Abstract
Despite high rates of exposure, only 5–10% of people infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis will develop active tuberculosis (TB) disease, suggesting a significant role for genetic variation in the human immune response to this infection. Here, we studied TB association and expression of 18 genes involved in the Toll-like receptor (TLR) pathways. Initially, we genotyped 149 sequence polymorphisms in 375 pulmonary TB patients and 387 controls from Indonesia. We found that four polymorphisms in the TLR8 gene on chromosome X showed evidence of association with TB susceptibility in males, including a non-synonymous polymorphism rs3764880 (Met1Val; P = 0.007, odds ratio (OR) = 1.8, 95% c.i. = 1.2–2.7). We genotyped these four TLR8 polymorphisms in an independent collection of 1,837 pulmonary TB patients and 1,779 controls from Russia and again found evidence of association in males (for rs3764880 P = 0.03, OR = 1.2, 95% c.i. = 1.02–1.48). Combined evidence for association is P = 1.2×10−3–6×10−4. In addition, a quantitative PCR analysis indicated that TLR8 transcript levels are significantly up-regulated in patients during the acute phase of disease (P = 9.36×10−5), relative to baseline levels following successful chemotherapy. A marked increase in TLR8 protein expression was also observed directly in differentiated macrophages upon infection with M. bovis bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG). Taken together, our results provide evidence, for the first time, of a role for the TLR8 gene in susceptibility to pulmonary TB across different populations.
Author Summary
One third of the world population is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis; however, only 5–10% of those infected will develop active disease. Difference in polymorphisms within genes involved in host immune response has been proposed as a plausible reason to explain this phenomenon. Here, we show genetic association of four polymorphisms of TLR8, a member of a well-known receptor family involved in pathogen recognition, in an Indonesian population. The association was replicated in males of a follow up cohort from Russia. Expression levels of TLR8 transcripts and protein showed a marked increase during bacterial infection, confirming our initial findings. To our knowledge, this is the first time that TLR8 has been associated with response to M. tuberculosis. Our results suggest that it may play a significant role in tuberculosis susceptibility and disease activity, and thus should be the focus of concerted studies in human systems.
Introduction
Although one-third of the world's population is infected with M. tuberculosis [1], fewer than 10% of infected –otherwise immunocompetent- individuals will develop clinical disease during their lifetime [2]. The immunological mechanisms that distinguish the majority of individuals who successfully contain these organisms from the minority who develop progressive mycobacterial disease are largely unknown.
It is becoming increasingly clear that innate immunity plays a crucial role in directing many aspects of the host response, including the ensuing adaptive response, making it a primary host defense mechanism. The initial phase of this process is pathogen sensing involving a wide range of pattern recognition molecules. We and others have postulated that pathogen recognition could be a key component in determining the outcome of infection [3],[4]. At the same time, evidence is building in a number of diseases, including TB [5] and meningococcal disease [6], that variations in genes of a related pathway may have similar functional consequences, and thus result in a similar phenotype upon infection.
These observations led us to investigate genetic variants in the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) [7]–[11] and related adaptors for association with human susceptibility to pulmonary TB. So far fifteen functional TLRs have been identified in mammals and implicated in specific recognition of pathogen associated molecules [12]. Upon ligand binding, TLRs initiate a cascade of events leading to the transcription of NFkB-dependent genes, mostly inflammatory genes. All functional TLRs, except TLR5 (GeneID:7100), were studied. The latter was excluded due to a low level of polymorphism and to complex sequence duplications that could make SNP genotyping difficult. We also studied cytoplasmic TLR adaptors including MYD88 (GeneID:4615), TOLLIP (GeneID:54472), TIRAP (GeneID:114609), TICAM1 (GeneID:148022), TICAM2 (GeneID:353376) and the downstream signaling molecules, IRAK1 (GeneID:3654) and IRAK4 (GeneID:51135), LY96 (MD2) (GeneID:23643) [13] as well as CD14 (GeneID:929) [14], a surface molecule that partners with TLR4 (GeneID:7099).
Here we identified four single nucleotide polymorphisms within the TLR8 gene (GeneID:51311) on chromosome X that confer susceptibility to pulmonary TB in males in an Indonesian population and in a large independent sample of TB patients and controls from Russia. Additional evidence in support of TLR8 (NP_619542.1) in immunity to TB disease came from real-time PCR quantification of elevated levels of TLR8 transcripts (NM_016610.2; NM_138636.3) during active disease, relative to the same individuals following successful completion of anti-TB chemotherapy. In line with this, analysis of differentiated macrophages upon stimulation with BCG over time showed a significant increase of TLR8 expression. Taken together, these results provide strong evidence for the first time, of a role for TLR8 in adult pulmonary TB infection.
