Abstract
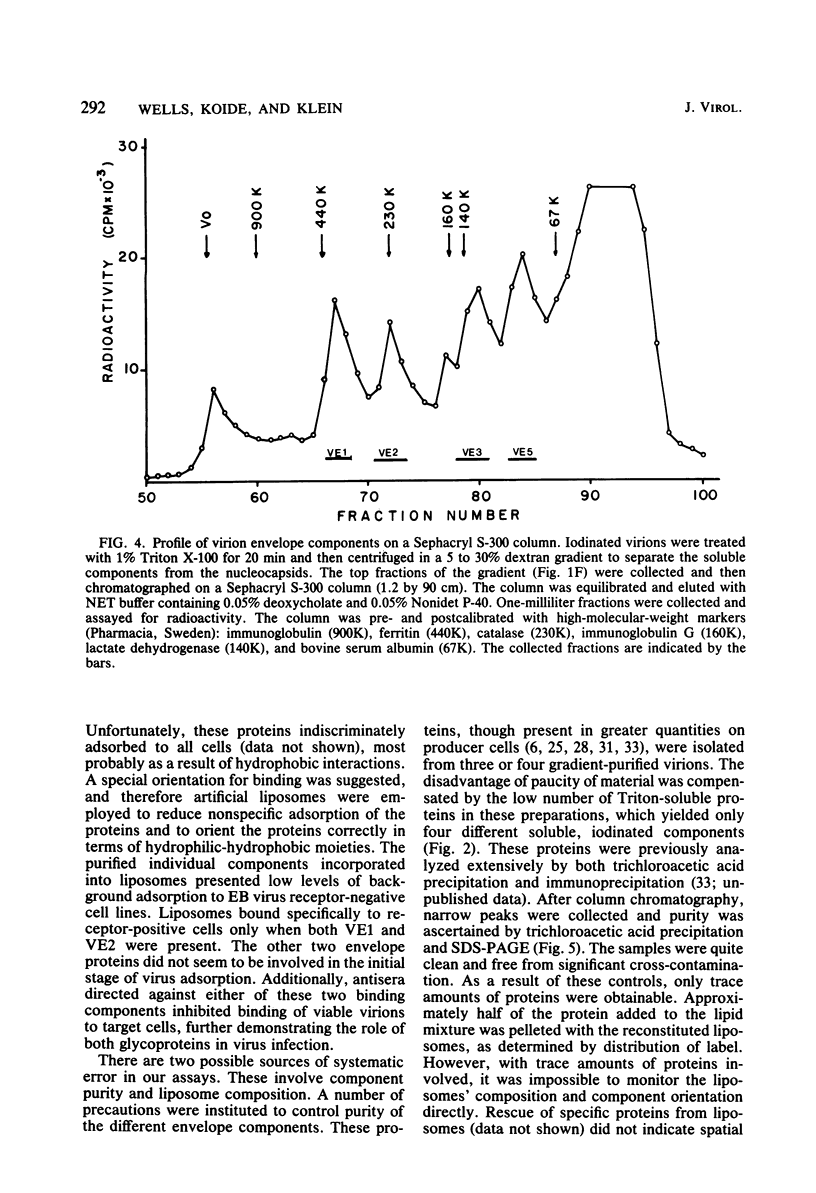
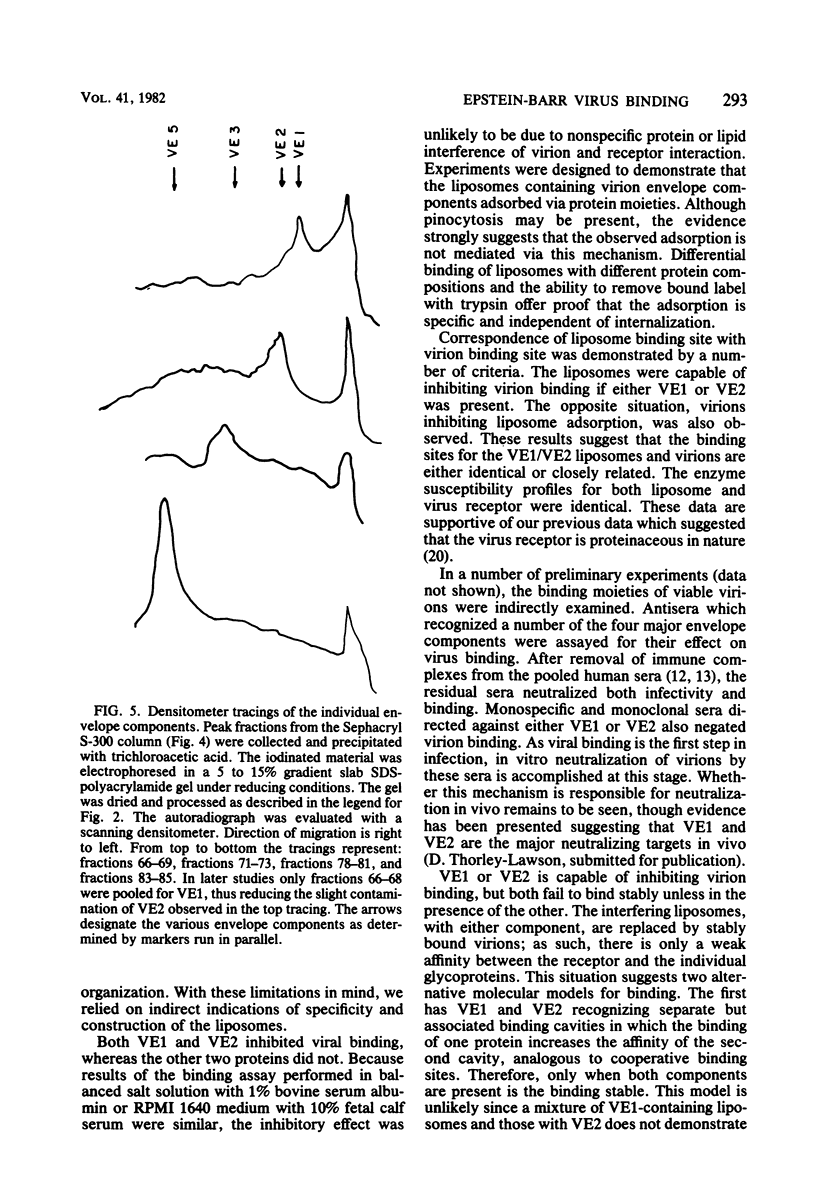
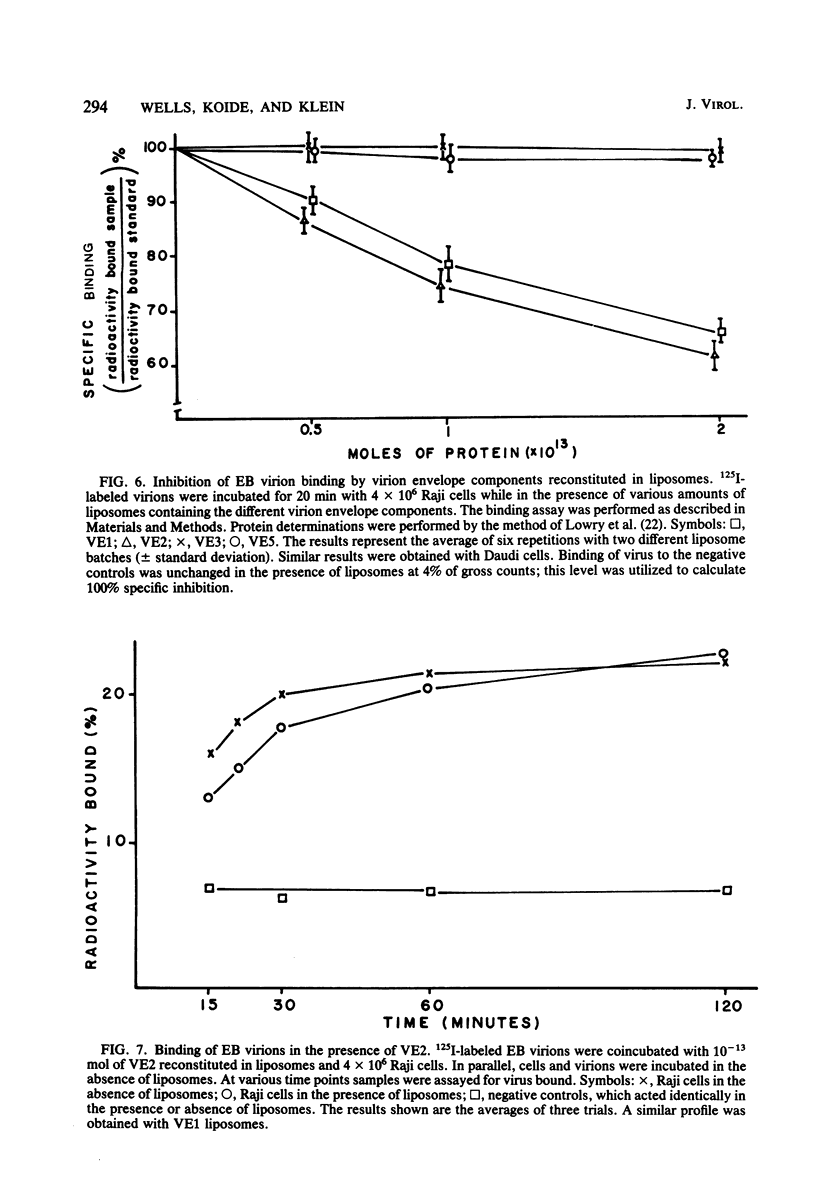
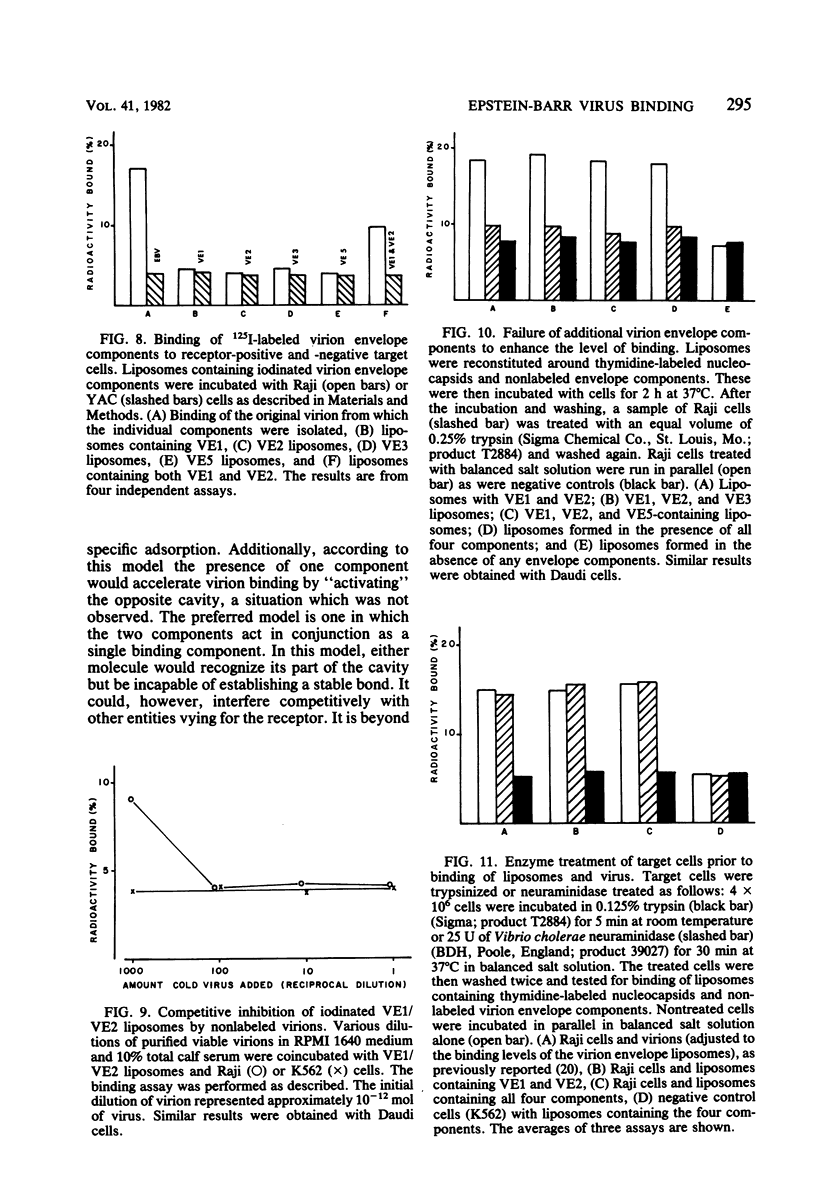
The four major Epstein-Barr virion envelope components were separated by column chromatography and reconstituted into artificial liposomes. These liposomes were tested for their ability to bind selectively to Epstein-Barr virus receptor-positive cells. Only when the two high-molecular-weight glycoproteins, VE1 and VE2, were present together was a stable binding complex formed. The addition of the other virion envelope components did not increase the levels of binding. This binding was inhibited by unlabeled viable virions and by neutralizing antisera, which recognized the two components. Adsorption of viable virus was also eliminated by the antisera. The enzyme susceptibility pattern of the cell-liposome interaction is similar to that of the virus-cell interaction, thus confirming the specificity of the binding site. A model for Epstein-Barr virus binding in which VE1 and VE2 coordinately recognize the same binding site is presented.
Full text
PDF


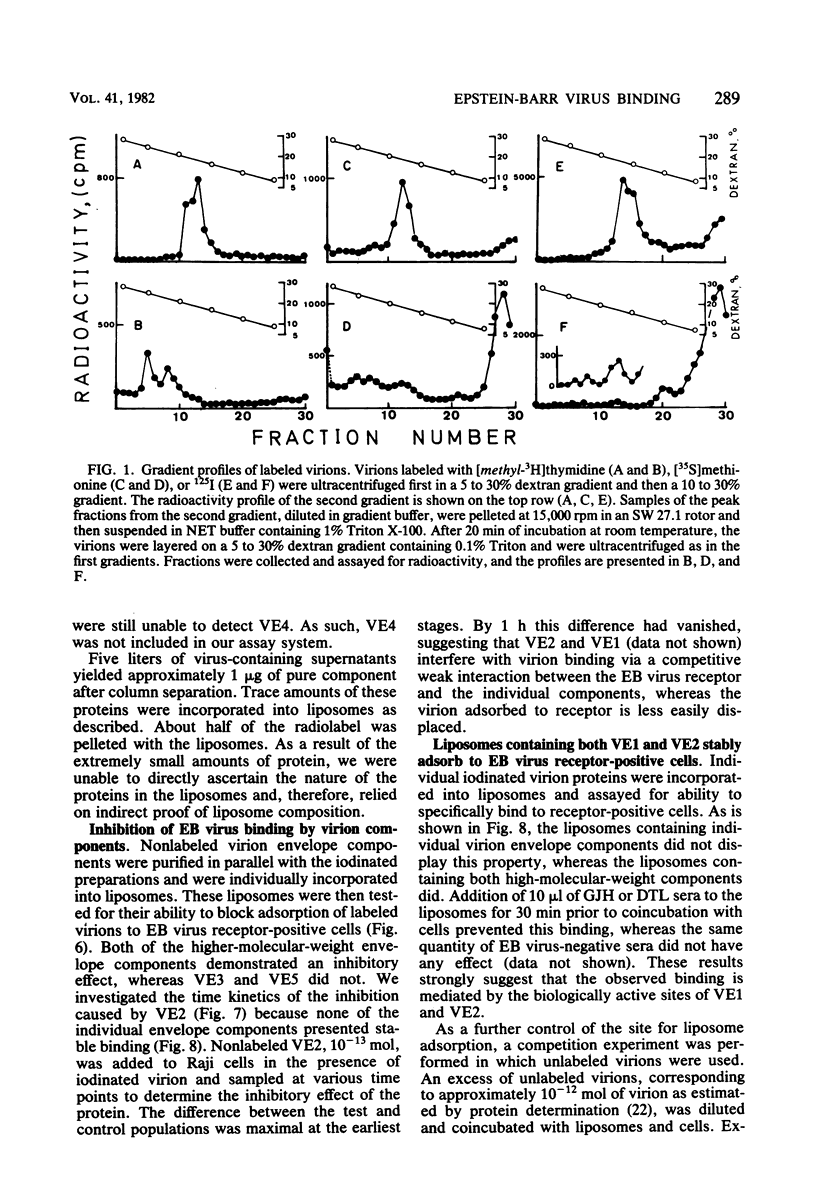
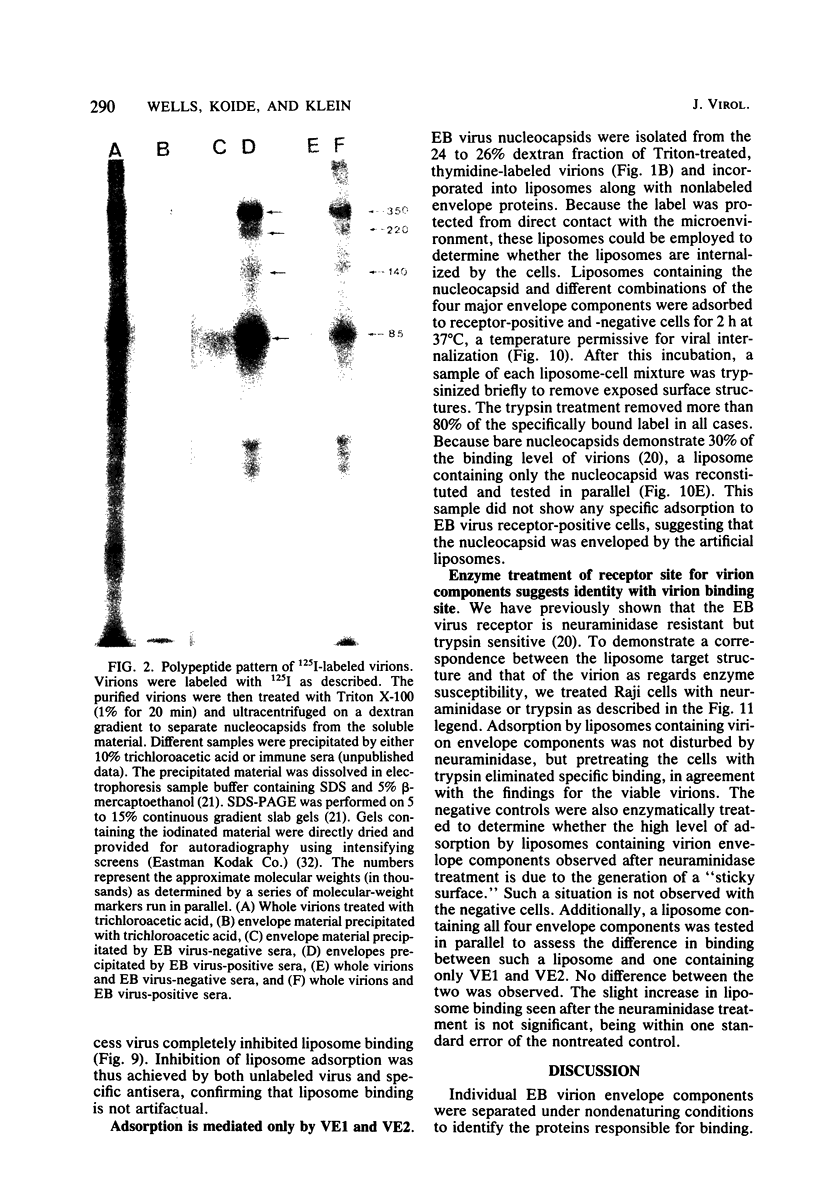
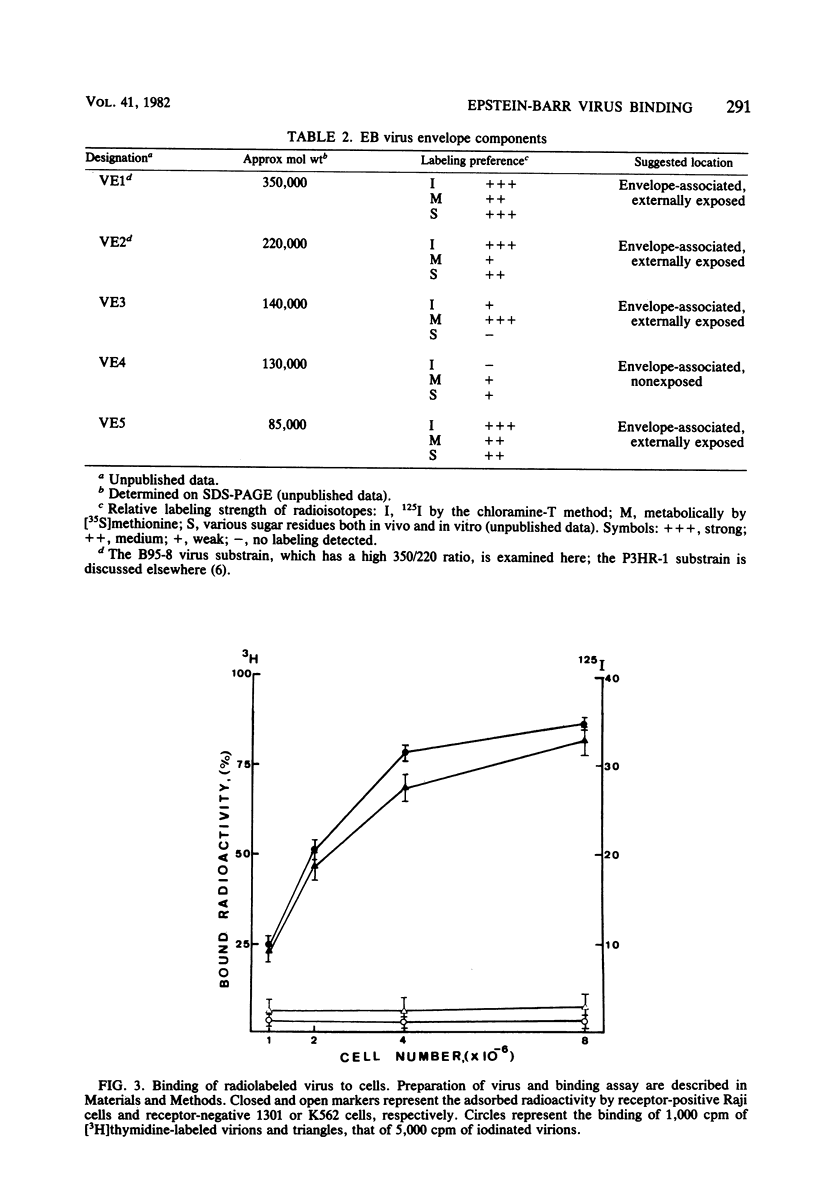


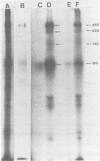
