Abstract
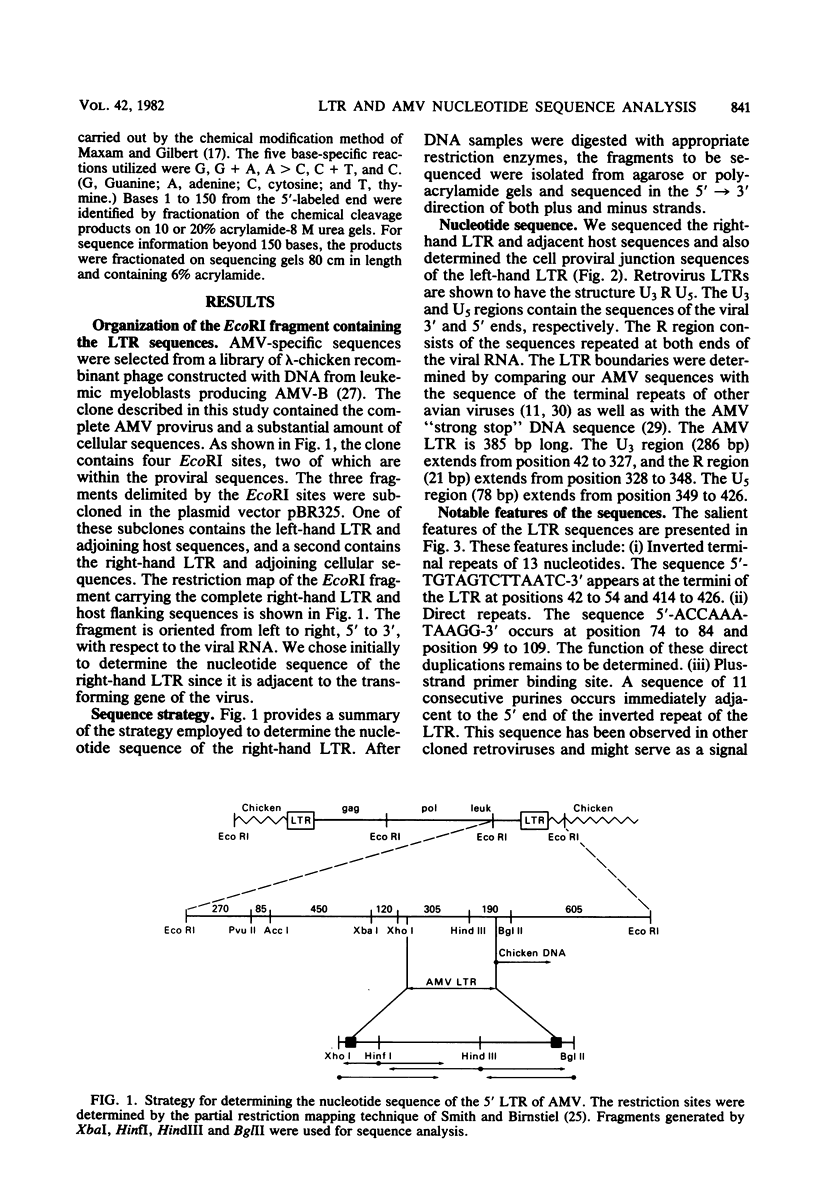
