Abstract
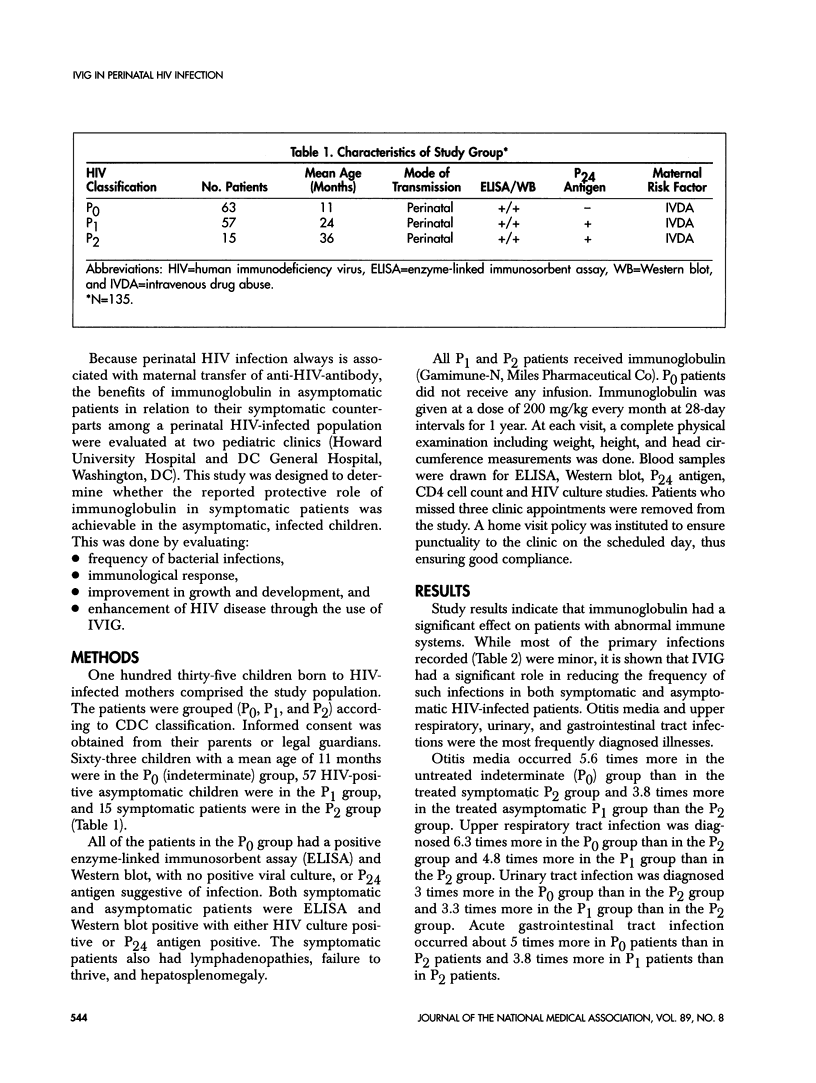
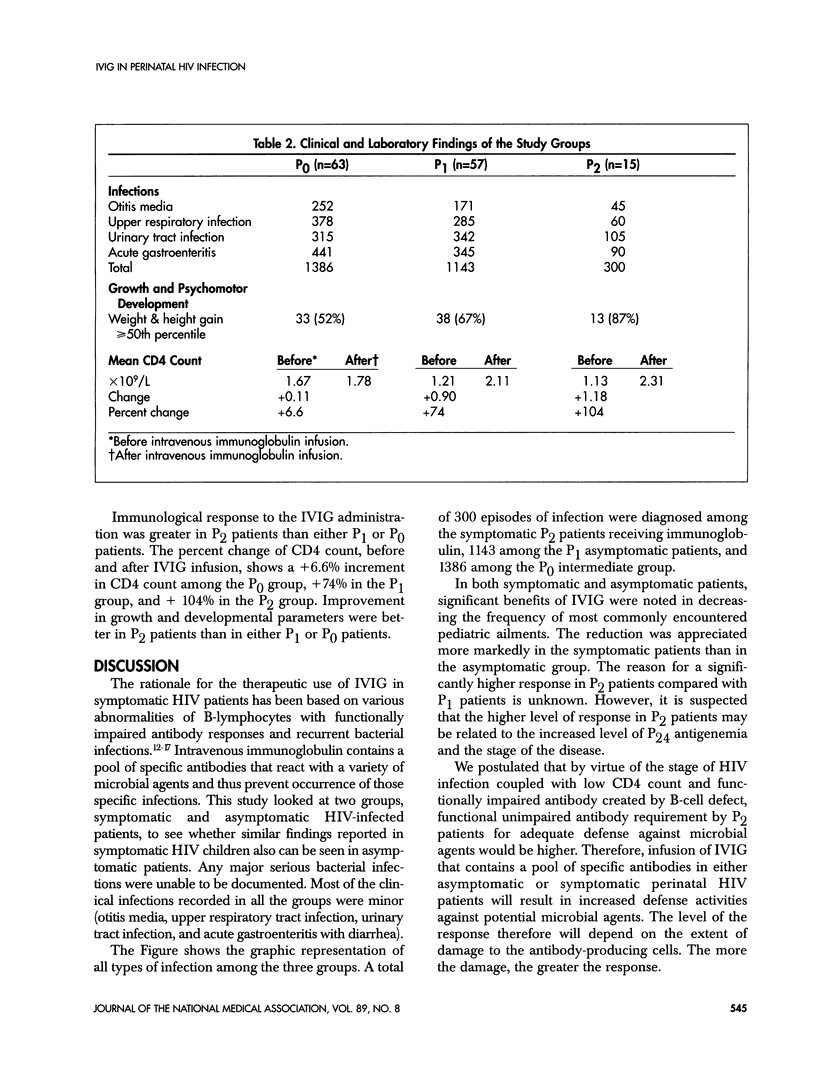
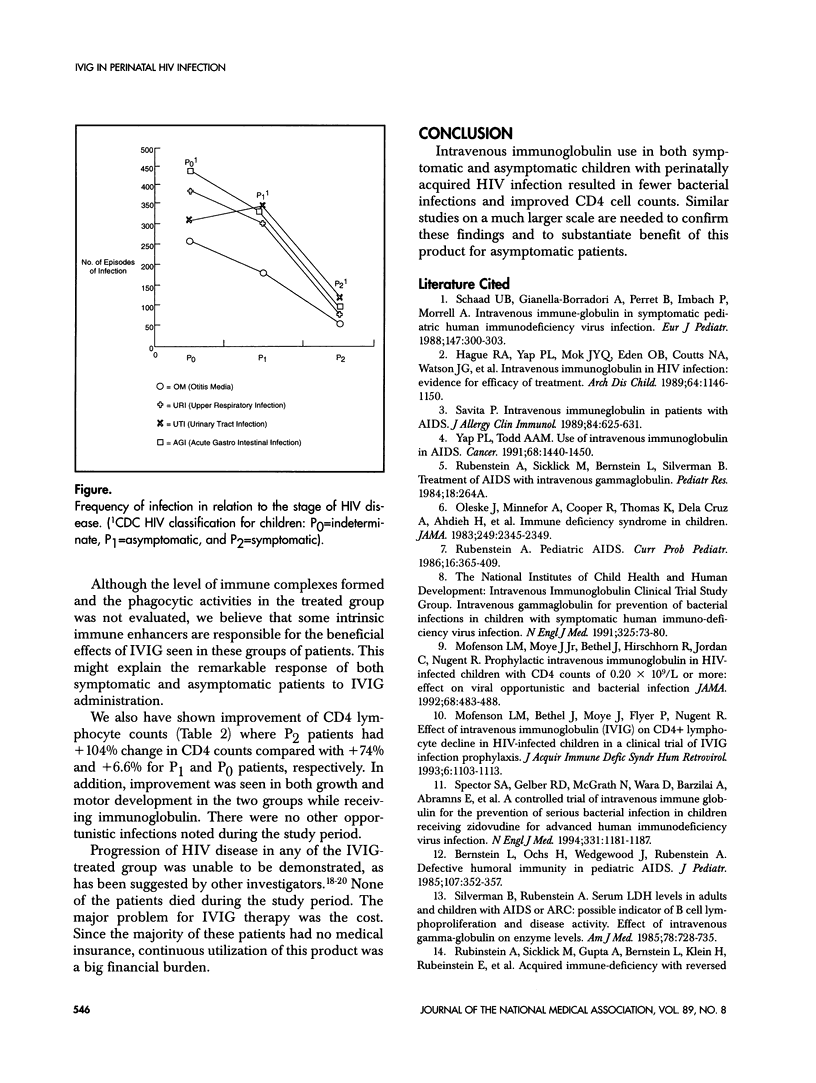
One hundred thirty-five children born to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected mothers were selected randomly to receive immunoglobulin (Gamimune-N, Miles Pharmaceutical Co) 200 mg/kg monthly for 1 year. All patients were seropositive by ELISA and Western blot at birth. At the time of the study, 15 symptomatic (P2) and 57 asymptomatic (P1) patients with evidence of viral infection (positive HIV culture or P24 antigen) received the immunoglobulin. Sixty-three indeterminate (PO) patients with no evidence of infection served as the control. Mean age for infants in group P2 was 32 months, 26 months for group P1, and 11 months for group PO. Significant reduction in the frequency of bacterial infections (ie, otitis media, upper respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and acute gastroenteritis) was seen in the symptomatic group compared with both the asymptomatic and the control groups. Growth as measured by weight and height > 50th percentile was also markedly better in the symptomatic group than either asymptomatic or control patients. There was no significant difference in head circumference in all three groups. These results indicate that monthly intravenous immunoglobulin infusion (IVIG) appears to be beneficial to both symptomatic and asymptomatic HIV patients in reducing the frequency of bacterial infection and also enhancement of the immune response. However, symptomatic patients responded much better than the asymptomatic patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein L. J., Ochs H. D., Wedgwood R. J., Rubinstein A. Defective humoral immunity in pediatric acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Pediatr. 1985 Sep;107(3):352–357. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80505-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hague R. A., Yap P. L., Mok J. Y., Eden O. B., Coutts N. A., Watson J. G., Hargreaves F. D., Whitelaw J. M. Intravenous immunoglobulin in HIV infection: evidence for the efficacy of treatment. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Aug;64(8):1146–1150. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.8.