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu Sinna G., Lundgren E., Nilsson K., Roos G. Isozymes of amino acid naphthylamidase in human haematopoietic cell lines. Br J Haematol. 1980 Jan;44(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb01180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acuto O., Pugliese O., Müller M., Tosi R. Preparation of liposomes incorporating membrane components from human lymphoid cells. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Nov;14(5):385–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb00867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coope D., Heston L., Brandsma J., Miller G. Cross-neutralization of infectious mononucleosis and Burkitt lymphoma strains of Epstein-Barr virus with hyperimmune rabbit antisera. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):232–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolyniuk M., Pritchett R., Kieff E. Proteins of Epstein-Barr virus. I. Analysis of the polypeptides of purified enveloped Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):935–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.935-949.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolyniuk M., Wolff E., Kieff E. Proteins of Epstein-Barr Virus. II. Electrophoretic analysis of the polypeptides of the nucleocapsid and the glucosamine- and polysaccharide-containing components of enveloped virus. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):289–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.289-297.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson C. M., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigens: characterization, distribution, and strain differences. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):172–184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.172-184.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G., Barr Y. M., Zajac B., Henle G., Henle W. Morphological and virological investigations on cultured Burkitt tumor lymphoblasts (strain Raji). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Oct;37(4):547–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY G. E., LAZARUS H., FARBER S., UZMAN B. G., BOONE B. A., MCCARTHY R. E. CONTINUOUS CULTURE OF HUMAN LYMPHOBLASTS FROM PERIPHERAL BLOOD OF A CHILD WITH ACUTE LEUKEMIA. Cancer. 1965 Apr;18:522–529. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196504)18:4<522::aid-cncr2820180418>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Wolf H., Bornkamm G. W. