Abstract
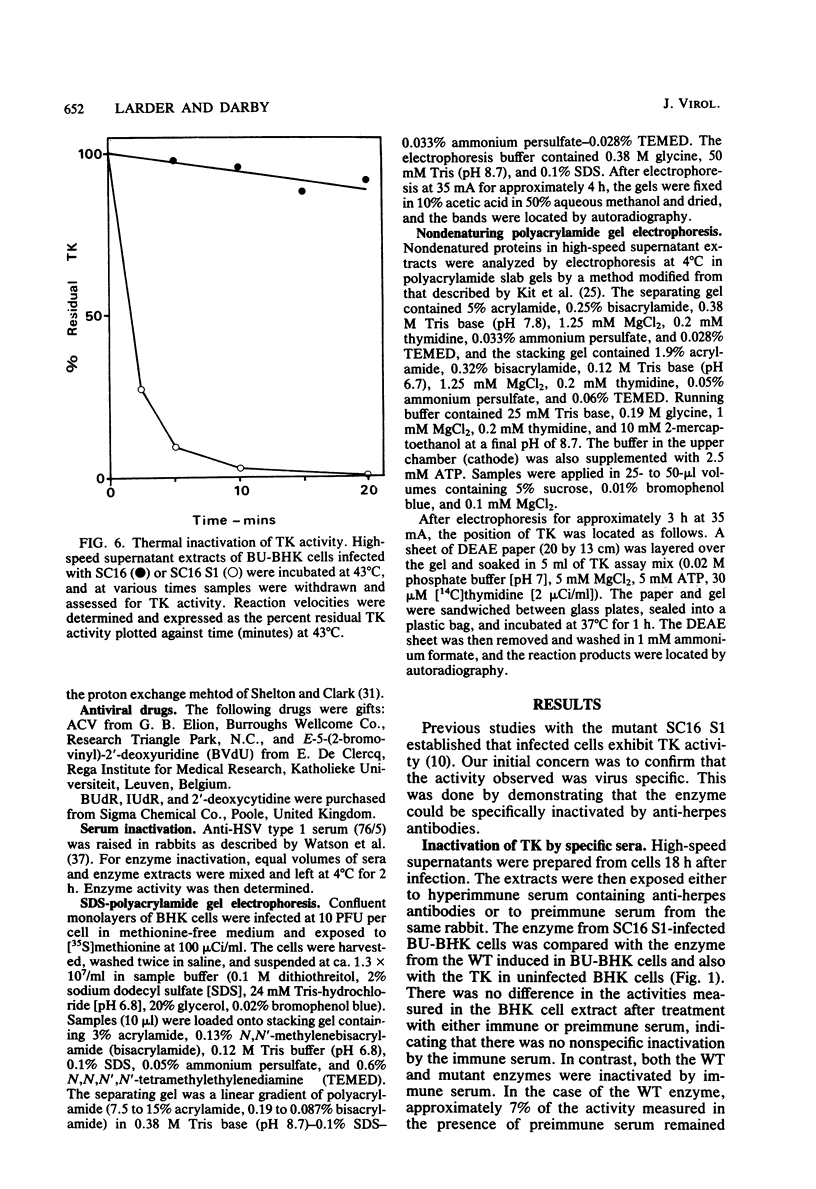
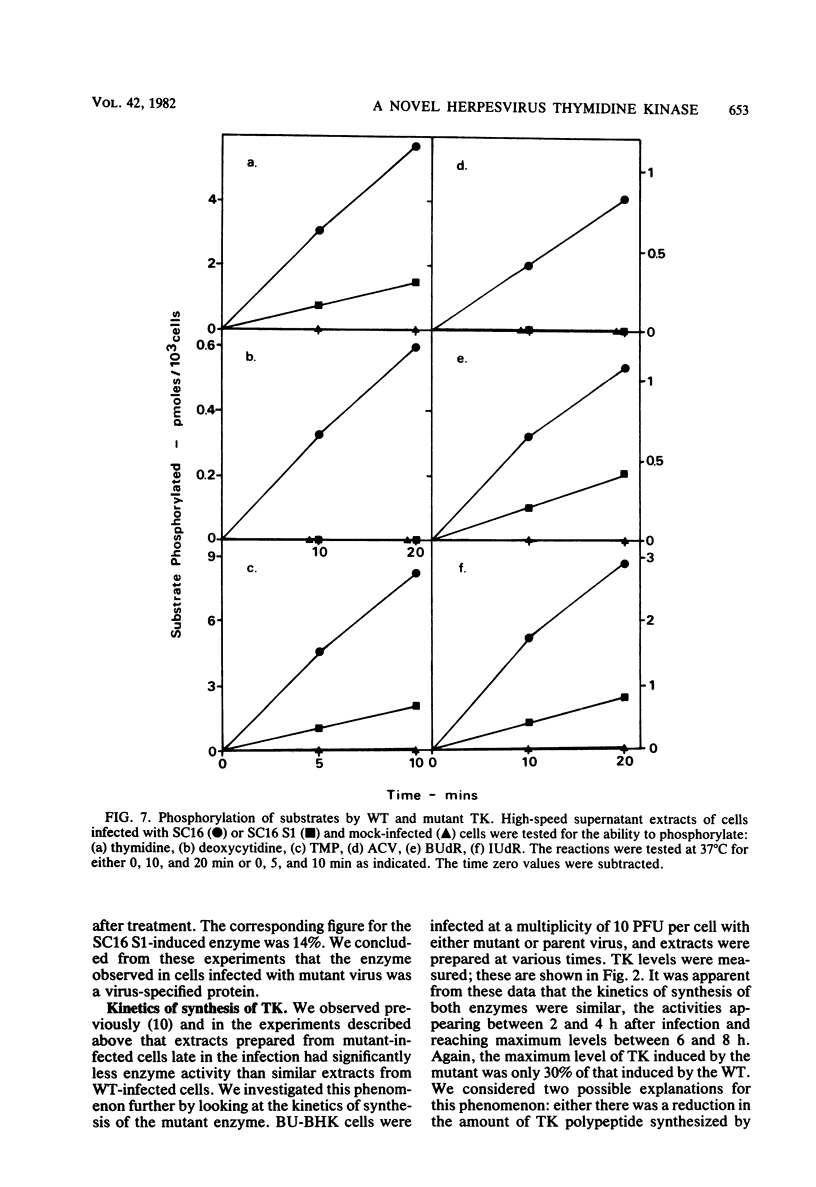
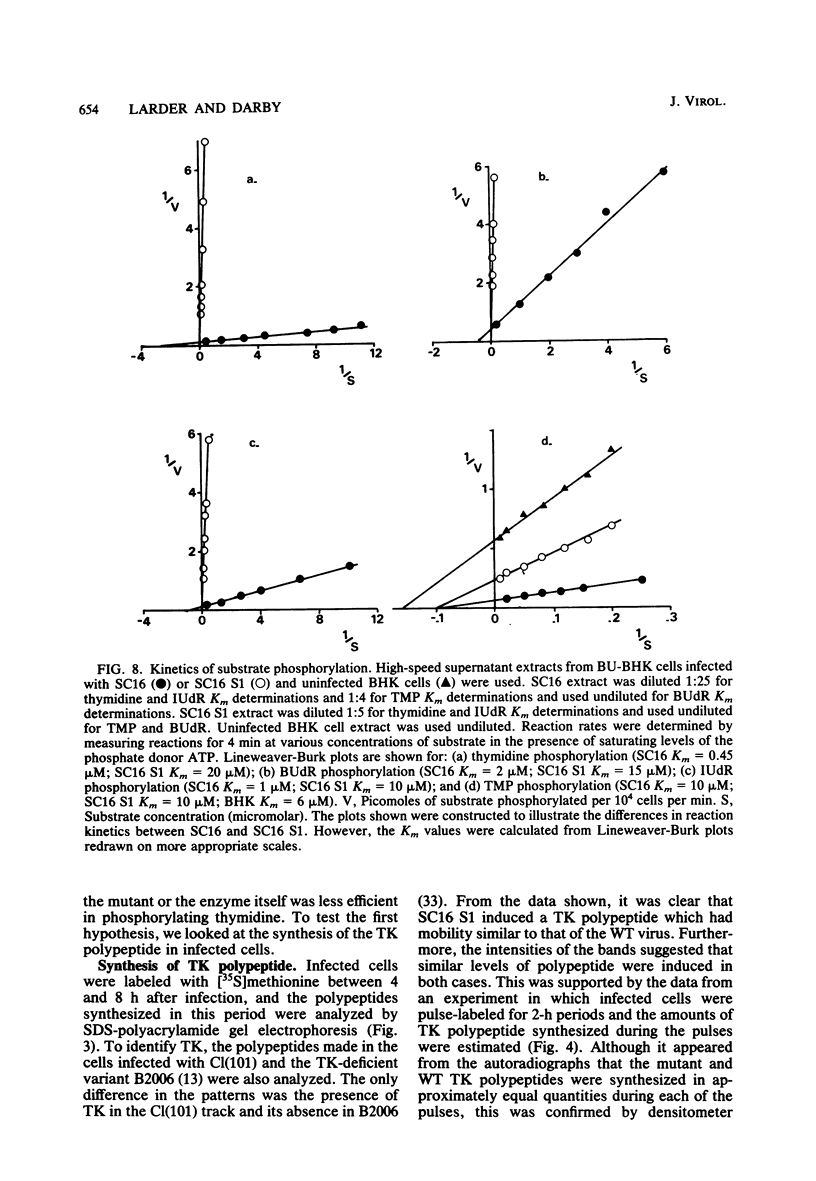
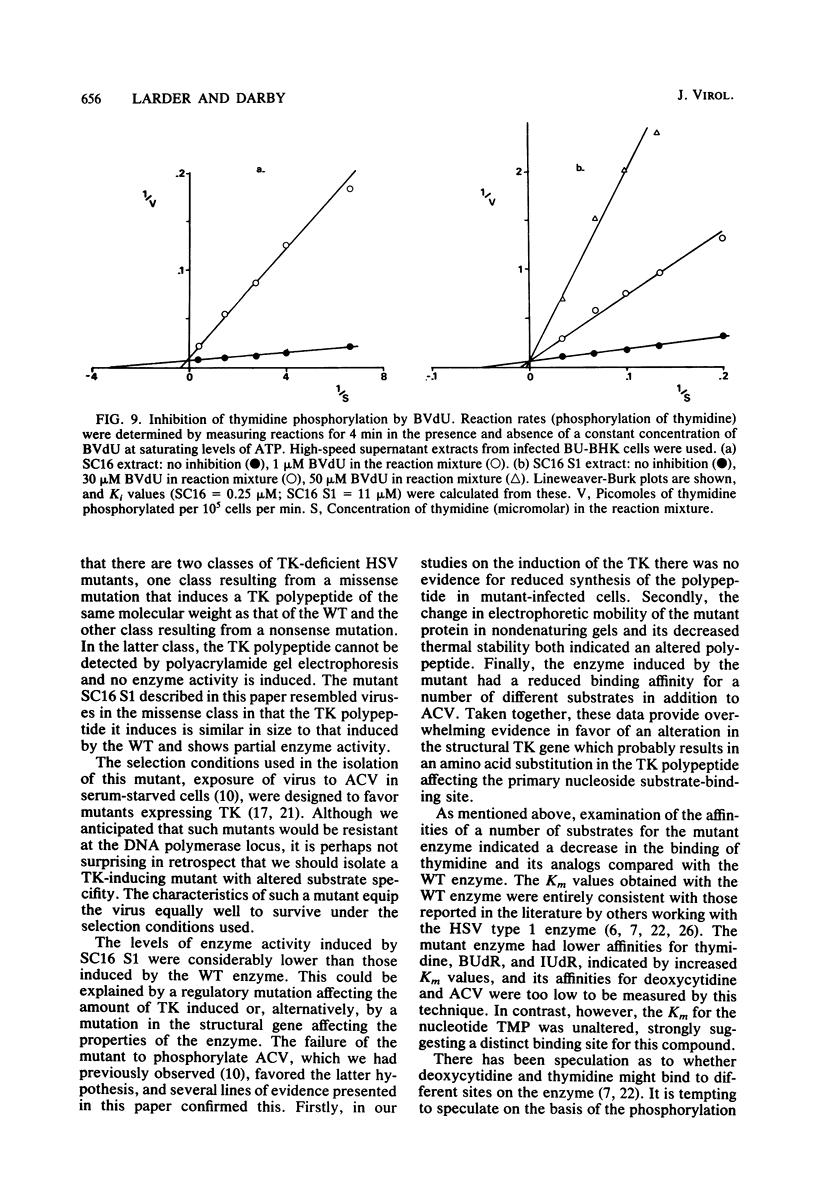
The acyclovir-resistant mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1, SC16 S1, induced reduced levels of thymidine kinase activity (ca. 25% reduction) in infected cells. The activity appeared with kinetics similar to that in wild type-infected cells, and pulse-labeling experiments showed that the thymidine kinase polypeptide was synthesized at a similar rate. We showed that the enzyme was virus specific by inactivating it with antiserum raised against herpes simplex virus-infected cell proteins. The enzyme induced by the mutant had reduced electrophoretic mobility in nondenaturing gels, decreased thermal stability, and decreased affinity for several different substrates (assessed by measurement of Km values) compared with the enzyme induced by the wild type. From the data obtained we conclude that the thymidine kinase induced by the mutant has an altered specificity, probably resulting from an amino acid substitution which affects the primary binding site for nucleosides and nucleoside analogs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allaudeen H. S., Kozarich J. W., Bertino J. R., De Clercq E. On the mechanism of selective inhibition of herpesvirus replication by (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2698–2702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A., Watson D. H. The immunological specificity of thymidine kinases in cells infected by viruses of the herpes group. J Gen Virol. 1969 Apr;4(3):461–463. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-3-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. S., Prusoff W. H. Association of thymidylate kinase activity with pyrimidine deoxyribonucleoside kinase induced by herpes simplex virus. