Abstract
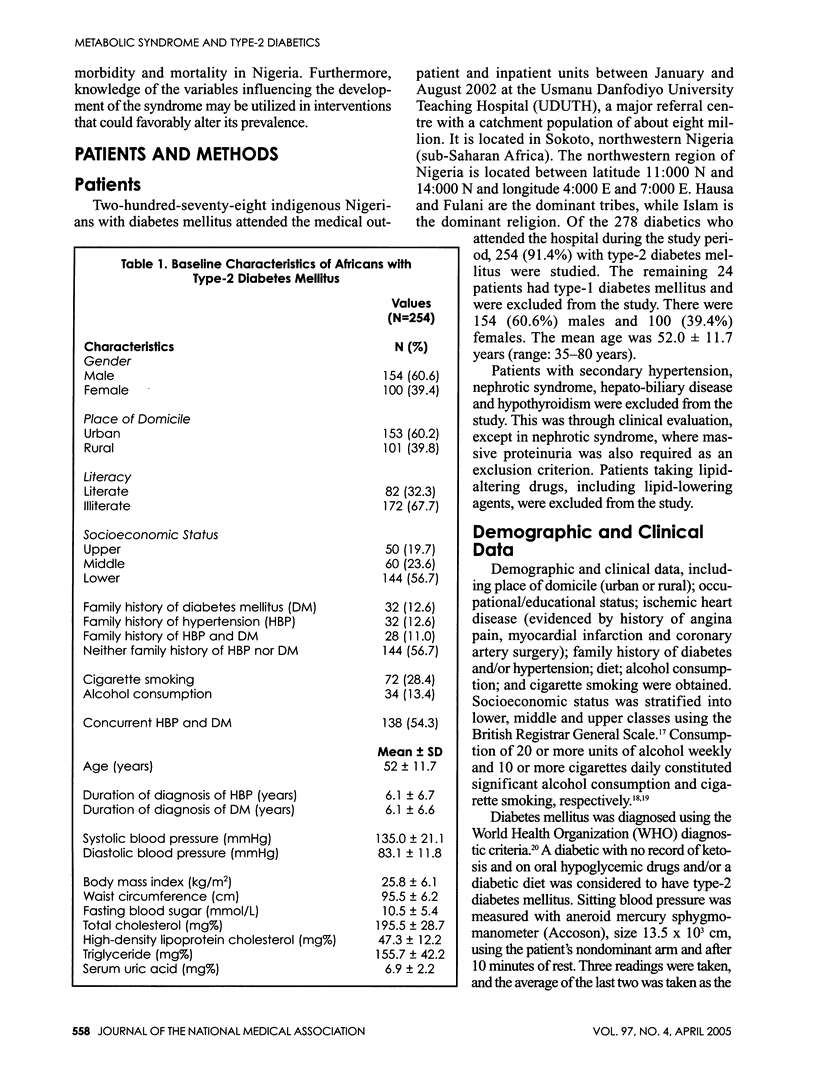
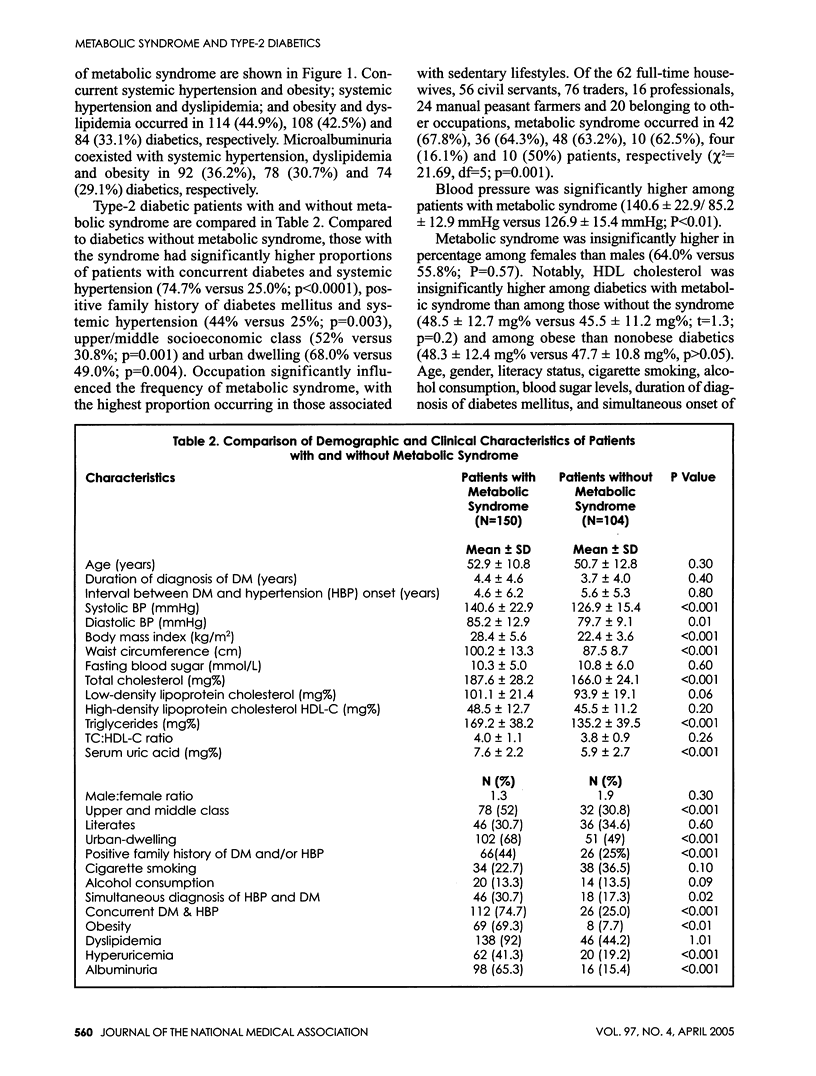
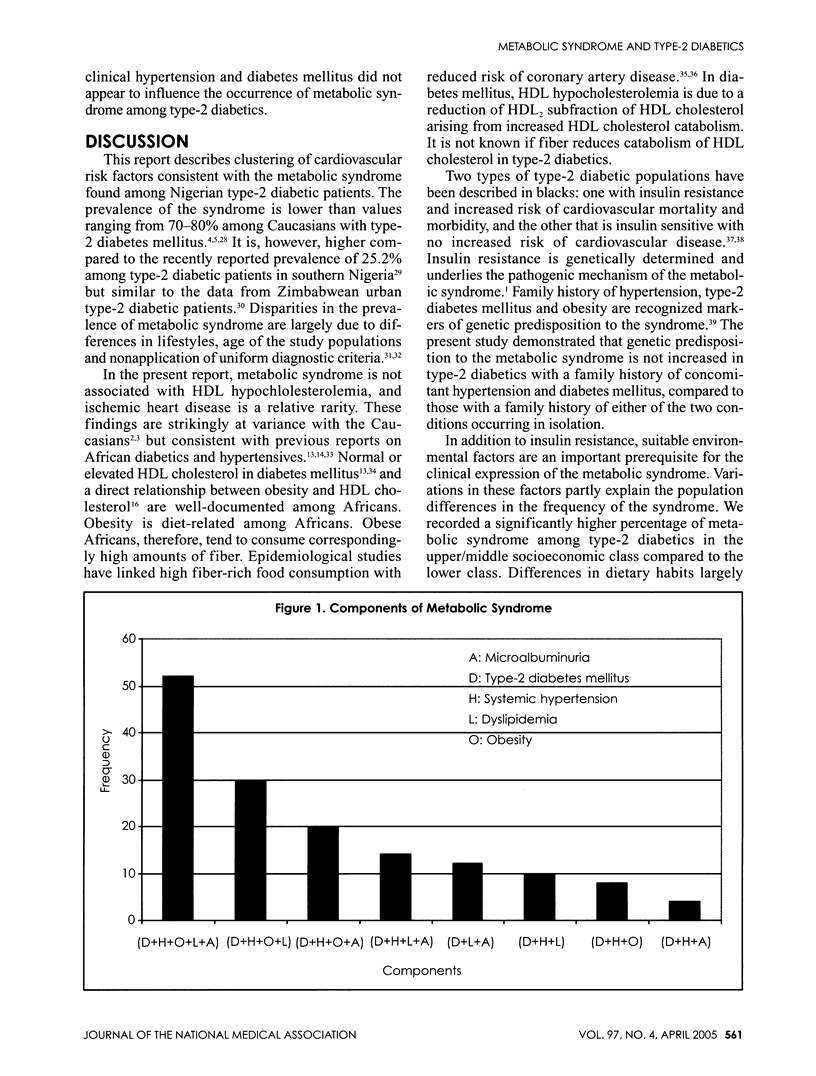
OBJECTIVES: To describe the metabolic syndrome and its demographic and clinical correlates in native African type-2 diabetic patients. METHODS: Cross-sectional analysis of 254 type-2 diabetic indigenous Nigerians consecutively recruited in a teaching hospital. The main outcome measure was metabolic syndrome. Variables of interest included family history/duration of diabetes mellitus and hypertension, gender, socioeconomic class, occupation and place of domicile (urban or rural). Intergroup comparisons were made with Chi-squared tests or t-tests. RESULTS: Patients were aged 35-80 years (mean: 52.0 +/- 11.7 years) and made of 154 (60.6%) males and 100 (39.4%) females. Full-blown metabolic syndrome was noted in 52 patients (20.5%). Metabolic syndrome, as defined by the WHO, was noted in 150 patients (59.1%). About 72.4% of patients were dyslipidemic, 54.3% were hypertensive, 42.5% were obese, 44.9% were microalbuminuric and 32.3% were hyperuricemic. Ischemic heart disease (myocardial infarction) occurred in only 2.4% of patients. Concurrent hypertension and dyslipidemia; obesity and dyslipidemia; and hypertension and obesity occurred in 44.4%, 42.5% and 33.1% of type-2 diabetics, respectively. Compared to the diabetics without metabolic syndrome, those with the syndrome had a significantly higher proportion of patients with a family history of hypertension and diabetes (44% versus 25%; p = 0.003); among the upper/middle socioeconomic class: 52.0% versus 30.8% (p = 0.001); and among the urban dwelling: 68.0% versus 49.0% (p = 0.004). Metabolic syndrome was inversely proportional to the physical activity of an individual (chi2 = 21.69, df = 5, p = 0.001). Blood pressure was significantly higher among patients with metabolic syndrome than those without it (140.6 +/- 22.9/85.2 +/- 12.9 mmHg versus 126.9 +/- 15.4 mmHg; P < 0.01). CONCLUSIONS: The development of metabolic syndrome in African type-2 diabetic patients is influenced by demographic and clinical factors. Vigilant dietary habit and physical exercise may reduce the chance of metabolic syndrome in urban Nigerian type-2 diabetics.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdul-Rahim H. F., Husseini A., Bjertness E., Giacaman R., Gordon N. H., Jervell J. The metabolic syndrome in the West Bank population: an urban-rural comparison. Diabetes Care. 2001 Feb;24(2):275–279. doi: 10.2337/diacare.24.2.