Results
Genetic Association Analysis
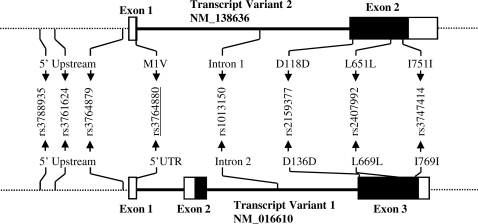
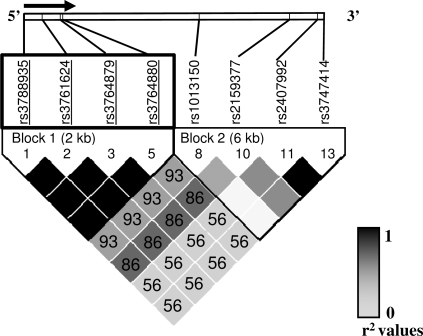
Of the 149 SNPs passing quality control as described in materials and methods, allelic and genotypic association analysis identified four SNPs in the TLR8 gene with nominal p-values below 0.05 (Table 1 and Table S1). We also observed two rare variants, within TOLLIP and TLR9 (GeneID:54106), with significant p-values that were not followed up in this study due to their very low allele frequencies. Three of the associated TLR8 variants, rs3764879, rs3788935 and rs3761624 localize in the putative regulatory regions, within five kilobases upstream of the gene (Figure 1). The fourth associated polymorphism was a missense variant, rs3764880 (Met1Val), which would ablate the putative start codon in one of the transcripts encoded by this gene. Given that TLR8 is located on the X chromosome, we performed separate tests for males and females (Table 2). We found a strong allelic association with the minor allele A of the putatively functional polymorphism, rs3764880, with susceptibility to pulmonary TB in males [OR (95% c.i.) = 1.8 (1.2–2.7), P = 0.007]. Very similar and significant association values were found in the three promoter variants, attributable to perfect linkage disequilibrium (r2 = 1) between all four polymorphisms (Figure 2).
Table 1. Allelic Distribution and Description of SNPs within TLR8 with p-values<0.05 in Indonesian TB Patients and Controls.
| dbSNP rs# | Alleles | No. of Casesa | MAF Cases | No. of Controlsa | MAF Controls | Locationb | p-value | Permutation p-valuec | OR (95% c.i.) |
| rs3764879 | G/C | 153 | 0.30 | 124 | 0.23 | Upstream | 0.01 | 0.038 | 1.4 (1.06–1.84) |
| rs3788935 | G/A | 152 | 0.30 | 125 | 0.23 | Upstream | 0.014 | 0.05 | 1.4 (1.07–1.86) |
| rs3761624 | G/A | 152 | 0.30 | 126 | 0.24 | Upstream | 0.016 | 0.059 | 1.4 (1.06–1.8) |
| rs3764880 | G/A | 152 | 0.30 | 126 | 0.24 | M1V, 5′UTR | 0.016 | 0.059 | 1.4 (1.06–1.8) |
Number of chromosomes carrying the minor allele.
Locations for both transcripts encoded by TLR8 are shown.
Number of permutations = 10,000.
Figure 1. Transcript variants of TLR8 and location of genotyped SNPs within both transcripts.
Exons are shown as rectangles, filled areas represent translated sequence, open areas indicate untranslated regions. The associated polymorphism resulting in a coding change exclusive of transcript variant 2 (rs3764880) is underlined.
Table 2. Allele Distribution of TLR8 Polymorphisms among Indonesian TB Patients and Controls by gender.
| dbSNP ID | Males | Females | |||||||
| No. of Cases (%)a | No. of Controls (%)a | p-value | Permutational p-valueb | O.R. (95% c.i.) | No. of Cases (%)a | No. of Controls (%)a | p-value | O.R. (95% c.i.) | |
| rs3764879 | 77 (34.6) | 49 (21.7) | 0.0024 | 0.012 | 1.9 (1.2–2.9) | 76 (27.1) | 74 (24.3) | 0.44 | 1.1 (0.8–1.7) |
| rs3788935 | 76 (34.3) | 50 (22.1) | 0.0039 | 0.017 | 1.8 (1.2–2.8) | 76 (27.1) | 74 (24.3) | 0.44 | 1.1 (0.8–1.7) |
| rs3761624 | 76 (34.3) | 51 (22.4) | 0.007 | 0.02 | 1.8 (1.2–2.7) | 76 (27.1) | 74 (24.3) | 0.44 | 1.1 (0.8–1.7) |
| rs3764880 | 76 (34.3) | 51 (22.4) | 0.007 | 0.02 | 1.8 (1.2–2.7) | 76 (27.1) | 74 (24.3) | 0.44 | 1.1 (0.8–1.7) |
Number and percent of chromosomes carrying the minor allele.
Number of permutations = 10,000.
Figure 2. Linkage Disequilibrium Plot and Haplotype Structure of TLR8.
D' values displayed within each diamond, missing value indicates D' = 100%. Color scheme gradient indicates r2 values. At the top, direction of transcription is designated by an arrow. Length of each block, in kilobases (kb), is shown between brackets. Underlined polymorphisms indicated associated SNPs in allelic analysis. Block with significant p-values is displayed within an open rectangle.
In order to address the significance of our findings, a permutation analysis of the allelic p-values was carried out (Table 1). One of the polymorphisms passed the permutation test (N = 10,000), with its p-value remaining statistically significant at an adjusted P<0.05. The same analysis was applied separately by gender. In this case, all four SNPs maintained statistical significance at an adjusted P<0.05 in males (Table 2).
Analysis of genotypes for polymorphisms located on Chromosome X was done using a likelihood ratio test. The same four variants on TLR8 were found to be more frequent in cases than controls, indicating susceptibility to disease for carriers of the minor allele. Due to the fact that males carry only one copy of each allele, the genotype association outcome was expected to be the same as for the previous allele association result. Thus, we analyzed genotypes of female subjects (Table S2). The observed number of homozygotes for the associated missense polymorphism, rs3764880 (AA), may have been too low to detect an effect (14 affected vs. 9 controls). Nevertheless there was an apparent trend towards the same outcome observed in the overall sample, with affected females showing an increase of homozygotes for the minor allele, compared to the control group.
