J., Mizutani S., Hoffman G., Fiandt M., Temin H. M. Infectious and noninfectious recombinant clones of the provirus of SNV differ in cellular DNA and are apparently the same in viral DNA. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):423–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90628-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Carcinogenesis by avian sarcoma viruses. Cancer Res. 1968 Sep;28(9):1835–1838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Kassner V. K. Replication of reticuloendotheliosis viruses in cell culture: acute infection. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):291–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.291-297.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Kassner V. K. Replication of reticuloendotheliosis viruses in cell culture: chronic infection. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):267–274. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Stimulation by serum of multiplication of stationary chicken cells. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Oct;78(2):161–170. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Heasley S., Kung H. J., Oppermann H., Smith V. C., Bishop J. M., Shank P. R. Kinetics of synthesis, structure and purification of avian sarcoma virus-specific DNA made in the cytoplasm of acutely infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):55–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Joy A. E., Temin H. M. Correlation between cell killing and massive second-round superinfection by members of some subgroups of avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):494–506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.494-506.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Temin H. M. Cell killing by avian leukosis viruses. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):713–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.713-721.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]