Abstract
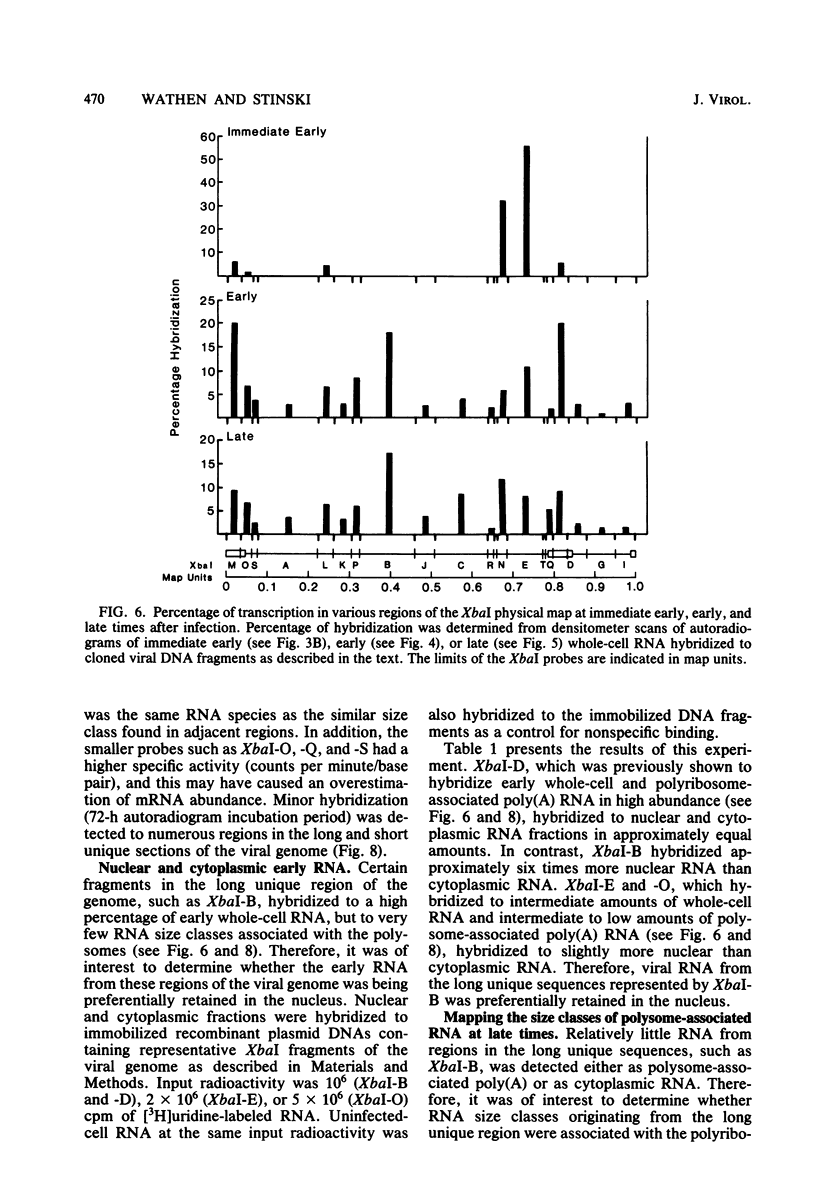
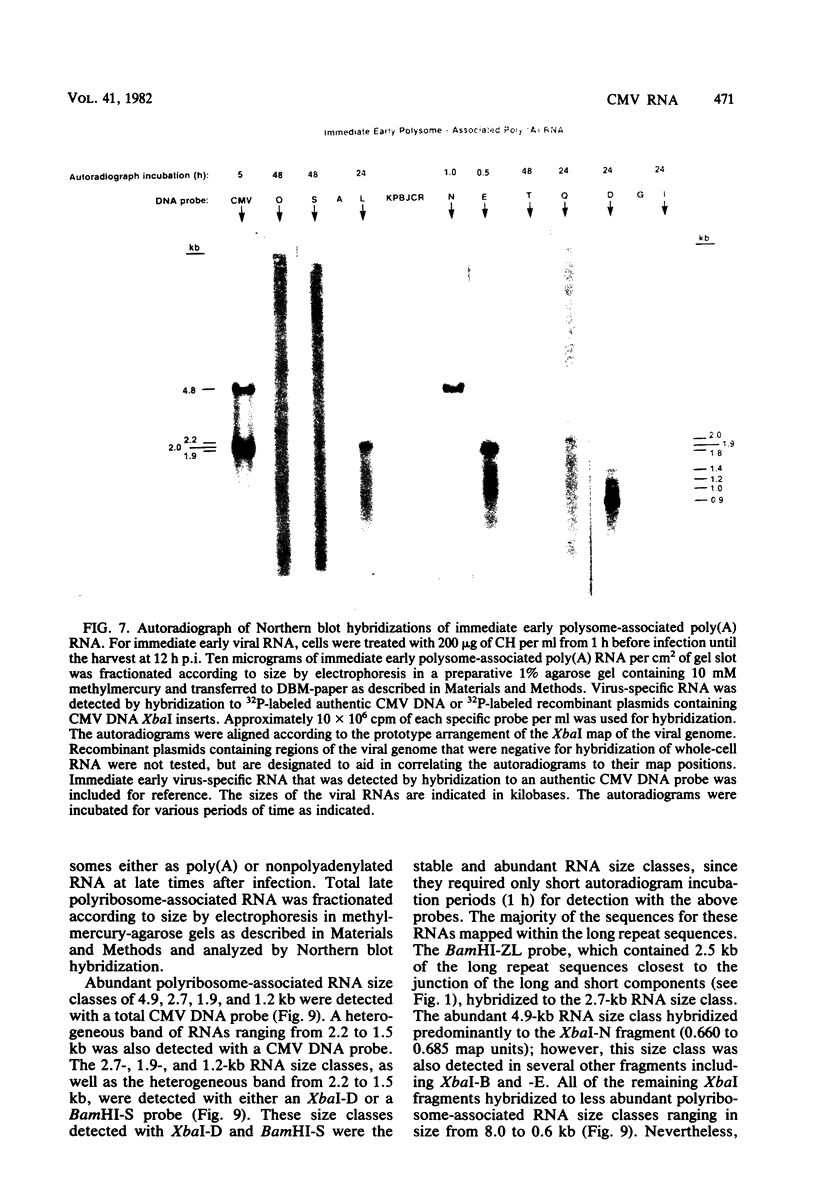
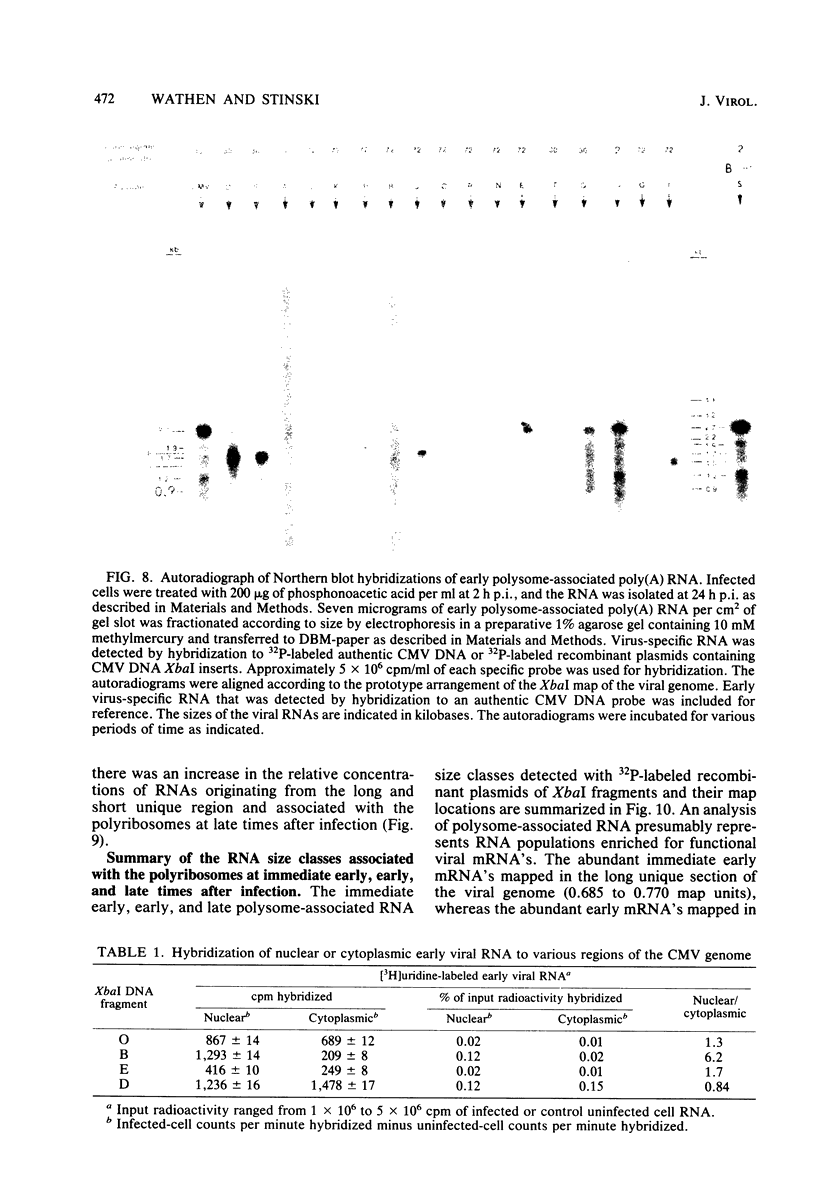
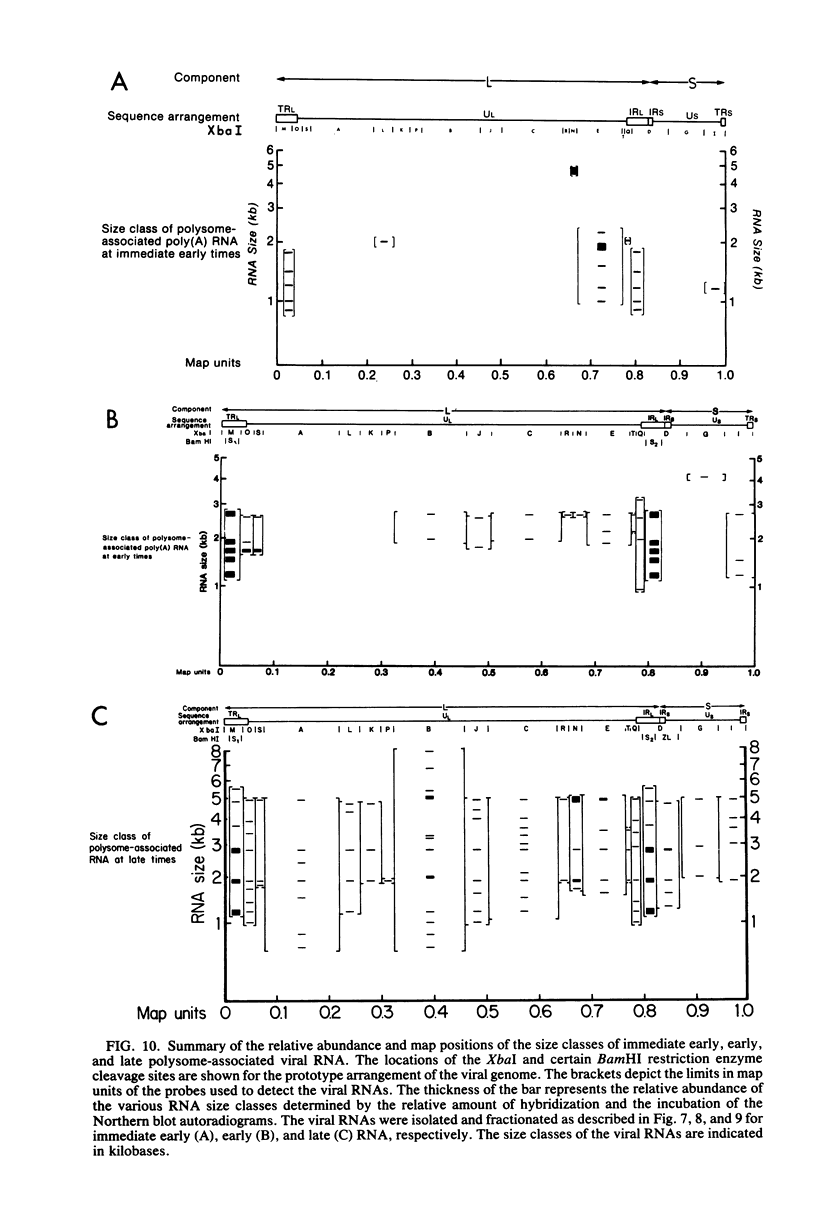
The transcription of the human cytomegalovirus genome was investigated at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. Viral RNAs associated with either the whole cell, the nucleus, the cytoplasm, or the polyribosomes were analyzed. At immediate early times, i.e., in the absence of de novo viral protein synthesis, the viral RNA in high abundance originated from a region of the long unique section of the prototype arrangement of the viral genome (0.660 to 0.770 map units). The viral RNA in low abundance originated from the long repeat sequences (0.010 to 0.035 and 0.795 to 0.825 map units) and a region in the long unique section (0.201 to 0.260 map units). Viral RNAs associated with the polyribosomes as polyadenylated RNA were mapped to these restricted regions of the viral genome and characterized according to size class in kilobases. At 24 h after infection in the presence of an inhibitor of viral DNA replication, i.e., at early times, the stable viral RNAs in highest abundance mapped in the long repeat sequences. Viral RNAs at intermediate abundance under these conditions mapped in two regions of the long unique section of the viral genome (0.325 to 0.460 and 0.685 to 0.770 map units). Stable viral RNAs that were associated with the polyribosomes in high abundance as polyadenylated RNA orginated from the long repeat sequences, but not from the long unique section of the viral genome. An analysis of whole-cell RNA at late times (72 h) indicated that the abundant transcription was in the regions of the long unique sequences (0.325 to 0.460 and 0.660 to 0.685 map units), and transcription of intermediate abundance was from the long repeat sequences. However, stable viral mRNA's derived from the long repeat sequences were associated with the polyribosomes at late times after infection. In addition, mRNA's originating from the long and short unique sequences were found associated with the polyribosomes at higher relative concentration than at early times after infection. It is proposed that expression of the immediate early viral genes is required to transcribe the early viral genes in the long repeat and adjacent sequences. These sequences are also transcribed at late times after infection while viral DNA synthesis continues. The expression of viral genes in most of the long and short unique sequences appears to require viral DNA replication.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Costa R. H., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA present in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):9–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.9-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Stringer J. R., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Isolation and localization of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):805–820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.805-820.