Investigation of the gene structure of TLR8 showed two distinct haplotype blocks (Figure 2) in our population. As expected from our initial results, all four associated polymorphisms appeared in the same haplotype block (Block1). Performing separate association analysis of haplotypes in males and females confirmed the genetic association in males (Table S3). The minor haplotype (H2) harboring allele A of rs3764880 showed a pronounced risk effect of disease among male carriers [OR (95% c.i.) = 1.8 (1.2–2.7)]. The population attributable risk of the associated haplotype in males was 4% [15].
In order to confirm these results, genotyping of the four associated polymorphisms was carried out in a follow-up cohort from Russia (1,873 tuberculosis cases, 1,779 controls). Importantly, the minor allele frequency of rs3764880 in the Indonesian population was strikingly different compared to frequencies in the Russian cohort, which was concordant with results obtained for the populations of European and Asian origin from the HapMap project [16]. Around 30% of the Indonesian subjects carried the A allele (Met) associated with risk to TB, whereas this same allele was present in 78% of Russians. Despite these obvious differences in frequencies, the genetic association with pulmonary TB was replicated in the Russian males for allele A of rs3764880 OR (95% c.i.) = 1.2 (1.02–1.48) P = 0.03 (Table 3). Combined evidence for association in males from both Indonesian and Russian populations was P = 1.2×10−3–6×10−4. Analysis of haplotype blocks showed the same trend of association as observed in the Indonesian cohort. In this case, however, the most common haplotype was the one harboring rs3764880A, and displayed a risk effect among male carriers [OR (95% c.i.) = 1.22 (1.01–1.47)] (Table S3).
Table 3. p-value of TLR8 Polymorphisms in Russian Males and combined (Russian and Indonesian) cohorts.
| dbSNP ID | Alleles | Russian cohort | Combined p-value | |||
| No. of Cases (%)a | No. of Controls (%)a | p-value | OR (95% c.i.) | |||
| rs3764879 | G/C | 1067 (79.7) | 994 (76.3) | 0.03 | 1.2 (1.02–1.48) | 6×10−4 |
| rs3788935 | G/A | 1069 (79.8) | 997 (76.4) | 0.03 | 1.2 (1.02–1.48) | 9×10−4 |
| rs3761624 | G/A | 1070 (79.8) | 1000 (76.5) | 0.04 | 1.2 (1.01–1.46) | 1.5×10−3 |
| rs3764880 | G/A | 1069 (79.7) | 997 (76.3) | 0.03 | 1.2 (1.02–1.48) | 1.2×10−3 |
Number and percent of chromosomes carrying the risk allele shown in bold.
mRNA Expression Study
A subset of 23 patients with active pulmonary TB was selected from the cohort recruited from the outpatient clinic in Jakarta, Indonesia. After informed consent, blood samples were taken from each of the patients during their initial diagnosis with active pulmonary TB disease (at the time of admission), and again following resolution of disease (6 months after completion of a standard anti-tuberculosis multi-drug chemotherapy). Real-time reverse transcription PCR was used to study the mRNA levels of 18 genes (Table S4). We observed that both TLR8 transcripts, TLR8v1 (p = 9.36×10−5), TLR8v2 (p = 5.29×10−5) and MYD88 (NM_002468.3) (p = 4.09×10−5) were the most significantly upregulated in TB patients during active disease, relative to their convalescence. Both variants of TLR8 showed a greater than two-fold increase in expression, whereas MYD88 increased by 1.9-fold (Table 4). Transcript levels of TLR7 (NM_016562.3) and CD14 (NM_001040021.1) were also significantly increased (p = 2.5×10−3; 3×10−2 respectively), whereas TIRAP (NM_148910.2) showed a downregulation of mRNA expression, fold change = 0.2, but without statistical significance (Table 4).
Table 4. Genes tested on mRNA Expression in Acute vs. Convalescence Indonesian TB Samples.
