Abstract
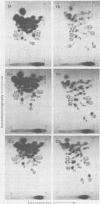
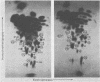
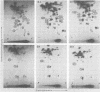
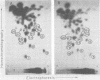
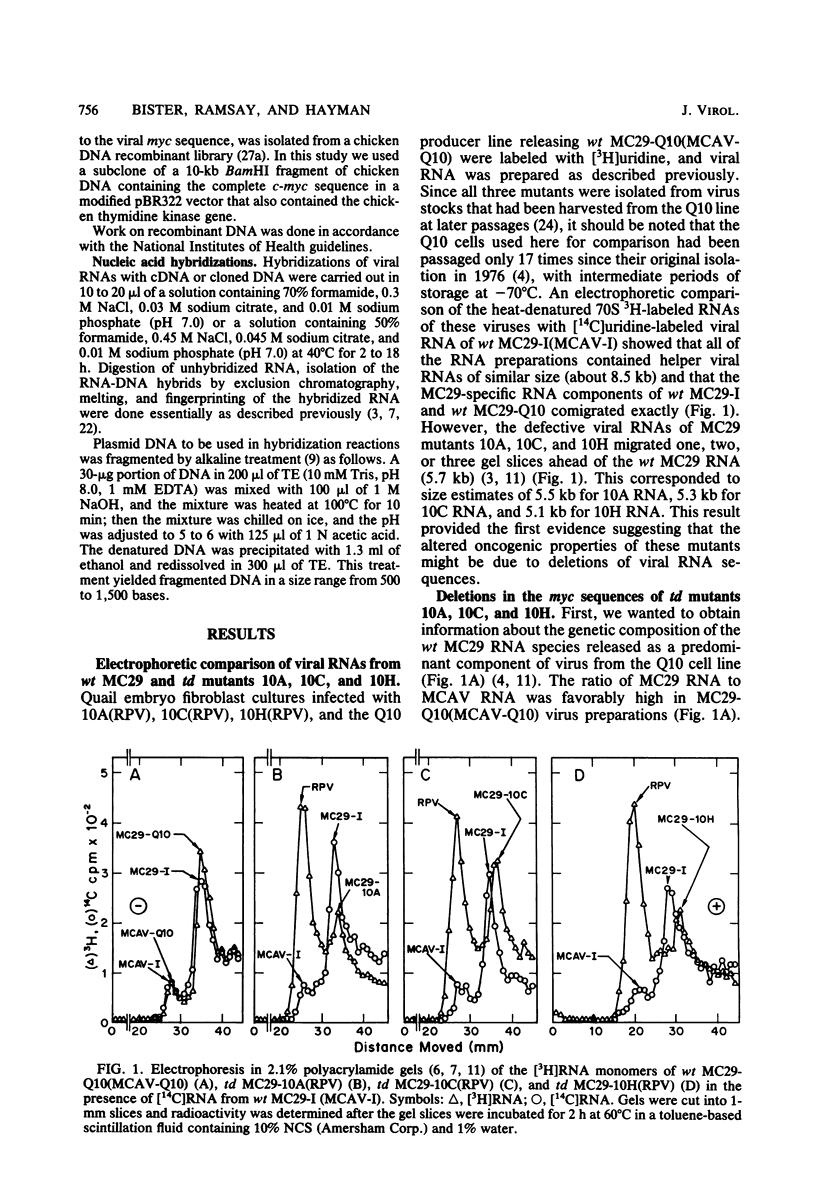
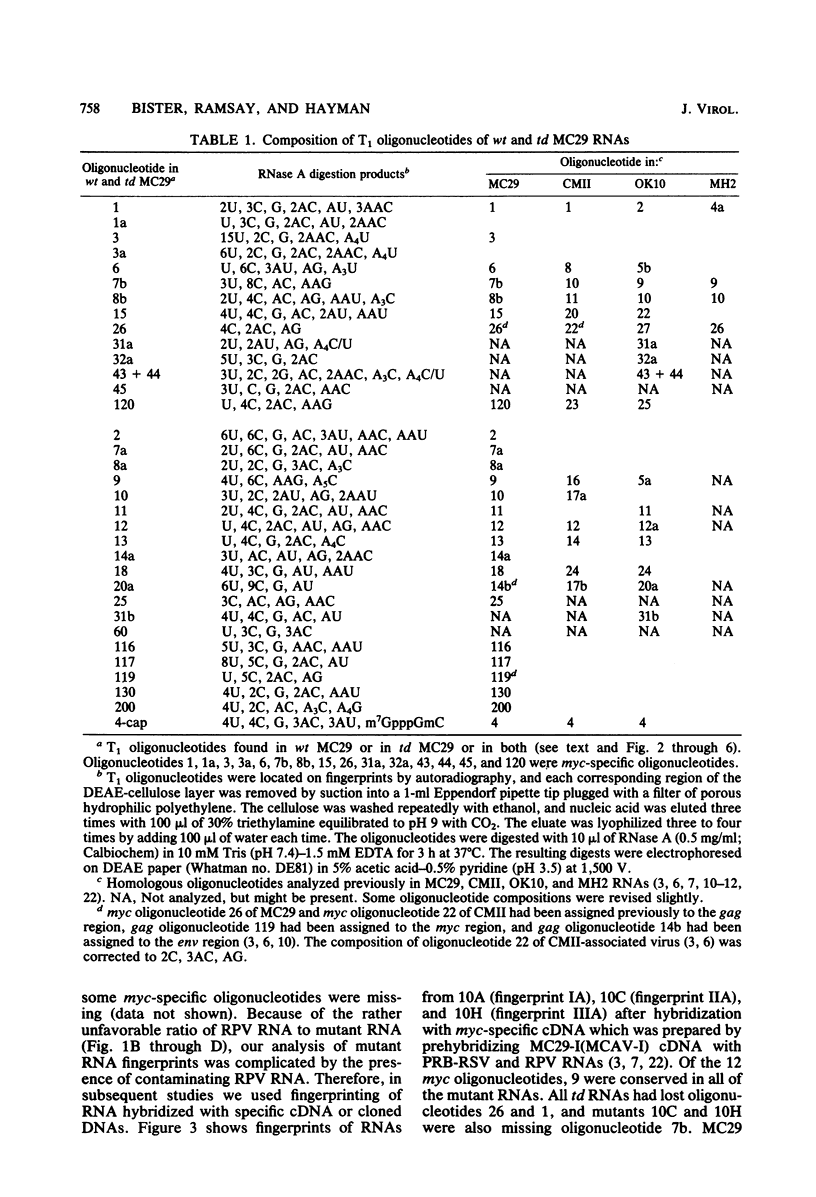
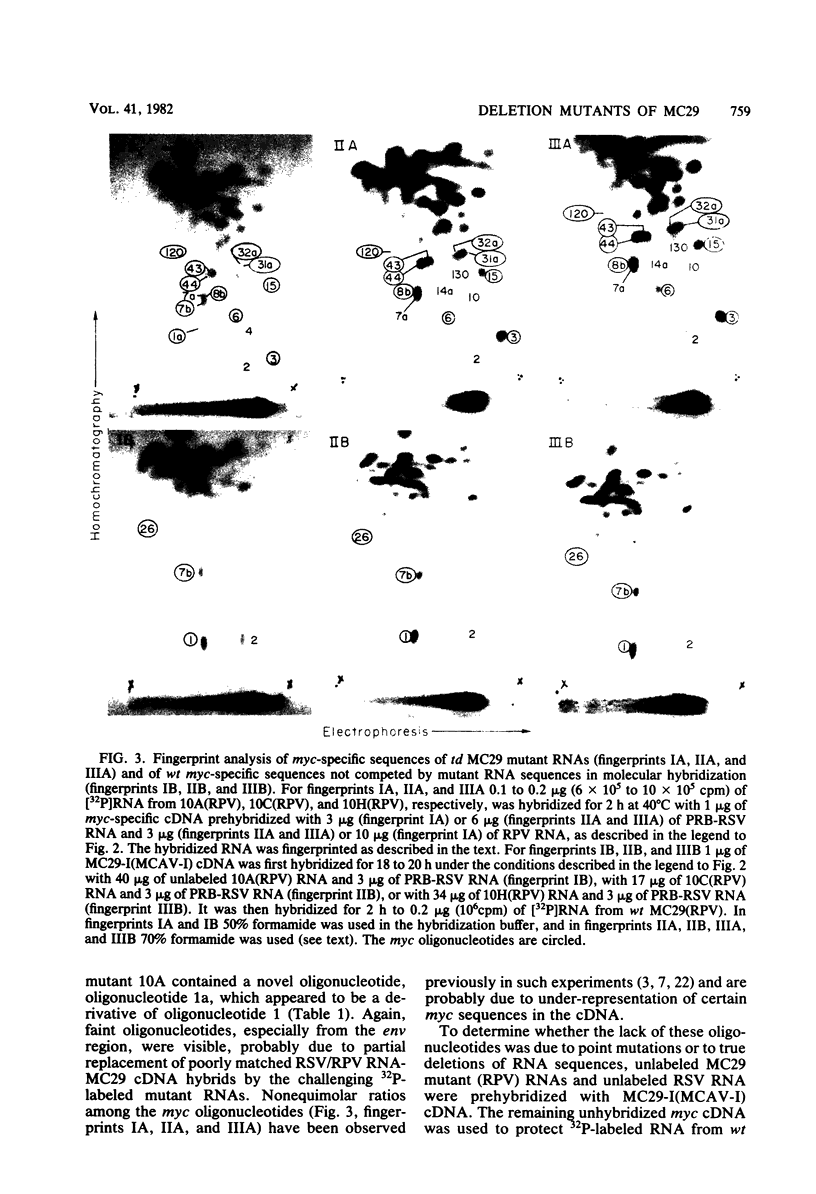
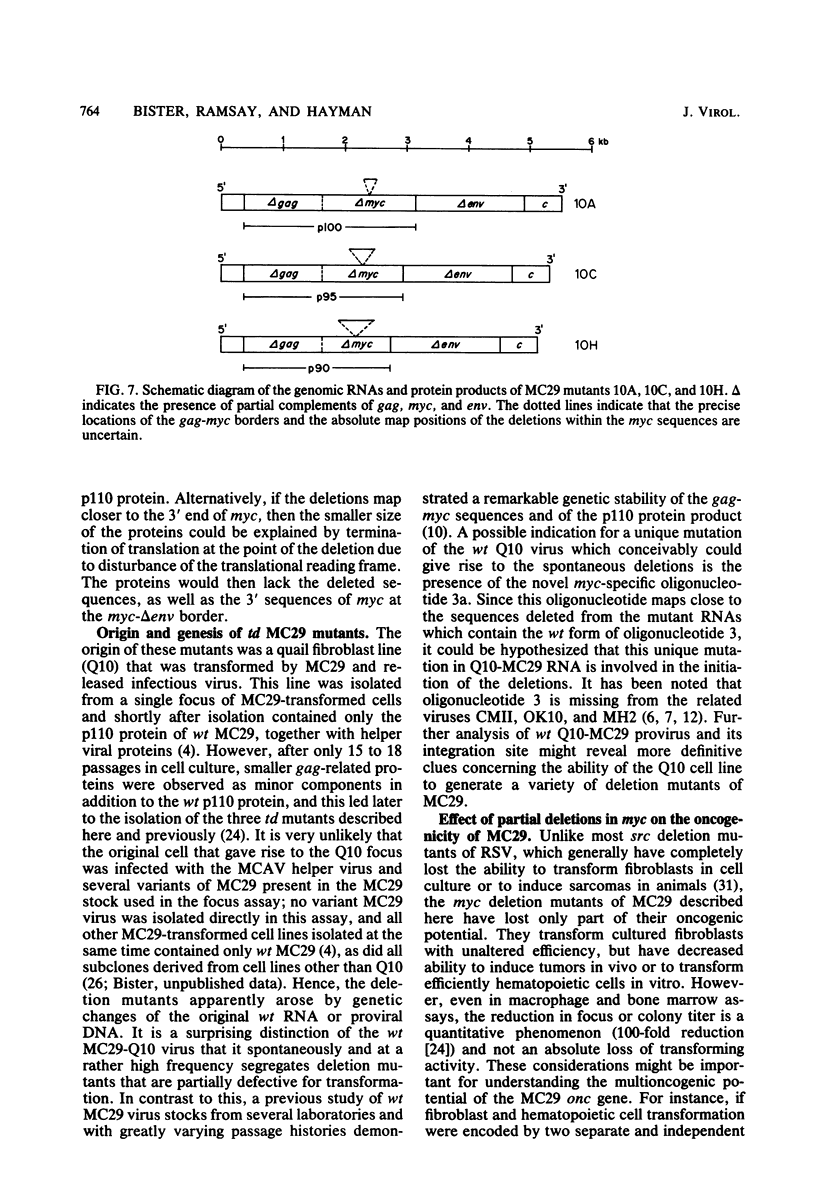
The viral RNAs of three nonconditional mutants of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29 were analyzed. These mutants, which were originally isolated from the quail producer line Q10 and were designated 10A, 10C, and 10H, have lost most of the ability to transform hematopoietic cells in vitro and to induce tumors in vivo, but they still transform cultured fibroblasts with the same efficiency as wild-type (wt) MC29. Electrophoretic analyses showed that the mutant genomic RNAs were smaller than the 5.7-kilobase genome of wt MC29; the genomes of mutants 10A, 10C, and 10H were about 5.5, 5.3, and 5.1 kilobases long, respectively. Analyses of the transformation-specific sequences of these mutant RNAs by a combination of T1 oligonucleotide fingerprinting and hybridization with cDNA from the transformation-specific sequences myc of wt MC29 or competition hybridization including wt MC29 RNA revealed that deletions of myc-specific sequences had occurred. The deletions in all three mutants overlapped, since they all had lost one particular myc-specific oligonucleotide. In agreement with the size of the genomic RNAs, mutants 10C and 10H had lost two additional myc oligonucleotides, and mutant 10A contained a modified myc oligonucleotide. The locations of the deletions were deduced from comparisons with previously established oligonucleotide maps of several members of the MC29 subgroup of acute leukemia viruses and by hybridization of wt and mutant RNAs to molecularly cloned subgenomic fragments of wt MC29 proviral DNA, representing the 5′ and 3′ domains of the myc sequence. We found that the deleted sequences represented overlapping internal segments of the myc sequence and that the borders of myc with the partial complements of the virion genes gag and env appeared to be conserved in mutant and wt MC29 RNAs. The correlation between the altered transforming potential for hematopoietic cells and the partial deletion of myc in the mutant RNAs provided direct genetic evidence for the involvement of myc in oncogenesis. However, the unaffected efficiency of these mutants in fibroblast transformation suggested that the deleted sequences are not essential for the fibroblast-transforming potential of the onc gene of MC29.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Duesberg P. H. Genetic structure of avian acute leukemia viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):801–822. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Defectiveness of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: isolation of long-term nonproducer cultures and analysis of virus-specific polypeptide synthesis. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Lee W. H., Duesberg P. H. Phosphorylation of the nonstructural proteins encoded by three avian acute leukemia viruses and by avian fujinami sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):617–621. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.617-621.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Löliger H. C., Duesberg P. H. Oligoribonucleotide map and protein of CMII: detection of conserved and nonconserved genetic elements in avian acute leukemia viruses CMII, MC29, and MH2. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):208–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.208-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Ramsay G., Hayman M. J., Duesberg P. H. OK10, an avian acute leukemia virus of the MC 29 subgroup with a unique genetic structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7142–7146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Vogt P. K. Genetic analysis of the defectiveness in strain MC29 avian leukosis virus. Virology. 