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aduba O., Onwuamaeze I., Oli J., Udeozo K. Serum cholesterol and high density lipoprotein cholesterol in Nigerian diabetics. East Afr Med J. 1984 Jan;61(1):35–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa T., Kobayashi M., Sato Y., Tozuka M., Ishihara F., Okada N., Shigematsu S., Komatsu M., Hiramatsu K., Yamauchi K. Possible link between a low prevalence of cardiovascular disease and mild dyslipidaemia: a study in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 1993 Jun;10(5):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1993.tb00094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alebiosu Christopher Olutayo, Odusan B. Olatunde. Metabolic syndrome in subjects with type-2 diabetes mellitus. J Natl Med Assoc. 2004 Jun;96(6):817–821. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkau Beverley, Charles Marie-Aline, Drivsholm Thomas, Borch-Johnsen Knut, Wareham Nick, Yudkin John S., Morris Richard, Zavaroni Ivana, van Dam Rob, Feskins Edith. Frequency of the WHO metabolic syndrome in European cohorts, and an alternative definition of an insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2002 Nov;28(5):364–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno Graziella, Merletti Franco, Biggeri Annibale, Bargero Giuseppe, Ferrero Stefania, Runzo Cristina, Prina Cerai Stefano, Pagano Gianfranco, Cavallo-Perin Paolo, Casale Monferrato Study Metabolic syndrome as a predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in type 2 diabetes: the Casale Monferrato Study. Diabetes Care. 2004 Nov;27(11):2689–2694. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.11.2689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein M., Scholnick H. R., Morfin R. Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):583–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaiken R. L., Banerji M. A., Pasmantier R., Huey H., Hirsch S., Lebovitz H. E. Patterns of glucose and lipid abnormalities in black NIDDM subjects. Diabetes Care. 1991 Nov;14(11):1036–1042. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.11.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chobanian Aram V., Bakris George L., Black Henry R., Cushman William C., Green Lee A., Izzo Joseph L., Jr, Jones Daniel W., Materson Barry J., Oparil Suzanne, Wright Jackson T., Jr The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003 May 14;289(19):2560–2572. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.19.2560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll R., Peto R., Hall E., Wheatley K., Gray R. Mortality in relation to consumption of alcohol: 13 years' observations on male British doctors. BMJ. 1994 Oct 8;309(6959):911–918. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6959.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll R., Peto R., Wheatley K., Gray R., Sutherland I. Mortality in relation to smoking: 40 years' observations on male British doctors. BMJ. 1994 Oct 8;309(6959):901–911. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6959.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford Earl S., Giles Wayne H., Dietz William H. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 2002 Jan 16;287(3):356–359. doi: 10.1001/jama.287.3.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedewald W. T., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972 Jun;18(6):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giner V., Coca A., de la Sierra A. Increased insulin resistance in salt sensitive essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2001 Jul;15(7):481–485. doi: 10.1038/sj.jhh.1001216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta Rajeev, Deedwania Prakash C., Gupta Arvind, Rastogi Shweta, Panwar Raja B., Kothari Kunal. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in an Indian urban population. Int J Cardiol. 2004 Nov;97(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2003.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil G. S. The role of TNFalpha and TNF receptors in obesity and insulin resistance. J Intern Med. 1999 Jun;245(6):621–625. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.1999.00490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikem R. T., Akinola N. O., Balogun M. O., Ohwovoriole A. E., Akinsola A. What does the presence of hypertension portend in the Nigerian with non insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. West Afr J Med. 2001 Apr-Jun;20(2):127–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isezuo S. A., Badung S. L. H., Omotoso A. B. O. Comparative analysis of lipid profiles among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension and concurrent type 2 diabetes, and hypertension: a view of metabolic syndrome. J Natl Med Assoc. 2003 May;95(5):328–334. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE J. B., ZAK B. AUTOMATED DETERMINATION OF SERUM TOTAL CHOLESTEROL. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Oct;10:381–384. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makuyana D., Gomo Zar, Munyombwe T., Matenga J. A., Hakim J. G. Metabolic syndrome disorders in urban black Zimbabweans with type 2 Diabetes mellitus. Cent Afr J Med. 2004 Mar-Apr;50(3-4):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesini G., Forlani G., Cerrelli F., Manini R., Natale S., Baraldi L., Ermini G., Savorani G., Zocchi D., Melchionda N. WHO and ATPIII proposals for the definition of the metabolic syndrome in patients with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2004 Apr;21(4):383–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan M. W., Artiss J. D., Strandbergh D. R., Zak B. A peroxidase-coupled method for the colorimetric