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus genes in different cell types after microinjection of viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):433–436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood A. M. Characteristics of Sendai virus receptors in a model membrane. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90504-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer R., Klein G. Circulating immune complexes in sera of patients with Burkett's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Sep 15;18(3):310–316. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer R., Klein G. The affinity of soluble immune complexes for concanavalin A. Scand J Immunol. 1978 Apr;7(4):315–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman G. J., Lazarowitz S. G., Hayward S. D. Monoclonal antibody against a 250,000-dalton glycoprotein of Epstein-Barr virus identifies a membrane antigen and a neutralizing antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2979–2983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. C., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Reconstitution of membranes with individual paramyxovirus glycoproteins and phospholipid in cholate solution. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):476–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Luka J., Klein G. Immunochemical characterization of Epstein-Barr virus-associated early and late antigens in n-butyrate-treated P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):710–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.710-716.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Manneborg A., Steinitz M. Differences in EBV receptor concentration between in vitro EBV-converted lymphoma sublines reflect biological differences between the converting viral substrains. Int J Cancer. 1979 Feb;23(2):197–200. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Yefenof E., Falk K., Westman A. Relationship between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-production and the loss of the EBV receptor/complement receptor complex in a series of sublines derived from the same original Burkitt's lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1978 May 15;21(5):552–560. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide N., Wells A., Volsky D. J., Shapiro I. M., Klein G. The detection of Epstein-Barr virus receptors utilizing radiolabelled virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):191–195. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuller-Lantzsch N., Georg B., Yamamoto N., zur Hausen H. Epstein-Barr virus-induced proteins. II. Analysis of surface polypeptides from EBV-producing and -superinfected cells by immunoprecipitation. