Abstract
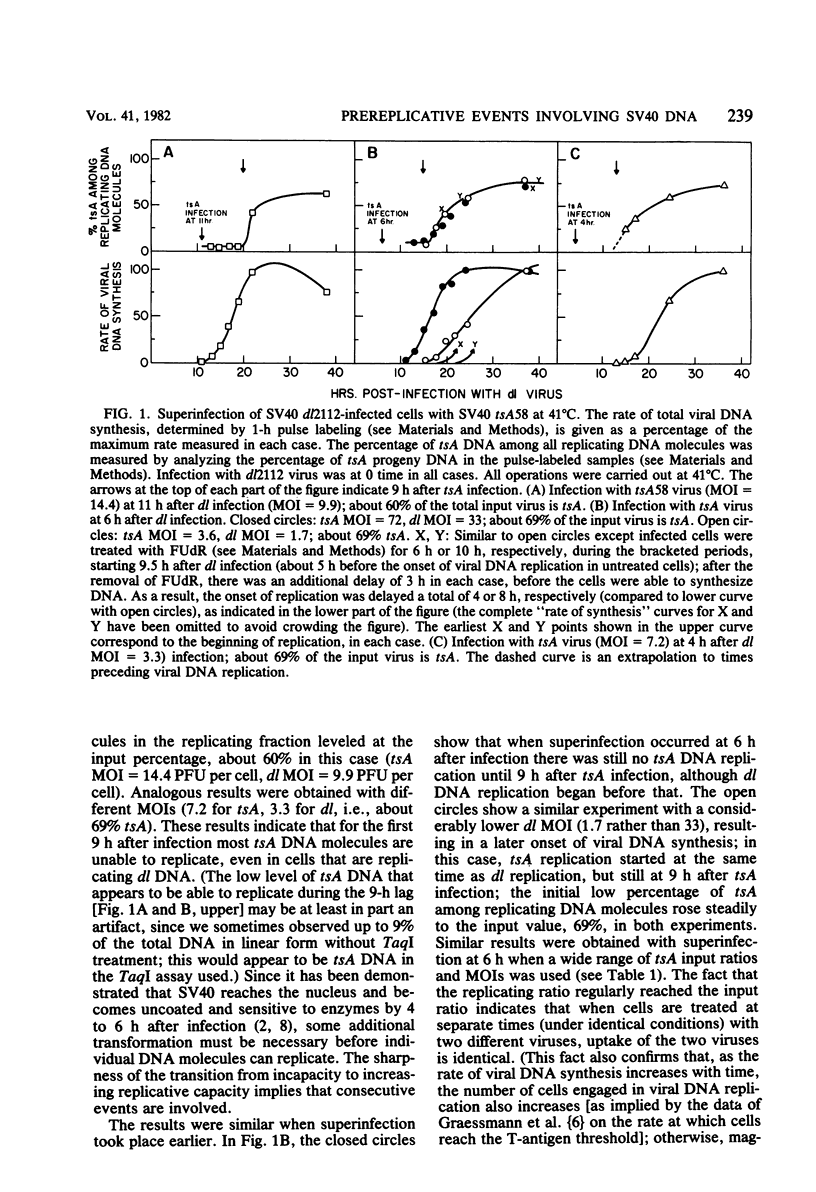
Simian virus 40 DNA molecules were found to be unable to replicate for 9 h after infection, even in cells that were already replicating the DNA of preinfecting simian virus 40; after 9 h, the ability of the DNA to replicate began to rise sharply. The kinetics of activation indicated that each DNA molecule undergoes a series of slow consecutive reactions, not involving T-antigen, before it can replicate. These pre-replicative molecular transformations probably involve configurational changes; their nature and their relation to the initiation of viral DNA synthesis is discussed. Observation of the replicative behavior of one viral DNA in the presence of another was made possible by the use of two different mutants with distinguishable DNAs: a viable deletion mutant containing DNA insensitive to TAqI restriction enzyme was used to provide viral functions required for replication, and a tsA mutant with TaqI-sensitive DNA was introduced at various times as a probe to determine the ability of the DNA to replicate under different conditions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbanti-Brodano G., Swetly P., Koprowski H. Early events in the infection of permissive cells with simian virus 40: adsorption, penetration, and uncoating. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):78–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.78-86.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan P. An electron microscopic comparison of transcription on linear and superhelical DNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):161–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feunteun J., Kress M., Gardes M., Monier R. Viable deletion mutants in the simian virus 40 early region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Hirt B., Oudet P., Gross-Bellark M., Chambon P. Folding of the DNA double helix in chromatin-like structures from simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummeler K., Tomassini N., Sokol F. Morphological aspects of the uptake of simian virus 40 by permissive cells. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.87-93.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay E., Roychoudhury R., Wu R. Nucleotide sequence with elements of an unusual two-fold rotational symmetry in the region of origin of replication of SV40 DNA+. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 5;69(3):678–686. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90929-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Characterization of purified DNA-relaxing enzyme from human tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2550–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pages J., Manteuil S., Stehelin D., Fiszman M., Marx M., Girard M. Relationship between replication of simian virus 40 DNA and specific events of the host cell cycle. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.99-107.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Initiation of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase from supercoiled and non-supercoiled bacteriophage PM2 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 5;91(4):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M. E., Thoenen H. Selective binding, uptake, and retrograde transport of tetanus toxin by nerve terminals in the rat iris. An electron microscope study using colloidal gold as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1978 Apr;77(1):1–13. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K., Hearst J. E. Mapping of sequences with 2-fold symmetry on the simian virus 40 genome: a photochemical crosslinking approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1363–1367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Warnaar S. O., Winocour E. Isolation and characterization of simian virus 40 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.193-201.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Champoux J. J. Interaction of the DNA untwisting enzyme with the SV40 nucleoprotein complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):623–635. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