| Gene Name | mRNA ID | Fold change | p value | Bonferroni p-value |
| TLR1 | NM_003263.3 | 1.556 | 5.5*10−2 | NS |
| TLR2 | NM_003264.3 | 1.595 | 7.8*10−2 | NS |
| TLR3 | NM_003265.2 | 0.825 | 0.63 | - |
| TLR4 | NM_138554.2 | 1.45 | 0.86 | - |
| TLR6 | NM_006068.2 | 1.885 | 0.17 | - |
| TLR7 | NM_016562.3 | 1.78 | 2.5*10−3 | 0.047 |
| TLR8 | NM_016610.2 (variant 1) | 2.278 | 9.4*10−5 | 1.8*10−3 |
| TLR8 | NM_138636.3 (variant 2) | 2.41 | 5.3*10−5 | 1*10−3 |
| TLR9 | NM_017442.2 | 1.453 | 0.18 | - |
| TLR10 | NM_030956.2 | 0.949 | 0.84 | - |
| MYD88 | NM_002468.3 | 1.898 | 4.1*10−5 | 7.8*10−4 |
| TICAM1 | NM_182919.1 | 0.87 | 0.52 | - |
| TICAM2 | NM_021649 | 0.6 | 0.37 | - |
| LY96 | NM_015364.2 | 1.28 | 0.12 | - |
| TOLLIP | NM_019009.2 | 0.964 | 0.99 | - |
| TIRAP | NM_148910.2 | 0.236 | 7*10−2 | NS |
| CD14 | NM_001040021.1 | 2.457 | 3*10−2 | NS |
| IRAK1 | NM_001569.3 | 1.26 | 0.1 | - |
| IRAK4 | NM_016123.1 | 1.283 | 0.3 | - |
TLR8 Protein Expression Study
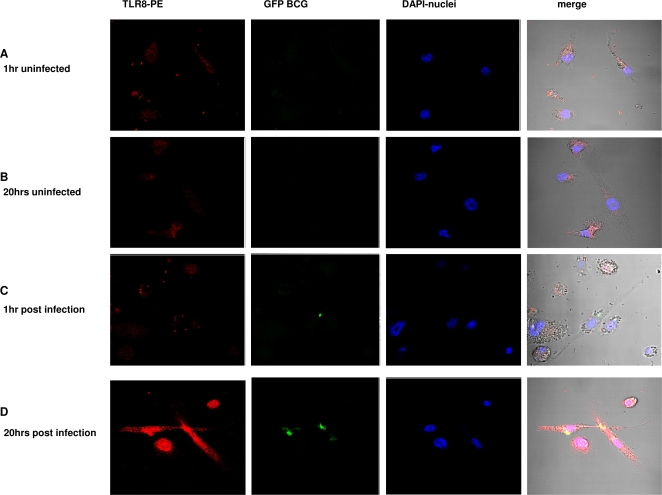
Expression of TLR8 over time was assessed in human THP1 macrophages after infection by M. bovis BCG (Figure 3). Uninfected control cells showed no change of TLR8 protein levels over time (Figure 3A, B). However, infected macrophages showed a marked raise of TLR8 expression at 20 hours post-infection (Figure 3D). It is noteworthy that even cells that didn't take up the whole bacteria displayed an important increase on TLR8 (Figure 3D).
Figure 3. Increased Expression of TLR8 in THP1 cells upon BCG stimulation.
THP-1 differentiated macrophages were either uninfected (a,b) or infected with GFP BCG (c,d). Macrophages were harvested for TLR8 expression measured by phycoerytrhin (PE) intensity at 1 hr (c) or 20 hrs (d) post infection and fixed cells were imaged by confocal microscopy.
Discussion
Here we describe a genetic association study aiming to identify polymorphisms within the TLR pathway which confer increased susceptibility to adult pulmonary TB and for the first time report evidence implicating TLR8. Association of the TLR8 sequence variants with pulmonary TB disease was seen in two independent case-control collections from Indonesia and Russia. Real-time PCR experiments showed the up regulation of TLR8 transcripts in TB patients during acute disease. Protein expression levels of TLR8 were also shown to increase in macrophage cell lines after infection with BCG.
The cloning and characterization of human TLR7/8/9 revealed significant similarity of their protein sequences [17],[18], defining, together with TLR3 (GeneID:7098), a new sub-family within the Toll-like receptor genes. In contrast to the other TLRs, their protein products are localized intracellular rather than at the cell surface, mostly in association with the endosomal vacuolar system [19]. Although only TLR9 (NP_059138.1) has been experimentally proven to recognize mycobacterial DNA [20], single-stranded RNA derived from pathogens has been proposed as a likely ligand of TLR7 (NP_057646.1) and TLR8 [21],[22]. The translocation of TLR9 from the endoplasmic reticulum to the lysosome following CpG binding has recently been described [23]. TLR8 and TLR9 are very closely related to each other, raising the possibility that both receptors share a similar mode of activation. M. tuberculosis is an intracellular pathogen that resides in characteristic phagosomes, which are not acidic and generally do not mature into phagolysosomes [24],[25]. However, the mycobacterial phagosome interacts with early endosomes, where the bacteria could encounter TLR8.
We found evidence that TLR8 polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to pulmonary TB among males. Initially we detected association in the Indonesian population and then observed the same effect in a large independent Russian TB collection, suggesting that this might be a true effect. Nevertheless, our combined evidence (P = 6×10−4) does not completely exclude association by chance and further studies in statistically powerful sample collections are important. TLR8 is located on Chromosome X, which suggests that any allele conferring susceptibility to disease may well have a higher impact among males who carry only one copy of the gene. Indeed, the genetic association was more significant in affected males. Hence, inferences about gender-specific effects could possibly be drawn from our findings, where male carriers of rs3764880 allele A showed an increased susceptibility to pulmonary TB. One might expect to find the same association among females homozygous for the same allele, and a tendency towards an altered distribution of affected females homozygous for the minor allele (10%) was indeed observed when compared to female controls (6%) in the Indonesian cohort (Table S2).
