Abstract
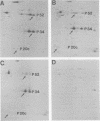
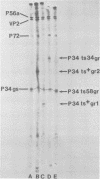
Extracts of cells infected with guanidine-resistant mutants of aphthovirus were examined for differences in virus-induced polypeptides by using electrofocusing. Four of 1 independent spontaneous mutants induced the synthesis of an altered nonstructural polypeptide, P34. The precursor of P34, P52, and a previously unmapped polypeptide, P20c, also carried these charge-change mutations. No mutations in other regions of the genome were detected, and the remaining six guanidine-resistant mutants appeared entirely normal by electrofocusing. However, when the P34 of one of the latter mutants was examined by tryptic peptide fingerprinting, it too differed from that of the guanidine-sensitive parent. The frequency of P34 alterations among guanidine-resistant mutants suggests that P34 is functionally involved in the antiviral action of guanidine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTIMORE D., EGGERS H. J., FRANKLIN R. M., TAMM I. Poliovirus-induced RNA polymerase and the effects of virus-specific inhibitors on its production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:843–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. N., Brown F. Effect of actinomycin D and guanidine on the formation of a ribonucleic acid polymerase induced by foot-and mouth-disease virus and on the replication of virus and viral ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(3):317–323. doi: 10.1042/bj1120317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F., Martin S. J., Underwood B. A study of the kinetics of protein and RNA synthesis induced by foot-and-mouth disease virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 24;129(1):166–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Shimshick E. J., Yin F. H. Association of the polioviral RNA polymerase complex with phospholipid membranes. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):457–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.457-466.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Mosser A. G. Proteins associated with the poliovirus RNA replication complex. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Action of guanidine on the replication of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. II. Nature of the defect. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):325–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D. A genetic map of poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1968 Aug;35(4):584–596. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Wentworth B. B., McCahon D. Guanidine inhibition of poliovirus: a dependence of viral RNA synthesis on the configuration of structural protein. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):480–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90191-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. I. Association of the viral RNA with coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., McCahon D., Slade W. R., Newman J. W. Biochemical evidence of recombination within the unsegmented RNA genome of aphthovirus. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):66–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.66-77.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Newman J. W. Temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus with altered structural polypeptides. I. Identification by electrofocusing. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.59-66.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Slade W. R., Newman J. W., McCahon D. Temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus with altered structural polypeptides. II. Comparison of recombination and biochemical maps. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):67–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.67-72.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Underwood B. O., McCahon D., Newman J. W., Brown F. Biochemical identification of viruses causing the 1981 outbreaks of foot and mouth disease in the UK. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):479–480. doi: 10.1038/293479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D. Poliovirus coat protein as the site of guanidine action. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Priston A. J., Slade W. R. A genetic recombination map of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):355–367. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., King A. M., McCahon D., Brown F., Newman J. W. Temperature-sensitive RNA polymerase mutants of a picornavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4448–4452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCahon D., Slade W. R., Priston R. A., Lake J. R. An extended genetic recombination map for foot-and-mouth diseases virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jun;35(3):555–565. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-3-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCahon D. The genetics of aphthovirus. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1981;69(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRINGLE C. R. INHIBITION OF MULTIPLICATION OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS BY GUANIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:1012–1013. doi: 10.1038/2041012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGHTSEL W. A., DICE J. R., McALPINE R. J., TIMM E. A., McLEAN I. W., Jr, DIXON G. J., SCHABEL F. M., Jr Antiviral effect of guanidine. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):558–559. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Kew O., Pallansch M., Rueckert R., Kaesberg P. Cell-free synthesis and processing of the proteins of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. S., Morrissett H., Gold L. An electrofocusing system for the analysis of proteins and their genetic variants. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin F. H. Involvement of viral procapsid in the RNA synthesis and maturation of poliovirus. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]