Abstract
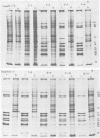
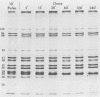
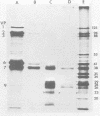
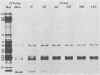
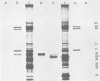
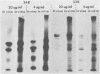
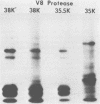
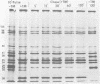
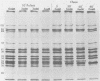
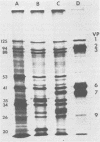
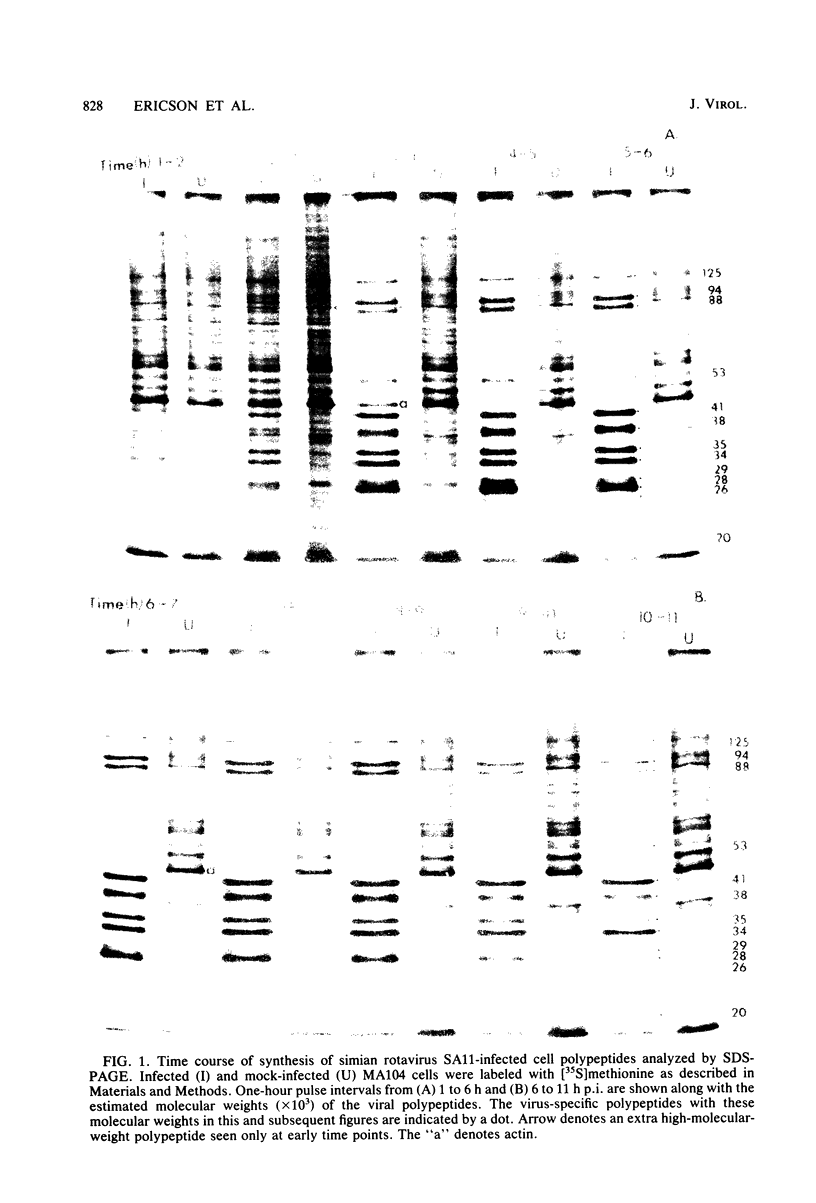
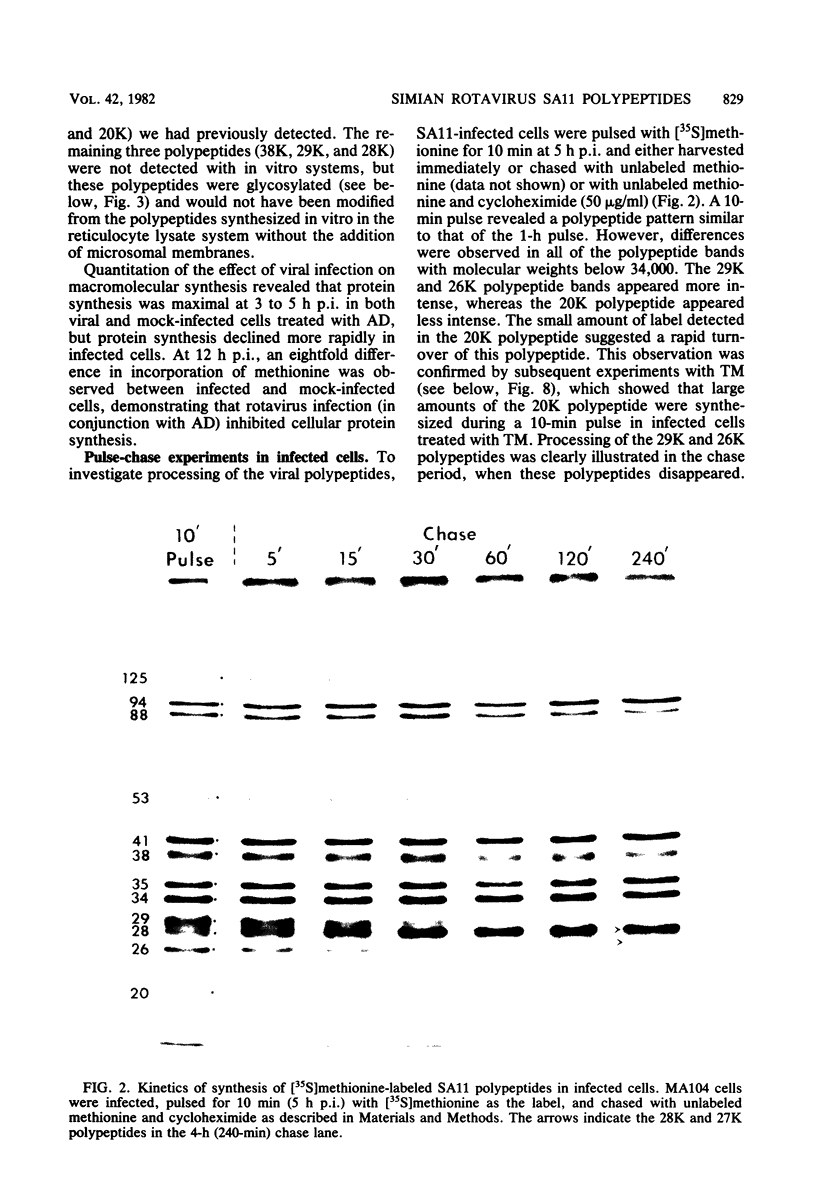
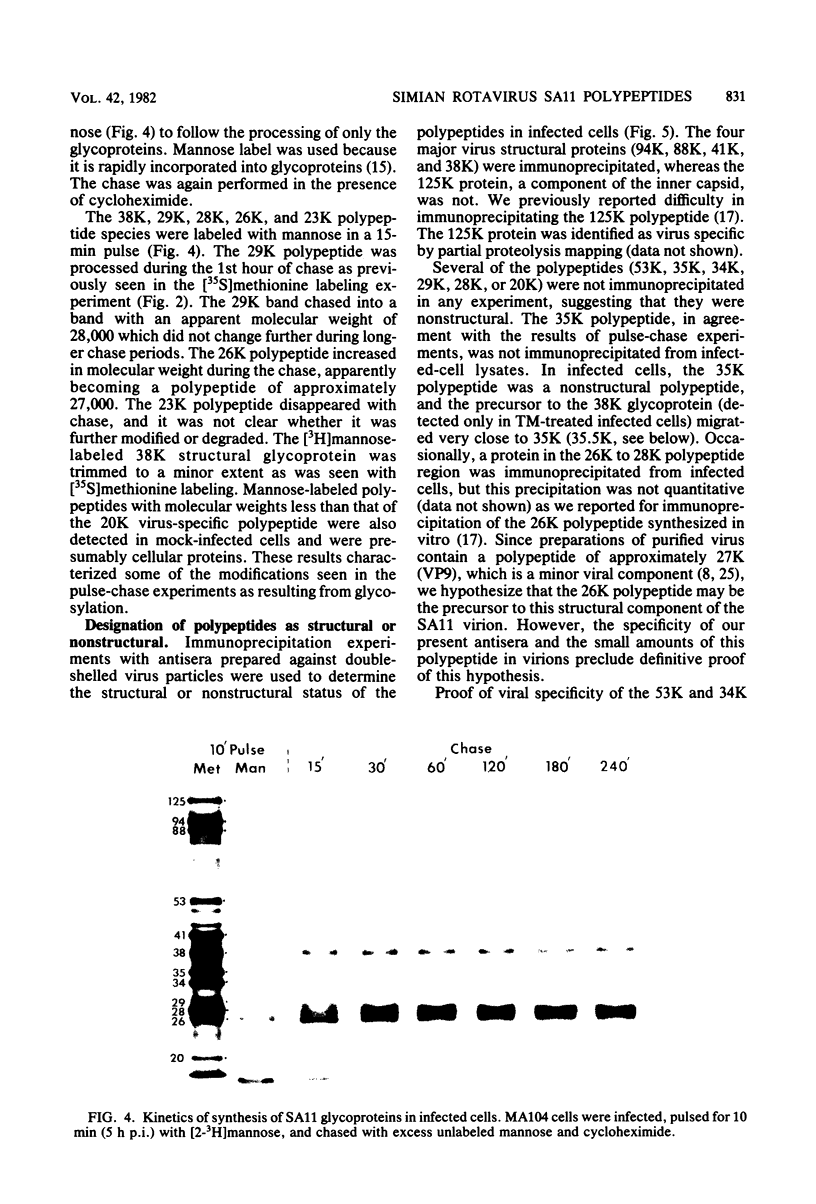
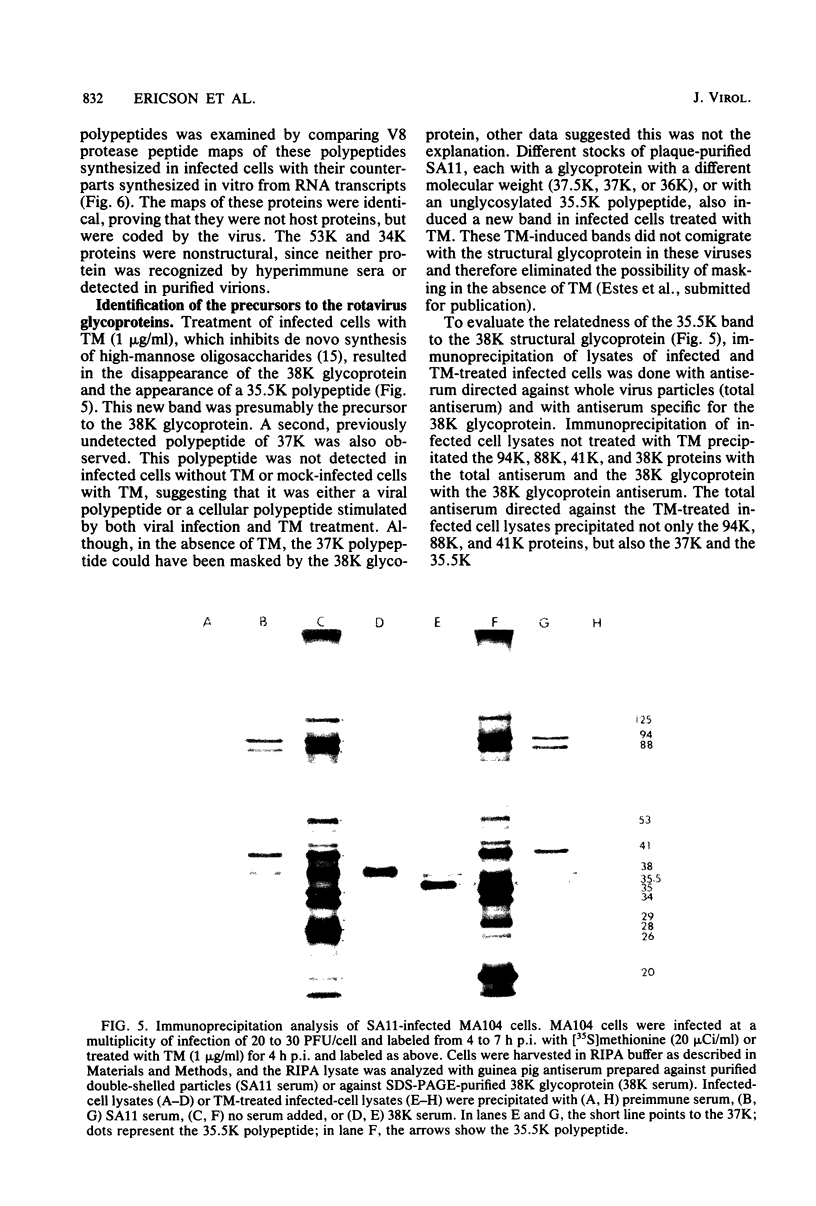
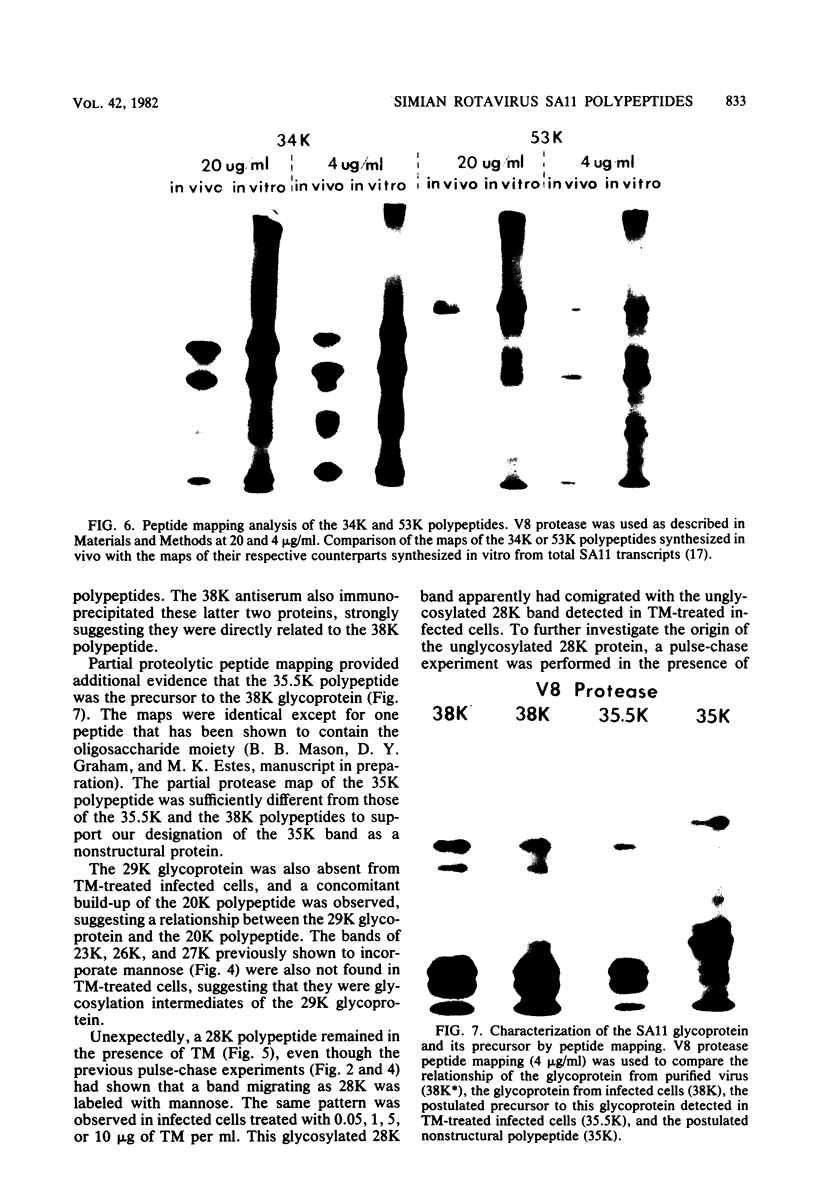
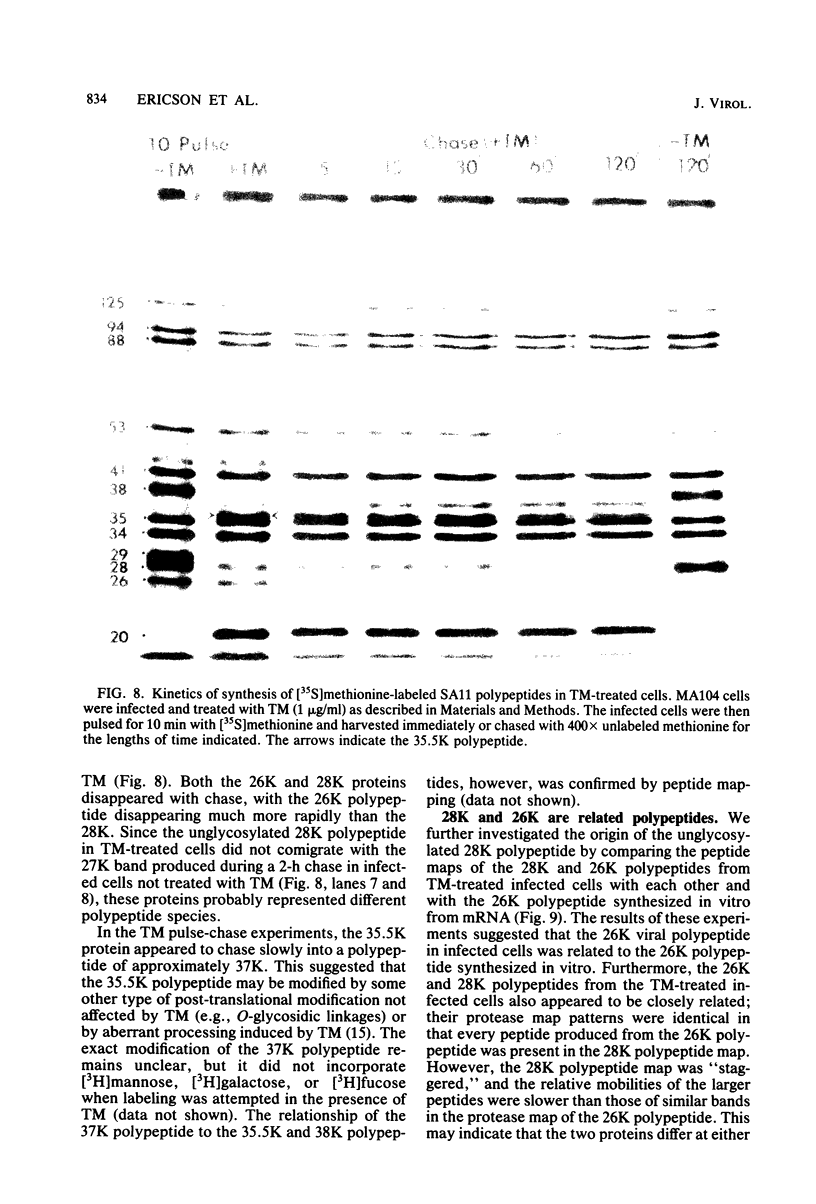
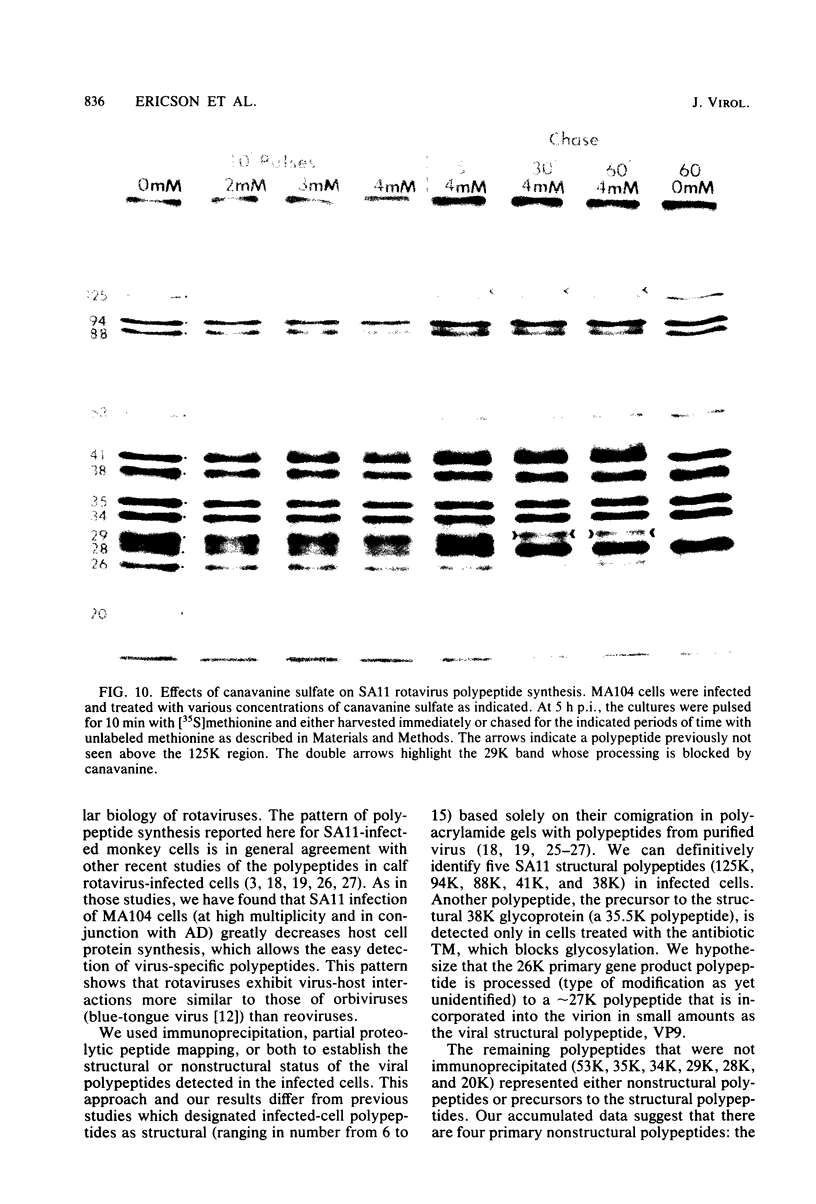
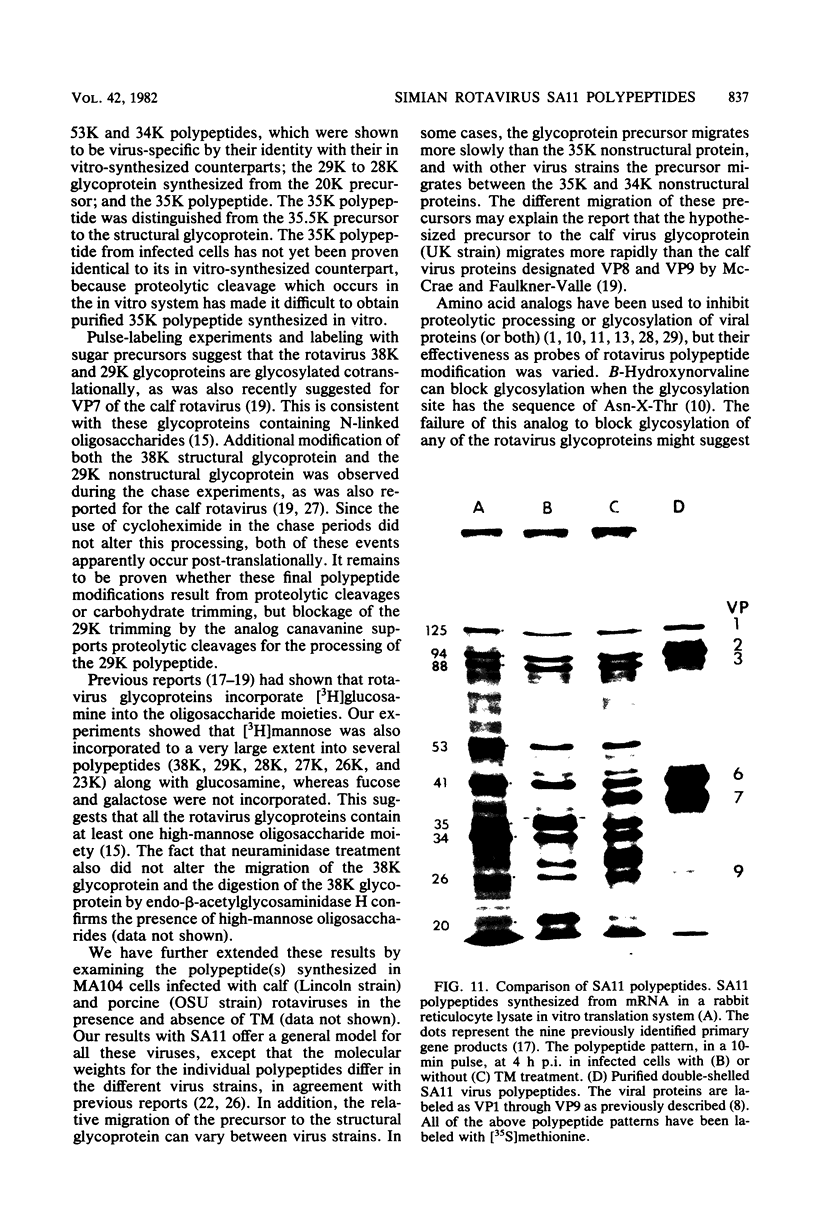
The synthesis and processing of simian rotavirus SA11 polypeptides was investigated after infection of MA104 cells. [35S]methionine- or 3H-amino acid-labeled cell extracts were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Viral