1978 Jul 15;88(2):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Yamamoto N., zur Hausen H. Differential inducibility of Epstein-Barr virus in cloned, non-producer Raji cells. Int J Cancer. 1979 Jun 15;23(6):818–825. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Essex M., Hardy W. D., Jr, Martin G. S., Rosenberg N. E., Scolnick E. M., Weinberg R. A., Vogt P. K. Proposal for naming host cell-derived inserts in retrovirus genomes. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):953–957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.953-957.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Bister K., Moscovici C. Avian acute leukemia virus MC29: conserved and variable RNA sequences and recombination with helper virus. Virology. 1979 Nov;99(1):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Bister K., Vogt P. K. The RNA of avian acute leukemia virus MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4320–4324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. Avian acute leukemia viruses MC29 and MH2 share specific RNA sequences: evidence for a second class of transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1633–1637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita D. J., Chen Y. C., Friis R. R., Vogt P. K. RNA tumor viruses of pheasants: characterization of avian leukosis subgroups F and G. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):558–571. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90350-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. S., Moscovici C., Vogt P. K. The defectiveness of Mill Hill 2, a carcinoma-inducing avian oncovirus. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):162–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki R., Langlois A. J., Chabot J., Beard J. W. Component of strain MC29 avian leukosis virus with the property of defectiveness. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):821–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.821-827.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchener G., Hayman M. J. Comparative tryptic peptide mapping studies suggest a role in cell transformation for the gag-related protein of avian erythroblastosis virus and avian myelocytomatosis virus strains CMII and MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1637–1641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautenberger J. A., Schulz R. A., Garon C. F., Tsichlis P. N., Papas T. S. Molecular cloning of avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29) transforming sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1518–1522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mladenov Z., Heine U., Beard D., Beard J. W. Strain MC29 avian leukosis virus. Myelocytoma, endothelioma, and renal growths: pathomorphological and ultrastructural aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1967 Mar;38(3):251–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G. M., Hayman M. J. Isolation and biochemical characterization of partially transformation-defective mutants of avian myelocytomatosis virus strain MC29: localization of the mutation to the myc domain of the 110,000-dalton gag-myc polyprotein. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):745–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.745-753.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Graf T., Hayman M. J. Mutants of avian myelocytomatosis virus with smaller gag gene-related proteins have an altered transforming ability. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):170–172. doi: 10.1038/288170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Hayman M. J. Analysis of cells transformed by defective leukemia virus OK10: production of noninfectious particles and synthesis of Pr76gag and an additional 200,000-dalton protein. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Anderson S. M., Riemen M. W., Hanafusa H. gag-Related polypeptides encoded by replication-defective avian oncoviruses. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):749–761. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.749-761.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins T., Bister K., Garon C., Papas T., Duesberg P. Structural relationship between a normal chicken DNA locus and the transforming gene of the avian acute leukemia virus MC29. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):635–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.635-642.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Bister K., Moscovici C., Fanshier L., Gonda T., Bishop J. M. Avian retroviruses that cause carcinoma and leukemia: identification of nucleotide sequences associated with pathogenicity. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):962–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.962-968.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stéhelin D., Saule S., Roussel M., Sergeant A., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Raes M. B. Three new types of viral oncogenes in defective avian leukemia viruses. I. Specific nucleotide sequences of cellular origin correlate with specific transformation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1215–1223. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., De Troy B., Roberts R. J., Sambrook J. Agarose slab-gel electrophoresis equipment. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):36–46. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]