In our data the four associated TLR8 polymorphisms correlate perfectly with each other both in the Indonesian and the Russian samples. Therefore, we were unable to distinguish the variant primarily associated with TB from the polymorphisms associated merely because of linkage disequilibrium. It is also possible that in this study we did not genotype the causal polymorphism. Hence, future experiments should cover all common variation in the associated TLR8 gene region in order to pinpoint the causal polymorphism. Nevertheless, one of the associated polymorphisms in this study, rs3764880 (Met1Val), is a good functional candidate. Its allele G, associated with protection from TB, abolishes a putative start codon within the alternative transcript variant 2 (Figure 1). Asian populations appear to have an unusually elevated derived allele frequency for this missense variant compared to other ethnic groups [16]. It is remarkable that despite the large differences in allele frequencies between the two populations studied, a genetic association was detected with the same SNPs and in the same direction. Such a significant rise in allele frequency, presumably occurring in Asia, could indicate an important selective advantage or disadvantage for this allele in some environments. Some of the effects of replacing the first methionine of transcript 2 by valine has recently been established [26]. In vitro studies have shown that the G variant affects NF-kappa B activation, as well as response to different TLR8 ligands. Furthermore, the initial amino acids are predicted to act as a signal peptide for this intracellular membrane-bound protein. Therefore, the loss of this sequence could, among other possibilities, affect intracellular trafficking, proper protein folding, or the stability of the mature protein [27],[28]. Further genetic and functional studies of the associated polymorphisms, and other polymorphisms identified by gene resequencing, should add considerably to our understanding of TLR8 function in general, and specifically in response to TB infection.
Two TLR8 transcript variants have been characterized thus far [17],[18]. Using quantitative RT-PCR we show here that both display significantly upregulated expression in TB patients during the acute phase of their disease, suggesting a functional role for TLR8 during MTB infection. THP1 differentiated macrophages displayed an increase of TLR8 protein levels after infection with M. bovis BCG. Interestingly, the rise in expression could be observed even in cells that had not visibly phagocytosed whole bacteria. Although TLR8 ligands remain as yet unidentified, our results are compatible with the hypothesis that a secreted bacterial product might be involved in triggering a TLR8 response, after being taken up by the host cell.
In summary, we report for the first time evidence of associations of TLR8, a key gene implicated in the innate immune response, with pulmonary TB in Indonesian and Russian populations. Because it is not expressed in mouse, TLR8 is among the least studied members of the toll-like receptor family, but our results suggest that it may play a significant role in TB susceptibility, and thus should be the focus of concerted studies in human systems.
Material and Methods
Subject Recruitment
Indonesia
439 new pulmonary tuberculosis patients above 15 years of age were recruited from an outpatient tuberculosis clinic in central Jakarta (Indonesia) [29]. Diagnosis was based on clinical presentation and chest X-ray examination, confirmed by sputum microscopy positive for mycobacteria [30]. 490 randomly selected control subjects with the same sex and age (+/−10%), were recruited from neighbouring households. First-degree relatives of patients were excluded. Control subjects with signs and symptoms suggesting active tuberculosis or a history of prior anti-TB treatment were also excluded. Self and parental ethnicities were recorded upon recruitment. A Javanese origin characterized three groups - the Jawa, Betawi, and Sunda - and altogether comprised more than 80% of the total sample. The non-Javanese category included individuals born on other Indonesian islands. Subjects were considered of mixed ethnicity when one parent was of Javanese ethnic origin and the other non-Javanese (Table 5).
Table 5. Demographic and Clinical Data of the Study Populations.
| Indonesian | Russian | |||
| TB Patients (N = 375) | Controls (N = 387) | TB Patients (N = 1,837) | Controls (N = 1,779) | |
| Age years (median) | 14–75 (28) | 15–70 (32) | 17–86 (43.8) | 16–66 (30) |
| Gender male(%):female(%) | 228(60.8%):147(39.2%) | 232(60%):155(40%) | 1341(73%):496(27%) | 1308(73.5%):471(26.5%) |
| BCG Scar Present (%) | 143 (38%) | 168 (43%) | - | - |
| Self reported ethnicity (%) | ||||
| Caucasian | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1,837 (100) | 1,779 (100) |
| Javanese | 326 (86.9) | 314 (81.1) | - | - |
| Non Javanese | 29 (7.7) | 21 (5.4) | - | - |
| Mixed | 19 (5.1) | 29 (7.5) | - | - |
| Unknown | 1 (0.3) | 23 (5.9) | - | - |
Prior to recruitment, subjects diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and HIV coinfection, both of which are considered to be major risk factors for tuberculosis development, were not considered. Further tests on recruited subjects were done to confirm absence of diabetes mellitus and HIV coinfection. (Details described elsewhere [31]). Briefly, subjects with levels of fasting blood glucose over 126 mg/dL were considered to have diabetes. HIV testing was performed using dipstick test (Abbott, Determine). Thirty five additional subjects were positive for diabetes.
In order to define a homogeneous phenotype, patients suspected of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis (N = 27) were not considered in the analyses. Controls with suspected tuberculosis after chest X-ray examination (N = 24) or a history of tuberculosis (N = 7) were also excluded.
Russia
1,837 cases of pulmonary TB and 1,779 controls were recruited from two Russian cities: St Petersburg and Samara. Clinical data has been described elsewhere [32]. In summary, all TB cases were confirmed by sputum culture of M. tuberculosis. Patients with extra-pulmonary TB or HIV-positive were not included in the study. Local blood bank donors with no known history of TB were recruited as controls.
The demographic and clinical data of the Indonesian and Russian cohorts are shown in Table 5. In both groups patients and controls showed a comparable male/female ratio, with males comprising 60% of the subjects in Indonesians and 73% in Russians. Only the Indonesian group had data available on BCG scarring, showing a smaller number of patients with evidence of scarring compared to the control group [38% vs. 43%] (see also ref. 29).
