Abstract
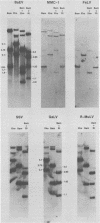
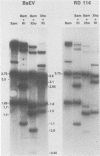
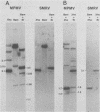
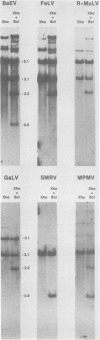
Baboon endogenous virus (BaEV) is a type C retrovirus present in multiple proviral copies in the DNA of baboons. Although interspecies antigenic determinants present on reverse transcriptase and gag proteins are shared among all mammalian type C viruses, no nucleic acid homology between BaEV and other type C viruses (except RD-114) has been found in conventional liquid hybridization experiments. In this study, we used restriction fragments of cloned BaEV DNA immobilized on nitrocellulose to test for relatedness with [32P]cDNA's of various type C and type D viruses. We detected the following distant relationships previously found only through immunological and protein sequencing techniques: (i) eight type C viral cDNA's (the endogenous virus of rhesus monkeys, feline leukemia virus, simian sarcoma virus, gibbon ape leukemia virus, Rauscher murine leukemia virus, BALB-2, NZB, and RD-114) and two type D viral cDNA's (Mason-Pfizer monkey virus and squirrel monkey retrovirus) were able to hybridize with cloned BaEV DNA; (ii) the eight type C probes hybridized to restriction fragments spanning most of the BaEV genome, but only RD-114 hybridized to fragments within the 1.9 kilobases at the 3′ end of the genome; (iii) the two type D probes hybridized primarily to fragments within the 1.9 kilobases at the 3′ terminus and weakly or not at all elsewhere; and (iv) [32P]cDNA's of several other oncornaviruses (mouse mammary tumor virus, equine infectious anemia virus, bovine leukemia virus, and reticuloendotheliosis virus) exhibited no homology with BaEV DNA. DNA sequence analysis has allowed us to orient the BaEV restriction map with the genetic map at both ends of the genome. Homologies between retroviral cDNA's and BaEV clone restriction fragments could thus be related to specific BaEV genes. Whereas type C cDNA's hybridized to fragments from gag, pol, and the pol-env junction, squirrel monkey retrovirus cDNA hybridized only to a fragment coding for the p15E portion of env. Mason-Pfizer monkey virus cDNA also hybridized within the p15E region, but exhibited homology to the 3′ half of gp70 as well. These results are discussed relative to previously reported antigenic relatedness of retroviral proteins. The data suggest that BaEV represents an important link in oncornavirus evolution.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P. R., Barbacid M., Tronick S. R., Clark H. F., Aaronson S. A. Evolutionary relatedness of viper and primate endogenous retroviruses. Science. 1979 Apr 20;204(4390):318–321. doi: 10.1126/science.219480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z. Antigenic structure of myoglobin: the complete immunochemical anatomy of a protein and conclusions relating to antigenic structures of proteins. Immunochemistry. 1975 May;12(5):423–438. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Long L. K., Aaronson S. A. Major structural proteins of type B, type C, and type D oncoviruses share interspecies antigenic determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):72–76. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Evolutionary relationships between gag gene-coded proteins of murine and primate endogenous type C RNA viruses. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. gag Gene of mammalian type-C RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):554–559. doi: 10.1038/262554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battula N., Todaro G. J. Physical map of infectious baboon type C viral DNA and sites of integration in infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):709–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.709-718.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton C. V., Hodge H. M., Fine D. L. Comparative large-scale propagation of retroviruses from Old World (Mason-Pfizer monkey virus) and New World (squirrel monkey virus) primates. In Vitro. 1978 Feb;14(2):192–199. doi: 10.1007/BF02618222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Callahan R., Sherr C. J., Chapman V., Todaro G. J. Two distinct endogenous type C viruses isolated from the asian rodent Mus cervicolor: conservation of virogene sequences in related rodent species. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):849–862. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.849-862.