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1325–1327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. S., Prusoff W. H. Phosphorylation of 5-iodo-5'-amino-2',5',dideoxyuridine by herpes simplex virus type 1 encoded thymidine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10449–10452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. S., Summers W. P., Walker J., Summers W. C., Prusoff W. H. Characterization of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleoside kinase (thymidine kinase) and thymidylate kinase as a multifunctional enzyme in cells transformed by herpes simplex virus type 1 and in cells infected with mutant strains of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):942–945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.942-945.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. S., Walker J., Prusoff W. H. Kinetic studies of herpes simplex virus type 1-encoded thymidine and thymidylate kinase, a multifunctional enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10747–10753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C. Deoxythymidine kinase induced in the HELA TK- cells by herpes simplex virus type I and type II. Substrate specificity and kinetic behavior. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):370–381. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Prusoff W. H. A new rapid assay for measuring deoxycytidylate- and deoxythymidylate-kinase activities. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):545–550. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Schaffer P. A. Two distinct loci confer resistance to acycloguanosine in herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2265–2269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBBS D. R., KIT S. MUTANT STRAINS OF HERPES SIMPLEX DEFICIENT IN THYMIDINE KINASE-INDUCING ACTIVITY. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:493–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby G., Field H. J., Salisbury S. A. Altered substrate specificity of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase confers acyclovir-resistance. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):81–83. doi: 10.1038/289081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Descamps J., Verhelst G., Walker R. T., Jones A. S., Torrence P. F., Shugar D. Comparative efficacy of antiherpes drugs against different strains of herpes simplex virus. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):563–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E. New trends in antiviral chemotherapy. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1979 May;87(2):353–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., de Miranda P., Beauchamp L., Schaeffer H. J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5716–5720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Darby G. Pathogenicity in mice of strains of herpes simplex virus which are resistant to acyclovir in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):209–216. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Darby G., Wildy P. Isolation and characterization of acyclovir-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):115–124. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Wildy P. The pathogenicity of thymidine kinase-deficient mutants of herpes simplex virus in mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Oct;81(2):267–277. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Fyfe J. A., Rideout J. L., Keller P. M., Elion G. B. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase activity and viral DNA replication by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine and its triphosphate. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Keller P. M., Furman P. A., Miller R. L., Elion G. B. Thymidine kinase from herpes simplex virus phosphorylates the new antiviral compound, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8721–8727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. J., Field H. J., Blyth W. A. Acute and recurrent infection with herpes simplex virus in the mouse: a model for studying latency and recurrent disease. J Gen Virol. 1975 Sep;28(3):341–353. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-3-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Gentry G. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Induction of both thymidine and deoxycytidine kinase activity by herpes viruses. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):465–480. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Biochemical studies on the herpes simplex virus-specified deoxypyrimidine kinase activity. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):481–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R. Acquisition of thymidine kinase activity by herpes simplex-infected mouse fibroblast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Apr 2;11:55–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R. PROPERTIES OF DEOXYTHYMIDINE KINASE PARTIALLY PURIFIED FROM NONINFECTED MOUSE FIBROBLAST CELLS. Virology. 1965 May;26:16–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Leung W. C., Trkula D. Properties of mitochondrial thymidine kinases of parental and enzyme-deficient HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Oct;158(2):503–513. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90542-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemperer H. G., Haynes G. R., Shedden W. I., Watson D. H. A virus-specific thymidine kinase in BHK-21 cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. H., Miller R. L. Phosphorylation of acyclovir (acycloguanosine) monophosphate by GMP kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7204–7207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogino T., Rapp F. Differences in thermal stability of deoxythymidine kinase activity in extracts from cell infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 or type 2. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):953–955. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Beauchamp L., de Miranda P., Elion G. B., Bauer D. J., Collins P. 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine activity against viruses of the herpes group. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):583–585. doi: 10.1038/272583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnipper L. E., Crumpacker C. S. Resistance of herpes simplex virus to acycloguanosine: role of viral thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2270–2273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton K. R., Clark J. M., Jr A proton exchange between purines and water and its application to biochemistry. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2735–2739. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Kennell W. L., Poirier R. H., Lynd F. T. In vitro and in vivo resistance of herpes simplex virus to 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine (acycloguanosine). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):144–150. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Wagner M., Summers W. C. Possible peptide chain termination mutants in thymide kinase gene of a mammalian virus, herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4081–4084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Dunstan M. E. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase expression in infection of the trigeminal ganglion. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Miller R. L., Rapp F. Trigeminal ganglion infection by thymidine kinase-negative mutants of herpes simplex virus. Science. 1979 Aug 31;205(4409):915–917. doi: 10.1126/science.224454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Skinner G. R. Differences in the properties of thymidine kinase produced in cells infected with type 1 and type 2 herpes virus. J Gen Virol. 1971 Aug;12(2):195–197. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. H., Shedden W. I., Elliot A., Tetsuka T., Wildy P., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D., Gold E. Virus specific antigens in mammalian cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Immunology. 1966 Oct;11(4):399–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]