Abstract
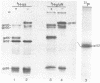
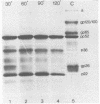
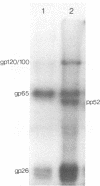
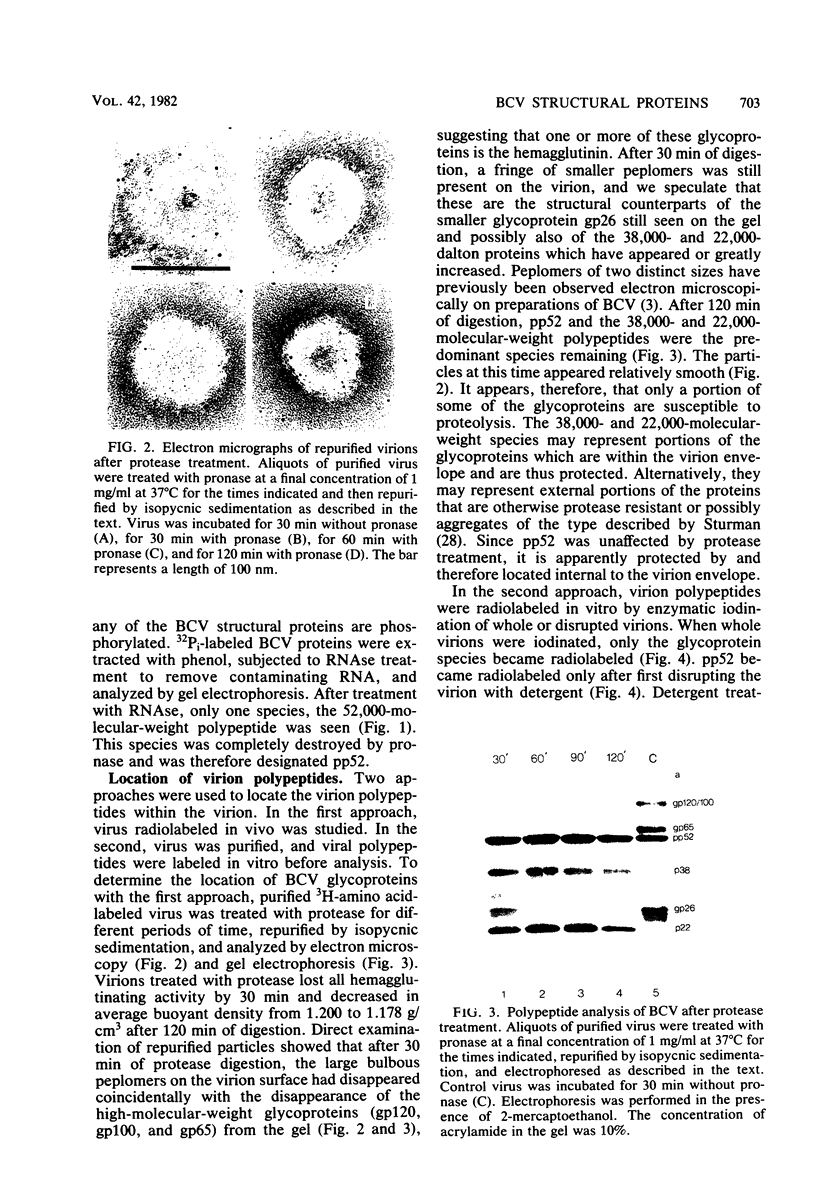
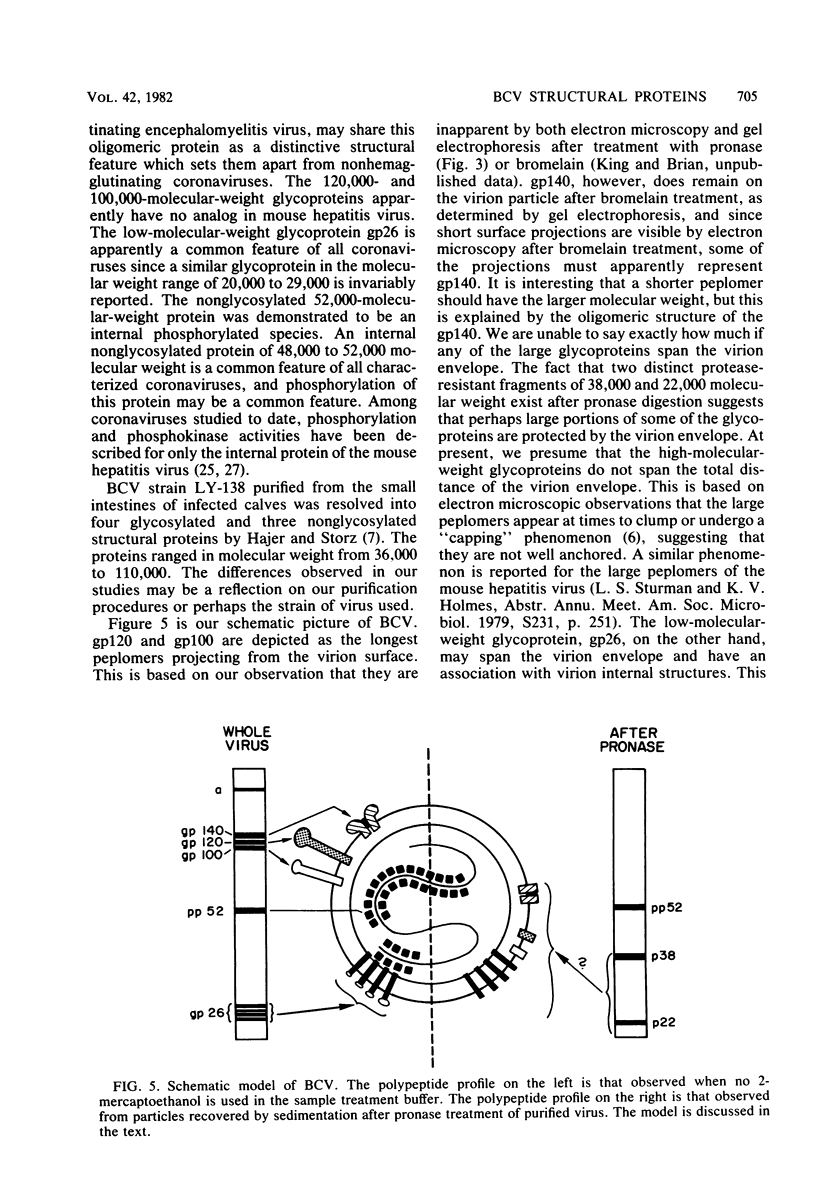
The tissue culture-adapted strain (Mebus) of bovine coronavirus was grown in the presence of isotopically labeled amino acids, glucosamine, or orthophosphate for the purpose of analyzing the virion structural proteins. Five species of polypeptides were identified when purified virions were solubilized in urea and sodium dodecyl sulfate and resolved by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Four species were glycosylated and had apparent molecular weights of 140,000, 120,000, 100,000, and 26,000. The glycoproteins were susceptible to proteolytic cleavage and enzymatic iodination when intact virions were studied and are thus at least partially external to the virion envelope. The 140,000-molecular-weight glycoprotein is apparently a dimer of 65,000-molecular-weight glycopolypeptides held together by disulfide linkages. Species 5 was phosphorylated and had an apparent molecular weight of 52,000. In the intact virion, it was unaffected by protease and was not enzymatically iodinated. It is therefore apparently an internal protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Expression of animal virus genomes. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):235–241. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.235-241.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brian D. A., Dennis D. E., Guy J. S. Genome of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.410-415.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Caul E. O., Egglestone S. I. Replication of an enteric bovine coronavirus in intestinal organ cultures. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):43–51. doi: 10.1007/BF01315636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callebaut P. E., Pensaert M. B. Characterization and isolation of structural polypeptides in haemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 May;48(1):193–204. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garwes D. J., Pocock D. H. The polypeptide structure of transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Oct;29(1):25–34. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy J. S., Brian D. A. Bovine coronavirus genome. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):293–300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.293-300.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajer I., Storz J. Structural polypeptides of the enteropathogenic bovine coronavirus strain LY-138. Arch Virol. 1979;59(1-2):47–57. doi: 10.1007/BF01317894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Palmer E. L., Whitfield S. G., Kaye H. S., Dowdle W. R. Protein composition of coronavirus OC 43. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):516–527. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90062-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba Y., Sato K., Kurogi H., Takahashi E., Ito Y. Replication of bovine coronavirus in cell line BEK-1 culture. Arch Virol. 1976;50(4):339–342. doi: 10.1007/BF01317959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy D. A., Johnson-Lussenburg C. M. Isolation and morphology of the internal component of human coronavirus, strain 229E. Intervirology. 1975;6(4-5):197–206. doi: 10.1159/000149474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Stohlman S. A. RNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):236–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.236-242.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser J. A., Howard C. R. The polypeptides of infectious bronchitis virus (IBV-41 strain). J Gen Virol. 1980 Feb;46(2):349–361. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B. Biological properties of avian coronavirus RNA. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):531–533. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Kennedy I. Genome of infectious bronchitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.99-107.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnaughton M. R., Madge M. H. The polypeptide composition of avain infectious bronchitis virus particles. Arch Virol. 1977;55(1-2):47–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01314478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macneughton M. R., Davies H. A. Ribonucleoprotein-like structures from coronavirus particles. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jun;39(3):545–549. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-3-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C., Ward J., Mengeling W. L. Antigenic relationship of the feline infectious peritonitis virus to coronaviruses of other species. Arch Virol. 1978;58(1):45–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01315534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Stevens R. H., Simpson R. W. Presence of infectious polyadenylated RNA in coronavirus avian bronchitis virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):772–782. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90498-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Wickus G. G., Burge B. W. Enzymatic iodination of Sindbis virus proteins. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):730–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.730-735.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpee R. L., Mebus C. A., Bass E. P. Characterization of a calf diarrheal coronavirus. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Sep;37(9):1031–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Barthel A., ter Meulen V. Coronavirus JHM: a virion-associated protein kinase. J Gen Virol. 1981 Feb;52(Pt 2):235–243. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stair E. L., Rhodes M. B., White R. G., Mebus C. A. Neonatal calf diarrhea: purification and electron microscopy of a coronavirus-like agent. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Jun;33(6):1147–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Phosphoproteins of murine hepatitis viruses. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):672–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.672-675.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V., Behnke J. Isolation of coronavirus envelope glycoproteins and interaction with the viral nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):449–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.449-462.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. Characterization of coronavirus II. Glycoproteins of the viral envelope: tryptic peptide analysis. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):650–660. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90489-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S. I. Structural proteins: effects of preparative conditions on the migration of protein in polyacrylamide gels. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):637–649. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90488-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. A., Alexander D. J., Almeida J. D., Cunningham C. H., Easterday B. C., Garwes D. J., Hierholzer J. C., Kapikian A., Macnaughton M. R., McIntosh K. Coronaviridae: second report. Intervirology. 1978;10(6):321–328. doi: 10.1159/000148996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Wege H., Nagashima K., ter Meulen V. Structural polypeptides of the murine coronavirus JHM. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jan;42(1):37–47. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]