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Spiegelman S. Electrophoretic separation of viral nucleic acids on polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):373–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton R. A., Tevethia M. J. Immunoprecipitation of virus-specific immediate-early and early polypeptides from cells lytically infected with human cytomegalovirus strain AD 169. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):262–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90631-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi B., Arber W. Physical mapping of BglII, BamHI, EcoRI, HindIII and PstI restriction fragments of bacteriophage P1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 24;153(3):311–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00431596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., McLauchlan J., McGeoch D. J. Orientation of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):77–91. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Raskas H. J. Effect of cycloheximide on RNA metabolism early in productive infection with adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):26–32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.26-32.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Kaplan A. S. Replication of human cytomegalovirus DNA: lack of dependence on cell DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1063–1070. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1063-1070.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Schmidt C. A., Kaplan A. S. Patterns of transcription of human cytomegalovirus in permissively infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):277–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.277-286.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton A. J., Clements J. B. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 2 transcription and characterization of virus immediate early mRNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2627–2645. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Fioretti A., Plotkin S. Growth characteristics of cytomegalovirus in human fibroblasts with demonstration of protein synthesis early in viral replication. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):991–997. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.991-997.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Tanaka S., Plotkin S. A. Stimulation of macromolecular synethesis in guinea pig cells by human CMV. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jan;148(1):211–214. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Stringer J. R., Wagner E. K. Isolation and localization of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA abundant before viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):447–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.447-462.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Bonner J. Preparation, molecular weight, base composition, and secondary structure of giant nuclear ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2330–2338. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeor S. C., Albrecht T. B., Funk F. D., Rapp F. Stimulation of cellular DNA synthesis by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):353–362. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.353-362.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA VII. alpha-RNA is homologous to noncontiguous sites in both the L and S components of viral DNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.268-276.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Thomas-Powell A. L., Raab-Traub N., Hawke M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA. V. Viral RNA in a restringently infected, growth-transformed cell line. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):506–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.506-518.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J. Cytomegalovirus infections in organ transplantation and post transfusion. An hypothesis. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;37(4):365–377. doi: 10.1007/BF01241460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: transcription-initiation sites and domains of alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7122–7126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. L., Henikoff S., Meselson M. Localization of RNA from heat-induced polysomes at puff sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Muller M. T., Chantler J. K., Hudson J. B. Regulation of murine cytomegalovirus gene expression. I. Transcription during productive infection. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):263–268. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.263-268.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Stinski M. F. Persistence of the cytomegalovirus genome in human cells. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):761–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.761-775.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer G. Cytomegaloviruses of man and animals. Prog Med Virol. 1973;15:92–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp F., Geder L., Murasko D., Lausch R., Ladda R., Huang E. S., Webber M. M. Long-term persistence of cytomegalovirus genome in cultured human cells of prostatic origin. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):982–990. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.982-990.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Jeor S. C., Hutt R. Cell DNA replication as a function in the synthesis of human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):65–73. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Mocarski E. S., Thomsen D. R. DNA of human cytomegalovirus: size heterogeneity and defectiveness resulting from serial undiluted passage. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):231–239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.231-239.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Sequence of protein synthesis in cells infected by human cytomegalovirus: early and late virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):686–701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.686-701.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Synthesis of proteins and glycoproteins in cells infected with human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):751–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.751-767.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R., Holland L. E., Swanstrom R. I., Pivo K., Wagner E. K. Quantitation of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA in infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):889–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.889-901.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Mapping early transcripts of herpes simplex virus type 1 by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):56–73. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.56-73.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Furukawa T., Plotkin S. A. Human cytomegalovirus stimulates host cell RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):297–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.297-304.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Temporal regulation of human cytomegalovirus transcription at immediate early and early times after infection. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):446–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.446-459.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Preston C. M., Clements J. B. Separation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):42–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.42-52.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Sullivan M., Vande Woude G. F. Structures of two spliced herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's which map at the junctions of the unique and reiterated regions of the virus DNA S component. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):431–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.431-444.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of cytomegalovirus strains of human origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):253–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]