protein synthesis was maximal 3 to 5 h postinfection, and 12 major viral polypeptides were detected. Immunoprecipitation and peptide mapping experiments, demonstrated five viral structural proteins (125,000 daltons [125K], 94K, 88K, 41K, and 38K). Three proteins (53K, 35K, and 34K) were identified as nonstructural by comparison of their partial proteolysis maps with those from polypeptides of similar molecular weight synthesized in vitro from viral RNA transcripts. Assignment as to structural or nonstructural status of two other primary gene products (26K and 20K) remains tentative. Pulse-chase experiments and tunicamycin blockage of glycosylation revealed cotranslational or post-translational modifications (or both) and precursor-product relationships of several of the polypeptides. Tunicamycin inhibition of glycosylation identified a 35.5K polypeptide which was proven to be the precursor to the 38K structural glycoprotein by immunoprecipitation and peptide mapping analyses. Tunicamycin treatment of infected cells also resulted in the disappearance of other glycoprotein species (23K to 29K) and in the concomitant build-up of an unglycosylated 20K polypeptide, suggesting a precursor-product relationship between those polypeptides. Labeling with [3H]glucosamine or [3H]mannose suggested that the rotavirus glycoproteins contained high mannose oligosaccharides. The effects of amino acid analogs on rotavirus polypeptide synthesis and processing were also investigated.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaud G., Dru A. Protein synthesis in vaccinia virus-infected cells in the presence of amino acid analogs: a translational control mechanism. Virology. 1980 Jan 15;100(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpio M. M., Babiuk L. A., Misra V., Blumenthal R. M. Bovine rotavirus-cell interactions: effect of virus infection on cellular integrity and macromolecular synthesis. