Abstract
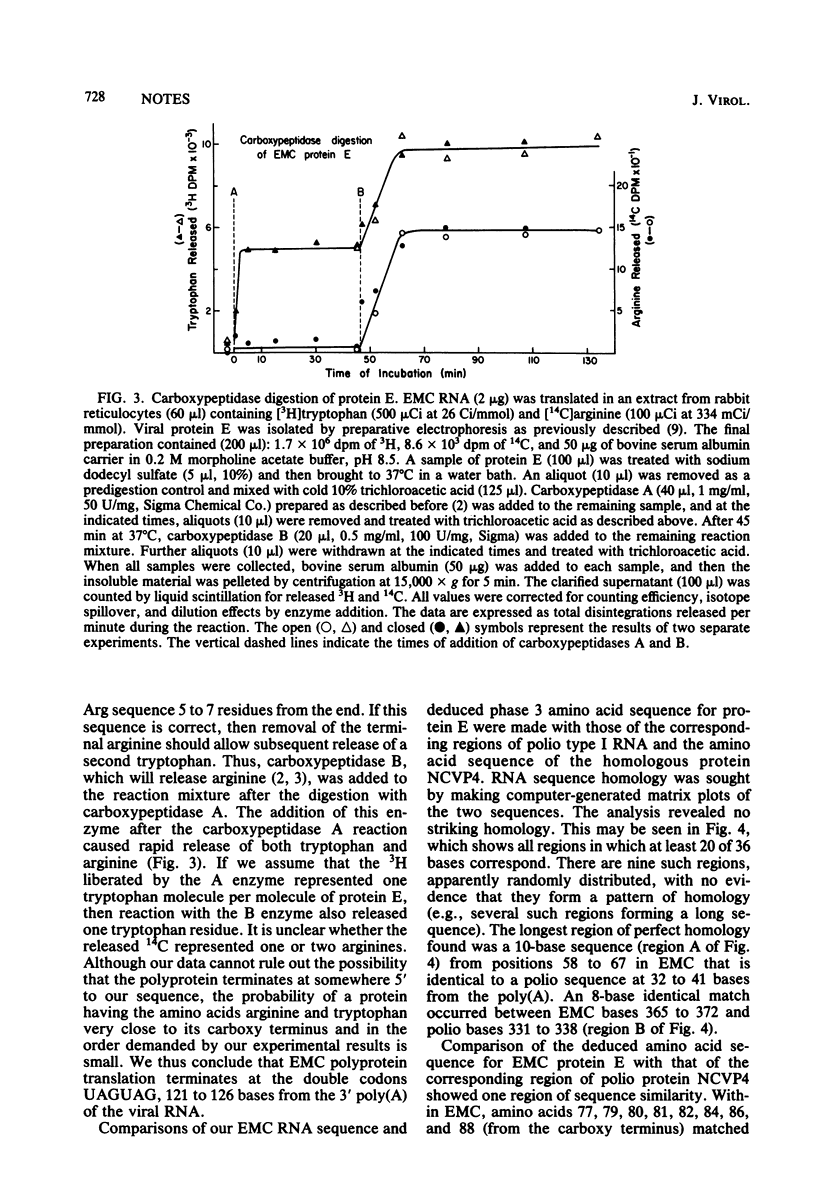
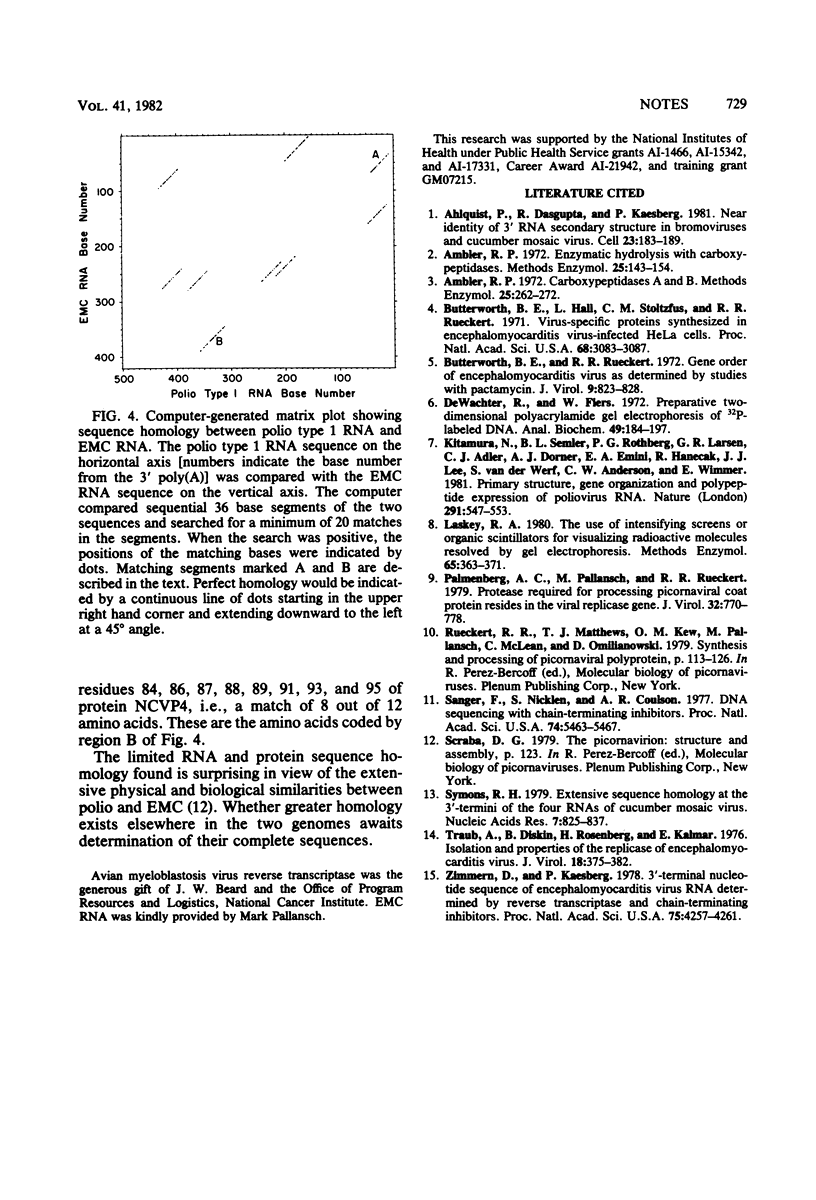
We show by sequence analysis of a 420-base-long region adjacent to the 3' polyadenylic acid of encephalomyocarditis viral RNA and by carboxy terminus analysis of protein E that the termination site of encephalomyocarditis virus polyprotein translation consists of two successive UAG codons located at positions 121 to 126 from the 3' polyadenylic acid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Near identity of 3- RNA secondary structure in bromoviruses and cucumber mosaic virus. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Hall L., Stoltzfus C. M., Rueckert R. R. Virus-specific proteins synthesized in encephalomyocarditis virus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Rueckert R. R. Gene order of encephalomyocarditis virus as determined by studies with pactamycin. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):823–828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.823-828.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A. The use of intensifying screens or organic scintillators for visualizing radioactive molecules resolved by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):363–371. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Pallansch M. A., Rueckert R. R. Protease required for processing picornaviral coat protein resides in the viral replicase gene. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):770–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.770-778.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Extensive sequence homology at the 3'-termini of the four RNAs of cucumber mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 25;7(4):825–837. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.4.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub A., Duskin B., Rosenberg H., Kalmar E. Isolation and properties of the replicase of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):375–382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.375-382.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmern D., Kaesberg P. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA determined by reverse transcriptase and chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