Analysis of population stratification
The self-reported ethnicity of each subject and his/her parents was carefully considered in an effort to avoid spurious genetic associations arising from population stratification. In order to detect traces of population stratification in the Indonesian cohort, a large subset of individuals included in this first stage of the study, 330 cases and 368 controls, were genotyped for an independent set of 299 SNPs. One of the SNPs was out of HWE and, thus, excluded from the analysis. These SNPs were chosen to be more than 10 kilobases away from any known gene, to have average minor allele frequencies around 30% and to be in linkage equilibrium with one another. The correction factor was calculated according to the method of Devlin and Roeder [33]. Briefly, an inflation factor was calculated as the median of the chi-square values for all 298 SNPs, divided by 0.675 and then squared. It resulted in a value below 1 (0.82), which indicated that there was no significant population stratification in the Indonesian group (Table S5). Evidence of absence of population stratification in the Russian cohort has been described previously [32].
DNA and RNA Extraction
Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood following a protocol described elsewhere [34]. After genotyping, 74 samples were excluded from the Indonesian cohort because of sample duplication and/or familial relationships not originally reported, but identified by RelPair [35].
RNA was successfully extracted using an RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Germany) from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of a subset of 23 patients.
Consent forms approved by local Institutional Review Boards of the Medical Faculty of University of Indonesia and the Eijkman Institute for Molecular Biology in Jakarta were signed upon recruitment by all participants. Written informed consents from all Russian subjects as well as permission from ethics committees were obtained [32].
SNP Genotyping
Selection of SNPs was carried out using an in-house database, GISSNP, which integrates data from public databases (Ensembl, Celera, dbSNP build 123/126) as well as proprietary data. Polymorphisms with the following characteristics were preferentially chosen: putative functional variants resulting in changes in the protein sequence, minor allele frequencies over 5%, average spacing of one SNP every 1 to 2 kilobases. To screen for possible regulatory elements, flanking regions five kilobases upstream and downstream of the gene were also covered.
Design of a custom Oligo Pool Assay (Illumina) was implemented following the manufacturer's specifications. Genotyping was performed with a BeadStation 500G Genotyping System (Illumina). Genotypes were analyzed with Beadstudio software also from Illumina. Ten SNPs were genotyped with a Sequenom primer extension-based protocol described elsewhere [36],[37]. The genotype concordance among the two systems used for genotyping in this study has been reported to be over 99.5% [37]. Assessment of genotypes was done by laboratory personnel without any prior knowledge of the diagnosis of the subjects.
Genotyping of 247 SNPs from 18 candidate genes was performed in the Indonesian cohort. We found that 75 SNPS (30%) of the genotyped polymorphisms were monomorphic in this population (Table S4). Variants with call-rates below 90% (N = 17) were not considered. Six SNPs showed deviations from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) in the control group, and were removed from further analysis (Table S4). Association analyses were applied to the remaining 149 polymorphic SNPs with reliable genotypes (Table S1).
Genetic Association Statistical Analysis
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was calculated in the control group using HelixTree v4.4.1 (GoldenHelix Inc., Bozeman, MT, United States) and Exemplar (Sapio Sciences, LLC, York, PA, United States). Similarly, allelic association analysis was carried out in both software packages. Allelic p-values were calculated by means of a 2×2 chi-square table. A two-sided Fisher Exact test, when counts in any cell fell below five, as well as odds ratios were calculated with Exemplar. Allelic analysis of SNPs located on Chromosome X was performed with Haploview v3.31 [38]. A likelihood ratio test was applied to calculate genotypic associations of SNPs on Chromosome X. Combined p-values were calculated by Fisher's combined probability test which allows pooled information across several tests that share the same null hypothesis [39].
The statistical significance of nominal allelic p-values was assessed by permutation analysis (N = 10,000) with Haploview v3.31.
Haplotype blocks and linkage disequilibrium plots were constructed with Haploview v3.31 using the default algorithm proposed by Gabriel et al [40].
Taqman Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR
A subset of 23 patients with active pulmonary TB was selected from a cohort recruited from an outpatient clinic in Jakarta, Indonesia. Blood samples were taken from each of the patients at 2 time points: the active phase of pulmonary TB disease (at the time of admission), and the convalescent phase (6 months after admission and standard anti-tuberculosis multi-drug chemotherapy). Real-time reverse transcription PCR was used to study expression levels of 18 genes (Table S4) on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Briefly, an aliquot of 10 µl RNA was reverse transcribed to cDNA using the high capacity cDNA kit (Applied biosystems Asia Pte Ltd). The obtained cDNA was diluted 1/5 with water and 10 µl was used for amplification.
Generation of GFP M. bovis BCG
The gfp cDNA cloned into mycobacterial-E.coli shuttle plasmid pMV206 was a gift from Dr. Alain Baulard (Pasteur Institute, France). The plasmid was incorporated into competent BCG cells by electroporation. GFP BCG was observed by the FACS Calibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson).