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Lantzsch N., Yamamoto N., zur Hausen H. Analysis of early and late Epstein-Barr virus associated polypeptides by immunoprecipitation. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):378–387. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B. Immunochemistry of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1980;90:67–106. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67717-5_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualtiere L. F., Pearson G. R. Radioimmune precipitation study comparing the Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigens expressed on P3HR-1 virus-superinfected Raji cells to those expressed on cells in a B-95 virus-transformed producer culture activated with tumor-promoting agent (TPA). Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):360–369. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestre D., Kourilsky F. M., Klein G., Yata Y., Neauport-Sautes C., Levy J. P. Relationship between the EBV-associated membrane antigen on Burkitt lymphoma cells and the viral envelope, demonstrated by immunoferritin labelling. Int J Cancer. 1971 Sep 15;8(2):222–233. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Shank P. R. X-Ray Intensifying Screens Greatly Enhance the Detection by Autoradiography of the Radioactive Isotopes 32P and 125I. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Edson C. M. Polypeptides of the Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigen complex. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):458–467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.458-467.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Geilinger K. Monoclonal antibodies against the major glycoprotein (gp350/220) of Epstein-Barr virus neutralize infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5307–5311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volsky D. J., Shapiro I. M., Klein G. Transfer of Epstein-Barr virus receptors to receptor-negative cells permits virus penetration and antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A., Koide N., Klein G. Difference in viral binding between two Epstein-Barr virus substrains to a spectrum of receptor-positive target cells. Int J Cancer. 1981 Mar 15;27(3):303–309. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yefenof E., Klein G., Kvarnung K. Relationships between complement activation, complement binding, and EBV absorption by human hematopoietic cell lines. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jun 15;31(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]