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsy J., Meyer M., Levy J. A. Serum enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection correlates with disease in HIV-infected individuals. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1437–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1437-1440.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline M. W., Hollinger F. B., Rosenblatt H. M., Bohannon B., Kozinetz C. A., Shearer W. T. Sensitivity, specificity and predictive value of physical examination, culture and other laboratory studies in the diagnosis during early infancy of vertically acquired human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1993 Jan;12(1):33–36. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199301000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mofenson L. M., Bethel J., Moye J., Jr, Flyer P., Nugent R. Effect of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) on CD4+ lymphocyte decline in HIV-infected children in a clinical trial of IVIG infection prophylaxis. The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Intravenous Immunoglobulin Clinical Trial Study Group. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993 Oct;6(10):1103–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mofenson L. M., Moye J., Jr, Bethel J., Hirschhorn R., Jordan C., Nugent R. Prophylactic intravenous immunoglobulin in HIV-infected children with CD4+ counts of 0.20 x 10(9)/L or more. Effect on viral, opportunistic, and bacterial infections. The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Intravenous Immunoglobulin Clinical Trial Study Group. JAMA. 1992 Jul 22;268(4):483–488. doi: 10.1001/jama.268.4.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J., Minnefor A., Cooper R., Jr, Thomas K., dela Cruz A., Ahdieh H., Guerrero I., Joshi V. V., Desposito F. Immune deficiency syndrome in children. JAMA. 1983 May 6;249(17):2345–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. Antibody-dependent enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Lancet. 1988 Apr 9;1(8589):790–794. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91657-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein A., Calvelli T., Rubinstein R. Intravenous gammaglobulin for pediatric HIV-1 infection. Effects on infectious complications, circulating immune complexes, and CD4 cell decline. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Oct 29;693:151–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb26263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein A., Sicklick M., Gupta A., Bernstein L., Klein N., Rubinstein E., Spigland I., Fruchter L., Litman N., Lee H. Acquired immunodeficiency with reversed T4/T8 ratios in infants born to promiscuous and drug-addicted mothers. JAMA. 1983 May 6;249(17):2350–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., Gianella-Borradori A., Perret B., Imbach P., Morell A. Intravenous immune globulin in symptomatic paediatric human immunodeficiency virus infection. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Apr;147(3):300–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00442700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. B., Buck B. E., Leterman J. G., Bloom F. L., Parks W. P. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in infants. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 12;310(2):76–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401123100202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A., Gelber R. D., McGrath N., Wara D., Barzilai A., Abrams E., Bryson Y. J., Dankner W. M., Livingston R. A., Connor E. M. A controlled trial of intravenous immune globulin for the prevention of serious bacterial infections in children receiving zidovudine for advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pediatric AIDS Clinical Trials Group. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 3;331(18):1181–1187. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411033311802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda A., Tuazon C. U., Ennis F. A. Antibody-enhanced infection by HIV-1 via Fc receptor-mediated entry. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):580–583. doi: 10.1126/science.2972065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap P. L., Todd A. A., Williams P. E., Hague R. A., Mok J., Burns S. M., Brettle R. P. Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Cancer. 1991 Sep 15;68(6 Suppl):1440–1450. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910915)68:6+<1440::aid-cncr2820681407>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