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):86–97. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Maget-Dana R., Roche A. C., Monsigny M. Calf rotavirus: detection of outer capsid glycoproteins by lectins. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):26–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyall-Smith M. L., Holmes I. H. Gene-coding assignments of rotavirus double-stranded RNA segments 10 and 11. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):1099–1103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.1099-1103.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
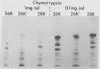
- Espejo R. T., López S., Arias C. Structural polypeptides of simian rotavirus SA11 and the effect of trypsin. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.156-160.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B. Proteolytic enhancement of rotavirus infectivity: molecular mechanisms. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):879–888. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.879-888.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Smith E. M., Gerba C. P. Rotavirus stability and inactivation. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):403–409. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortin G., Boime I. Inhibition of asparagine-linked glycosylation by incorporation of a threonine analog into nascent peptide chains. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8007–8010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortin G., Boime I. Miscleavage at the presequence of rat preprolactin synthesized in pituitary cells incubated with a threonine analog. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):453–461. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90336-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H. Macromolecular synthesis in bluetongue virus infected cells. II. Host cell metabolism. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1970 Dec;37(4):199–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Baltimore D. Further evidence on the formation of poliovirus proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. In vitro transcription and translation of simian rotavirus SA11 gene products. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1111-1121.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Mukoyama A. Polypeptides of bovine rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):309–316. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Faulkner-Valle G. P. Molecular biology of rotaviruses. I. Characterization of basic growth parameters and pattern of macromolecular synthesis. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.490-496.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Levintow L., Bishop J. M. Uninfected vertebrate cells contain a protein that is closely related to the product of the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene (src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Further biochemical characterization, including the detection of surface glycoproteins, of human, calf, and simian rotaviruses. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):91–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.91-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Two different mechanisms of the inhibition of the multiplication of enveloped viruses by glucosamine. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Gerba C. P. A plaque assay for the simian rotavirus SAII. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):513–519. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Lazdins I., Holmes I. H. Coding assignments of double-stranded RNA segments of SA 11 rotavirus established by in vitro translation. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):976–982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.976-982.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E. Rotavirus polypeptides. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):187–197. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urquidi V., Novo E., Esparza J. Protein synthesis in cells infected with bovine rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Apr;53(Pt 2):363–369. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zaane D., Dekker-Michielsen J. A., Bloemers H. P. Virus-specific precursor polypeptides in cells infected with Rauscher leukemia virus: synthesis, identification, and processing. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):113–129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaanie D., Gielkens A. L., Dekker-michielsen M. J., Bloemers H. P. Virus-specific precursor polypeptides in cells infected with Rauscher leukemia virus. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90454-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]