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of C-type viral genes: inheritance of exogenously acquired viral genes. Nature. 1974 Dec 6;252(5483):456–459. doi: 10.1038/252456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of type C viral genes: evidence for an Asian origin of man. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):101–108. doi: 10.1038/261101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Todaro G. J. The evolution of baboon endogenous type C virus: related sequences in the DNA of distant species. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. L., Sherr C. J., Sen A., Todaro G. J. Molecular diversity among five different endogenous primate retroviruses. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):300–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.300-313.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M., Davidson N., Gilden R. V., McAllister R. M., Nicolson M. O., Stephens R. M. The baboon endogenous virus genome. II. Provirus sequence variations in baboon cell DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4423–4440. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
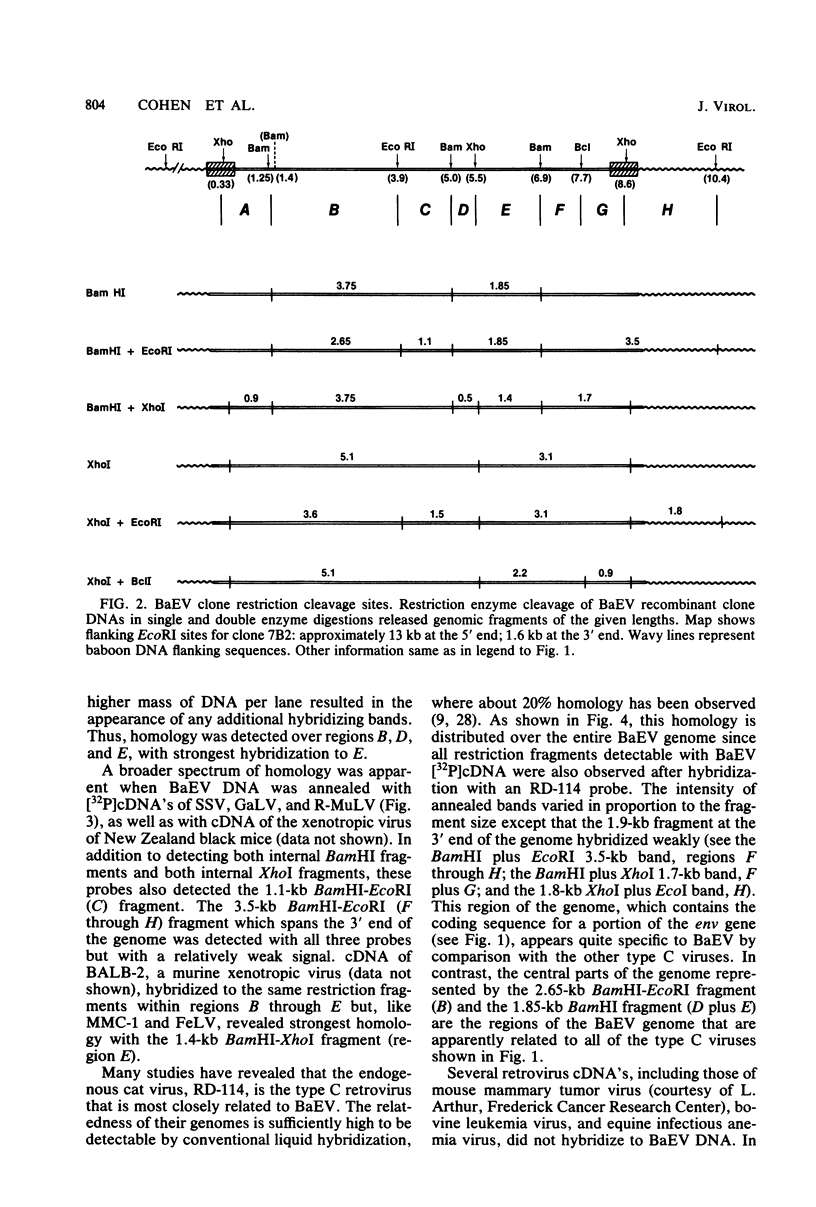
- Cohen M., Nicolson M. O., McAllister R. M., Shure M., Davidson N., Rice N., Gilden R. V. Baboon endogenous virus genome. I. Restriction enzyme map of the unintegrated DNA genome of a primate retrovirus. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):28–39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.28-39.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M., Rein A., Stephens R. M., O'Connell C., Gilden R. V., Shure M., Nicolson M. O., McAllister R. M., Davidson N. Baboon endogenous virus genome: molecular cloning and structural characterization of nondefective viral genomes from DNA of a baboon cell strain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5207–5211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colcher D., Teramoto Y. A., Schlom J. Interspecies radioimmunoassay for the major structural proteins of primate type-D retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5739–5743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland T. D., Henderson L. E., Vanlaningham-Miller E. S., Stephenson J. R., Smythers G. W., Oroszlan S. Amino- and carboxyl-terminal sequences of proteins coded by gag gene of endogenous baboon and cat type C viruses. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90467-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Immunological relationships of an endogenous guinea pig retrovirus with prototype mammalian type B and type D retroviruses. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):522–530. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.522-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devare S. G., Hanson R. E., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Primate retroviruses: envelope glycoproteins of endogenous type C and type D viruses possess common interspecies antigenic determinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):316–324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.316-324.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman A., Peebles P. T., Strickland J. E., Fowler A. K., Kalter S. S., Oroszlan K. S., Gilden R. V. Baboon virus isolate M-7 with properties similar to feline virus RD-114. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):133–138. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.133-138.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson I. C., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Mink cell line Mv 1 Lu (CCL 64). Focus formation and the generation of "nonproducer" transformed cell lines with murine and feline sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino S., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Antigenic determinants of the 70,000 molecular weight glycoprotein of woolly monkey type C RNA virus. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):922–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S., Davidson N., Nicolson M. O., McAllister R. M. Heteroduplex study of the sequence relations between RD-114 and baboon viral RNAs. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):345–352. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.345-352.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakower J. M., Aaronson S. A. Radioimmunologic characterization of RD-114 reverse transcriptase: evolutionary relatedness of mammalian type C viral pol gene products. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger G. G., Schochetman G. 5' terminal nucleotide sequences of type C retroviruses: features common to noncoding sequences of eucaryotic messenger RNAs. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90630-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Wagatsuma M., Tamura T., Takano T., Matsubara K. Structure of the baboon endogenous virus genome: cloning of circular virus DNA in bacteriophage lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2173–2185. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe H., Gilden R. V., Hatanaka M., Stephenson J. R., Gallagher R. E., Aaronson S. A., Gallo R. C., Tronick S. R. Immunological and biochemical characterisation of type C viruses isolated from cultured human AML cells. Nature. 1976 Mar 18;260(5548):264–266. doi: 10.1038/260264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Bonner T. I., Gilden R. V. Nucleic acid homology between avian and mammalian type C viruses: relatedness of reticuloendotheliosis virus cdna to cloned proviral DNA of the endogenous Colobus virus CPC-1. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):286–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P., Todaro G. J. Reverse transcriptases of primate viruses as immunological markers. Science. 1972 Sep 22;177(4054):1119–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4054.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Lieber M. M., Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Endogenous baboon type C virus (M7): biochemical and immunologic characterization. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):492–503. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Radioimmunoassay of the major group specific protein of endogenous baboon type C viruses: relation to the RD-114-CCC group and detection of antigen in normal baboon tissues. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):168–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90252-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin S. A., Todaro G. J. A new endogenous primate type C virus isolated from the Old World monkey Colobus polykomos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5041–5045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Hino S., Garrett E. W., Aaronson S. A. Immunological cross reactivity of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus with type C RNA viruses endogenous to primates. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):609–611. doi: 10.1038/261609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M., Verma I. M., Lerner R. A. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney leukemia virus: 3' end reveals details of replications, analogy to bacterial transposons, and an unexpected gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3302–3306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainsky M. A. Analysis of the virogenes related to the rhesus monkey endogenous type C retrovirus in monkeys and apes. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):922–930. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.922-930.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Malignant transformation of cells by viruses. Perspect Biol Med. 1970 Autumn;14(1):11–26. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1970.0006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Origin of retroviruses from cellular moveable genetic elements. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel H. J., Broughton E. M., Matthews T. J., Schäfer W., Bolognesi D. P. Interspecies reactivity of type C and D retrovirus p 15E and p 15C proteins. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):270–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90671-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Benveniste R. E., Sherwin S. A., Sherr C. J. MAC-1, a new genetically transmitted type C virus of primates: "low frequency" activation from stumptail monkey cell cultures. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):775–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Callahan R., Rapp U. R., De Larco J. E. Genetic transmission of retroviral genes and cellular oncogenes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Nov 19;210(1180):367–385. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronick S. R., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Immunological properties of two polypeptides of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):125–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.125-132.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]