Differentiation and Infection of THP-1 Cells
The monocytic cell line THP-1(ATCC, Rockville, MD) cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10%FBS, penicillin (100 U/ml) and streptomycin (100 ug/ml) (Invitrogen). Cells were plated at a density of 2×105/ml in 8-well chamber coverglass (LAB-TEK). Monocytes were allowed to adhere and differentiate into macrophages for 48 hours with 5 nM PMA (Sigma Aldrich) at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. Differentiated macrophages were infected with GFP BCG at an MOI of 20∶1 and incubated at 37°C, 5% CO2. Infected cells at 1 hr post infection were washed twice with RPMI without antibiotics to remove uningested and unadhered bacteria. Cells were then harvested for TLR8 expression as mentioned below. Infected cells at 20 hours post infection were washed to remove uningested and unadhered bacteria at 4 hours post infection to minimize cell death and re-incubated for a further 16 hours. Cells were then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (Sigma Aldrich) for 15 minutes at room temperature and cell membrane was disrupted with 1% saponin (Sigma Aldrich) for 20 mins at room temperature. Mouse anti-human TLR8 phycoerytrhin (PE) antibody (Imgenex) was used at 3 ug/ml for 1 hour at room temperature and excess antibody was washed twice with PBS (Sigma Aldrich). To prevent bleaching of the dyes during confocal viewing, anti fade prolong gold with DAPI (Invitrogen) was added to slides so that it formed a protective layer over the cells. Slides were stored at 4°C in the dark until confocal viewing.
Confocal Image Acquisition
The LSM 510 scanhead of the confocal laser-scanning microscope system (Zeiss 5 duo, Germany) was used to detect intracellular fluochrome. Cells were scanned by triple excitation for PE (red), GFP (green) and DAPI (blue) fluorescence. A 63× oil objective with numerical aperture of 1.4 was used and images were captured.
Supporting Information
Location, Allele, Genotype Frequencies, and Allelic p-values of 149 Analysed SNPs.
(0.06 MB XLS)
Genotype Distribution of TLR8 Polymorphisms among Indonesian TB Patients and Controls in All and Females.
(0.02 MB XLS)
Haplotype Analysis and Distribution of TLR8 Polymorphisms among Male TB Patients and Controls from Both Cohorts.
(0.02 MB XLS)
Candidate Genes and SNPs Analyzed.
(0.02 MB XLS)
Allele Frequencies of 298 SNPs Tested for Population Stratification in the Indonesian Cohort.
(0.07 MB XLS)
Acknowledgments
We thank Anugrah Maya and Erita Istriana for helping in clinical work at PPTI-Jakarta supervised by Dr. Halim Danusantoso; Iskandar Adnan from Eijkman Institute for Molecular Biology Jakarta for helping in the DNA isolation supervised by Prof. Sangkot Marzuki and Dr. Herawati Sudoyo. We thank Prof R.H.H. Nelwan from University of Indonesia for long-standing collaboration in Jakarta. We are grateful to our colleagues Meah Wee Yang, Jason Ong and Heng Khai Koon for genotyping; Rick Ong for helping on the management of the genotyping data and Frans Verhoeff for maintaining the GISSNP database at the Genome Institute of Singapore; to Xiao Yong from the Biopolis Shared Facility who helped with the acquisition of confocal data. We thank Dr. Alain Baulard (Pasteur Institute, France), who kindly provided the gfp cDNA cloned into mycobacterial-E.coli shuttle plasmid pMV206. We thank Prof. John A. Todd for his help and advice in establishing the Russian TB sample collection. We are grateful to Drs L. Stcheglova, Y. Korneev, I. Fedorin, N. Lebedeva and S. Zakharova for their help in recruiting study participants and collecting blood samples in Russia.
Footnotes
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
This work has been supported by funding from the Agency for Science & Technology and Research of Singapore (A*STAR), by the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW, project 99MED01), and the PRIOR project sponsored by the Netherlands Foundation for the Advancement of Tropical Research (NWO-WOTRO). The Diabetes and Inflammation Laboratory is funded by the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation and the Wellcome Trust. The funding agencies had no role in any aspect of the direction of the study or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.The World Health Organization. Tuberculosis. Fact sheet number 104. World Health Organization 2006 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bloom BR, Small PM. The evolving relation between humans and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:677–678. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199803053381008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aderem A, Underhill DM. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:593–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van Crevel R, Ottenhoff TH, van der Meer JW. Innate immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002;15:294–309. doi: 10.1128/CMR.15.2.294-309.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ferguson JS, Weis JJ, Martin JL, Schlesinger LS. Complement Protein C3 Binding to Mycobacterium tuberculosis Is Initiated by the Classical Pathway in Human Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid. Infect Immun. 2004;72:2564–2573. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.5.2564-2573.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hibberd ML, Sumiya M, Summerfield JA, Booy R, Levin M. Association of variants of the gene for mannose-binding lectin with susceptibility to meningococcal disease. Meningococcal Research Group. Lancet. 1999;353:1049–1053. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)08350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bulut Y, Michelsen KS, Hayrapetian L, Naiki Y, Spallek R, et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Heat Shock Proteins Use Diverse Toll-like Receptor Pathways to Activate Pro-inflammatory Signals. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:20961–20967. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411379200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ben-Ali M, Barbouche MR, Bousnina S, Chabbou A, Dellagi K. Toll-like receptor 2 Arg677Trp polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis in Tunisian patients. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004;11:625–626. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.11.3.625-626.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:135–145. doi: 10.1038/35100529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Takeda K, Akira S. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int Immunol. 2005;17:1–14. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. doi: 10.1038/nri1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Divanovic S, Trompette A, Atabani SF, Madan R, Golenbock DT, et al. Inhibition of TLR-4/MD-2 signaling by RP105/MD-1. J Endotoxin Res. 2005;11:363–368. doi: 10.1179/096805105X67300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pacheco E, Fonseca C, Montes C, Zabaleta J, Garcia LF, et al. CD14 gene promoter polymorphism in different clinical forms of tuberculosis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004;40:207–213. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00369-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rockhill B, Newman B, Weinberg C. Use and misuse of population attributable fractions. Am J Public Health. 1998;88:15–19. doi: 10.2105/ajph.88.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.The International HapMap Project. The International HapMap Project. Nature. 2003;426:789–796. doi: 10.1038/nature02168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Du X, Poltorak A, Wei Y, Beutler B. Three novel mammalian toll-like receptors: gene structure, expression, and evolution. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000;11:362–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chuang TH, Ulevitch RJ. Cloning and characterization of a sub-family of human toll-like receptors: hTLR7, hTLR8 and hTLR9. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000;11:372–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Heil F, Ahmad-Nejad P, Hemmi H, Hochrein H, Ampenberger F, et al. The Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7)-specific stimulus loxoribine uncovers a strong relationship within the TLR7, 8 and 9 subfamily. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:2987–2997. doi: 10.1002/eji.200324238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, et al. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature. 2000;408:740–745. doi: 10.1038/35047123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Diebold SS, Kaisho T, Hemmi H, Akira S, Reis e Sousa C. Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science. 2004;303:1529–1531. doi: 10.1126/science.1093616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Heil F, Hemmi H, Hochrein H, Ampenberger F, Kirschning C, et al. Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via toll-like receptor 7 and 8. Science. 2004;303:1526–1529. doi: 10.1126/science.1093620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Latz E, Schoenemeyer A, Visintin A, Fitzgerald KA, Monks BG, et al. TLR9 signals after translocating from the ER to CpG DNA in the lysosome. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:190–198. doi: 10.1038/ni1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Crowle AJ, Dahl R, Ross E, May MH. Evidence that vesicles containing living, virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Mycobacterium avium in cultured human macrophages are not acidic. Infect Immun. 1991;59:1823–1831. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1823-1831.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kuijl C, Savage ND, Marsman M, Tuin AW, Janssen L, et al. Intracellular bacterial growth is controlled by a kinase network around PKB/AKT1. Nature. 2007;450:725–730. doi: 10.1038/nature06345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Oh DY, Taube S, Hamouda O, Kucherer C, Poggensee G, et al. A Functional Toll-Like Receptor 8 Variant Is Associated with HIV Disease Restriction. J Infect Dis. 2008 doi: 10.1086/590431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Beuret N, Rutishauser J, Bider MD, Spiess M. Mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum retention of mutant vasopressin precursor caused by a signal peptide truncation associated with diabetes insipidus. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18965–18972. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.27.18965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Christensen JH, Siggaard C, Corydon TJ, deSanctis L, Kovacs L, et al. Six novel mutations in the arginine vasopressin gene in 15 kindreds with autosomal dominant familial neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus give further insight into the pathogenesis. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004;12:44–51. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sahiratmadja E, Alisjahbana B, de Boer T, Adnan I, Maya A, et al. Dynamic changes in pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine profiles and gamma interferon receptor signaling integrity correlate with tuberculosis disease activity and response to curative treatment. Infect Immun. 2007;75:820–829. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00602-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.The World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Control. Surveillance, planning, financing. World Health Organization 2005 [Google Scholar]
- 31.Alisjahbana B, van Crevel R, Sahiratmadja E, den Heijer M, Maya A, et al. Diabetes mellitus is strongly associated with tuberculosis in Indonesia. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006;10:696–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Szeszko JS, Healy B, Stevens H, Balabanova Y, Drobniewski F, et al. Resequencing and association analysis of the SP110 gene in adult pulmonary tuberculosis. Hum Genet. 2007;121:155–160. doi: 10.1007/s00439-006-0293-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Devlin B, Roeder K. Genomic control for association studies. Biometrics. 1999;55:997–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.1999.00997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sambrook JR, Russell DW. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Epstein MP, Duren WL, Boehnke M. Improved inference of relationship for pairs of individuals. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;67:1219–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9297(07)62952-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Skipper L, Li Y, Bonnard C, Pavanni R, Yih Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of common genetic variation within LRRK2 reveals evidence for association with sporadic Parkinson's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14:3549–3556. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Einarsdottir K, Humphreys K, Bonnard C, Palmgren J, Iles MM, et al. Linkage disequilibrium mapping of CHEK2: common variation and breast cancer risk. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e168. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:263–265. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fisher R. Statistical methods for research workers. Edinburgh: Oliver & Boyd; 1932. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, Moore JM, Roy J, et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science. 2002;296:2225–2229. doi: 10.1126/science.1069424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Location, Allele, Genotype Frequencies, and Allelic p-values of 149 Analysed SNPs.
(0.06 MB XLS)
Genotype Distribution of TLR8 Polymorphisms among Indonesian TB Patients and Controls in All and Females.
(0.02 MB XLS)
Haplotype Analysis and Distribution of TLR8 Polymorphisms among Male TB Patients and Controls from Both Cohorts.
(0.02 MB XLS)
Candidate Genes and SNPs Analyzed.
(0.02 MB XLS)
Allele Frequencies of 298 SNPs Tested for Population Stratification in the Indonesian Cohort.
(0.07 MB XLS)