determination of serum triglycerides. Clin Chem. 1983 Mar;29(3):538–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan V., Shanthirani S., Deepa R., Premalatha G., Sastry N. G., Saroja R., Chennai Urban Population Study (CUPS No. 4) Intra-urban differences in the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in southern India -- the Chennai Urban Population Study (CUPS No. 4). Diabet Med. 2001 Apr;18(4):280–287. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2001.00421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Njelekela M. A., Negishi H., Nara Y., Sato T., Tomohiro M., Kuga S., Noguchi T., Kanda T., Yamori M., Mashalla Y. Obesity and lipid profiles in middle aged men and women in Tanzania. East Afr Med J. 2002 Feb;79(2):58–64. doi: 10.4314/eamj.v79i2.8901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park Hye Soon, Oh Sang Woo, Cho Sung-Il, Choi Woong Hwan, Kim Young Soel. The metabolic syndrome and associated lifestyle factors among South Korean adults. Int J Epidemiol. 2004 Apr;33(2):328–336. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyh032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosolová H. Sympatický nervový systém a inzulinová rezistence. Vnitr Lek. 2003 Jan;49(1):61–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma M. D., Pavlik V. N. Dyslipidaemia in African Americans, Hispanics and whites with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2001 Feb;3(1):41–45. doi: 10.1046/j.1463-1326.2001.00113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergès B. L. Dyslipidaemia in diabetes mellitus. Review of the main lipoprotein abnormalities and their consequences on the development of atherogenesis. Diabetes Metab. 1999 Jun;25 (Suppl 3):32–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamethee S. G., Shaper A. G., Alberti K. G. Physical activity, metabolic factors, and the incidence of coronary heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 2000 Jul 24;160(14):2108–2116. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.14.2108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirfält E., Hedblad B., Gullberg B., Mattisson I., Andrén C., Rosander U., Janzon L., Berglund G. Food patterns and components of the metabolic syndrome in men and women: a cross-sectional study within the Malmö Diet and Cancer cohort. Am J Epidemiol. 2001 Dec 15;154(12):1150–1159. doi: 10.1093/aje/154.12.1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf Myles, Sauk Jenny, Shah Anand, Vossen Smirnakis Karen, Jimenez-Kimble Ricardo, Ecker Jeffrey L., Thadhani Ravi. Inflammation and glucose intolerance: a prospective study of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2004 Jan;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


