Abstract
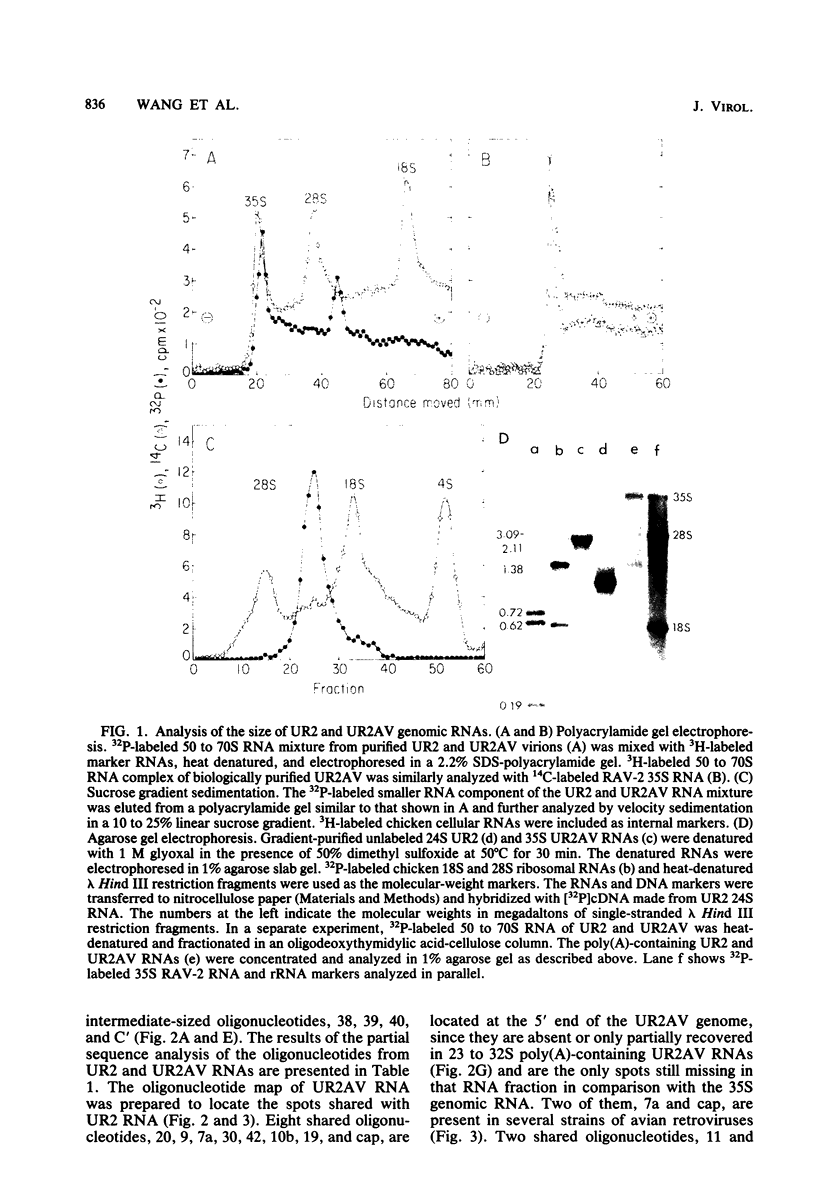
We have recently shown that a newly isolated avian sarcoma virus, UR2, is defective in replication and contains no sequences homologous to the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. In this study, we analyzed the genetic structure and transforming sequence of UR2 by oligonucleotide fingerprinting. The sizes of the genomic RNAs of UR2 and its associated helper virus, UR2AV, were determined to be 24S and 35S, respectively, by sucrose gradient sedimentation. The molecular weight of the 24S UR2 genomic RNA was estimated to be 1.1 x 10(6), corresponding to 3,300 nucleotides, by gel electrophoresis under the native and denatured conditions. RNase T1 oligonucleotide mapping indicated that UR2 RNA contains seven unique oligonucleotides in the middle of the genome and shares eight 5'- and six 3'-terminal oligonucleotides with UR2AV RNA. From these data, we estimated that UR2 RNA contains a unique sequence of about 12 kilobases in the middle of the genome, and contains 1.4 and 0.7 kilobases of sequences shared with UR2AV RNA at the 5' and 3' ends, respectively. Partial sequence analysis of the UR2-specific oligonucleotides by RNase A digestion revealed that there are no homologous counterparts to these oligonucleotides in the RNAs of other avian sarcoma and acute leukemia viruses studied to date. UR2-transformed non-virus-producing cells contain a single 24S viral RNA which is most likely the message coding for the transforming protein of UR2. On the basis of the uniqueness of the transforming sequence, we concluded that UR2 is a new member of the defective avian sarcoma viruses.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. M., Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Hanafusa H. Avian erythroblastosis virus produces two mRNA's. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):676–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.676-683.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balduzzi P. C., Notter M. F., Morgan H. R., Shibuya M. Some biological properties of two new avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):268–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.268-275.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Duesberg P. H. Structure and specific sequences of avian erythroblastosis virus RNA: evidence for multiple classes of transforming genes among avian tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5023–5027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H., Hayward W. S., Moscovici C. Size and genetic content of virus-specific RNA in myeloblasts transformed by avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV). Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):128–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Bister K., Moscovici C. Genetic structure of avian myeloblastosis virus, released from transformed myeloblasts as a defective virus particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5120–5124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. Avian acute leukemia viruses MC29 and MH2 share specific RNA sequences: evidence for a second class of transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1633–1637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. RNA species obtained from clonal lines of avian sarcoma and from avian leukosis virus. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Characterization of protein kinase activity associated with the transforming gene product of Fujinami sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90552-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysdael J., Neil J. C., Vogt P. K. A third class of avian sarcoma viruses, defined by related transformation-specific proteins of Yamaguchi 73 and Esh sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H. Rapid transformation of cells by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):318–325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Miyamoto T., Hanafusa H. A type of chick embryo cell that fails to support formation of infectious RSV. Virology. 1970 Jan;40(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90378-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Wang L. H., Anderson S. M., Karess R. E., Hayward W. S., Hanafusa H. Characterization of the transforming gene of Fujinami sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Rous sarcoma virus genome is terminally redundant: the 5' sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Braverman S. B., Astrin S. M. Transcriptional products and DNA structure of endogenous avian proviruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1111–1121. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S. Size and genetic content of viral RNAs in avian oncovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):47–63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.47-63.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Yoshida M., Segawa K., Sugiyama H., Ishizaki R., Toyoshima K. Characterization of Y73, an avian sarcoma virus: a unique transforming gene and its product, a phosphopolyprotein with protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6199–6203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bister K., Pawson A., Robins T., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Fujinami sarcoma virus: an avian RNA tumor virus with a unique transforming gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Breitman M. L., Vogt P. K. Characterization of a 105,000 molecular weight gag-related phosphoprotein from cells transformed by the defective avian sarcoma virus PRCII. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):98–110. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90530-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Delamarter J. F., Vogt P. K. Evidence for three classes of avian sarcoma viruses: comparison of the transformation-specific proteins of PRCII, Y73, and Fujinami viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Ghysdael J., Vogt P. K. Tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity associated with p105 of avian sarcoma virus PRCII. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90493-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saule S., Roussel M., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. Characterization of the oncogene (erb) of avian erythroblastosis virus and its cellular progenitor. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):409–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.409-419.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H., Stephenson J. R. Homology exists among the transforming sequences of avian and feline sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6536–6540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Vogt P. K. DNA related to the transforming gene(s) of avian sarcoma viruses is present in normal avian DNA. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):170–173. doi: 10.1038/260170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P. H., Robins T., Yokota H., Vogt P. K. The terminal oligonucleotides of avian tumor virus RNAs are genetically linked. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):472–492. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P., Beemon K., Vogt P. K. Mapping RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of avian tumor virus RNAs: sarcoma-specific oligonucleotides are near the poly(A) end and oligonucleotides common to sarcoma and transformation-defective viruses are at the poly(A) end. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1051–1070. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1051-1070.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P. Properties and location of poly(A) in Rous sarcoma virus RNA. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1515–1529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1515-1529.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Feldman R., Shibuya M., Hanafusa H., Notter M. F., Balduzzi P. C. Genetic structure, transforming sequence, and gene product of avian sarcoma virus UR1. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.258-267.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Snyder P., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Evidence for the common origin of viral and cellular sequences involved in sarcomagenic transformation. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):52–64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.52-64.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H. The gene order of avian RNA tumor viruses derived from biochemical analyses of deletion mutants and viral recombinants. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:561–592. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The size and genetic composition of virus-specific RNAs in the cytoplasm of cells producing avian sarcoma-leukosis viruses. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Kawai S., Toyoshima K. Genome structure of avian sarcoma virus Y73 and unique sequence coding for polyprotein p90. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):430–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.430-437.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Kawai S., Toyoshima K. Unifected avian cells contain structurally unrelated progenitors of viral sarcoma genes. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):653–654. doi: 10.1038/287653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