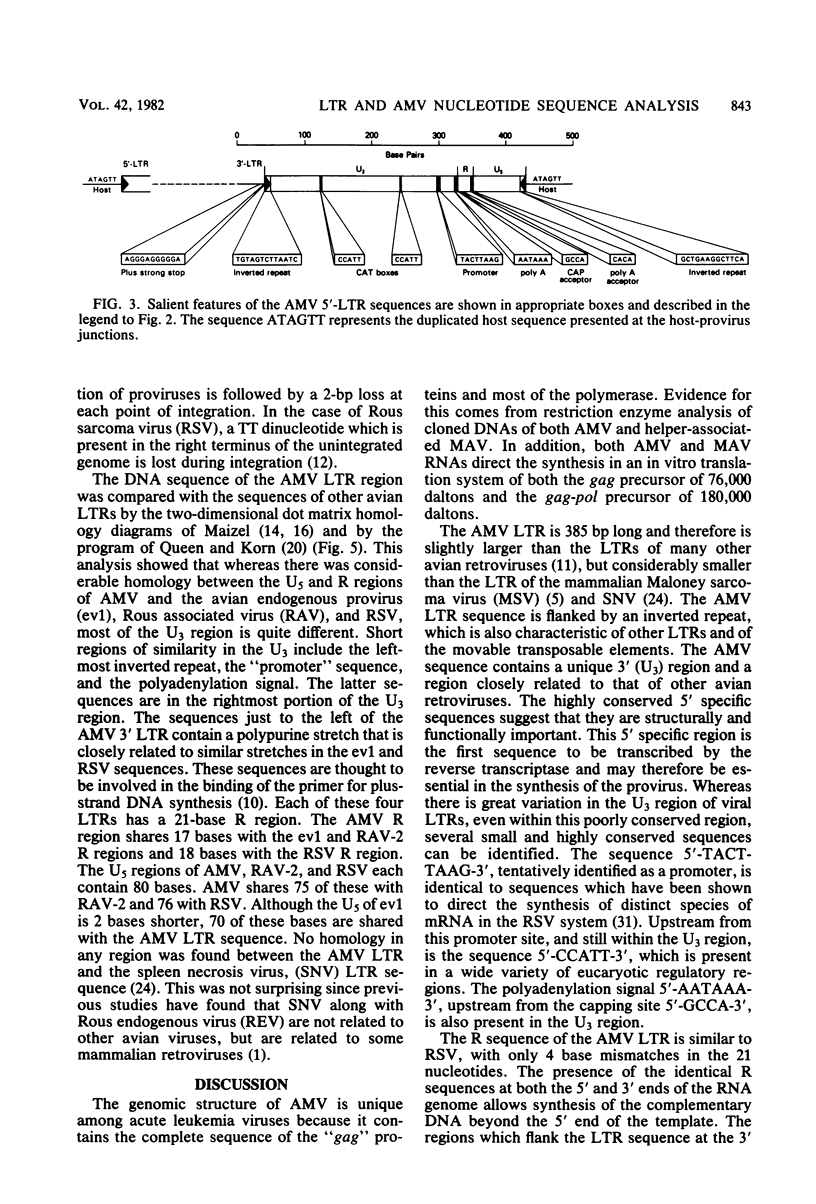
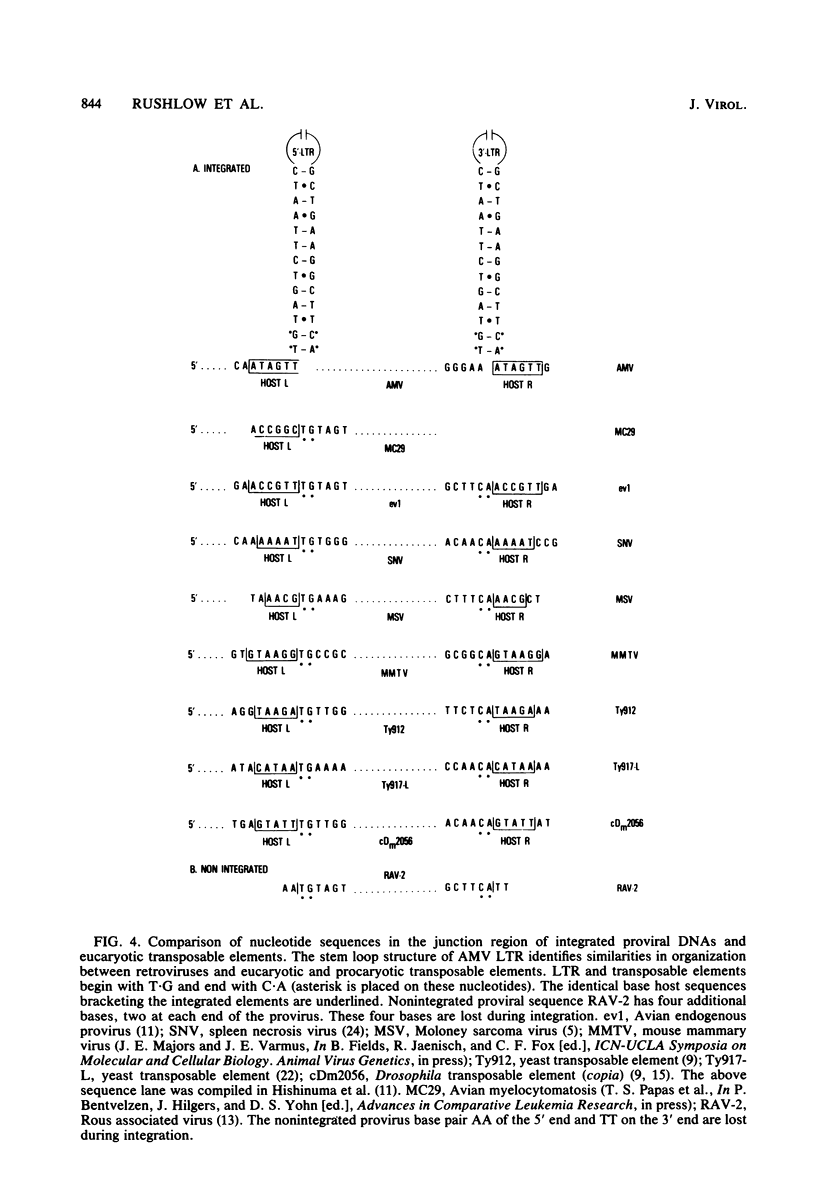
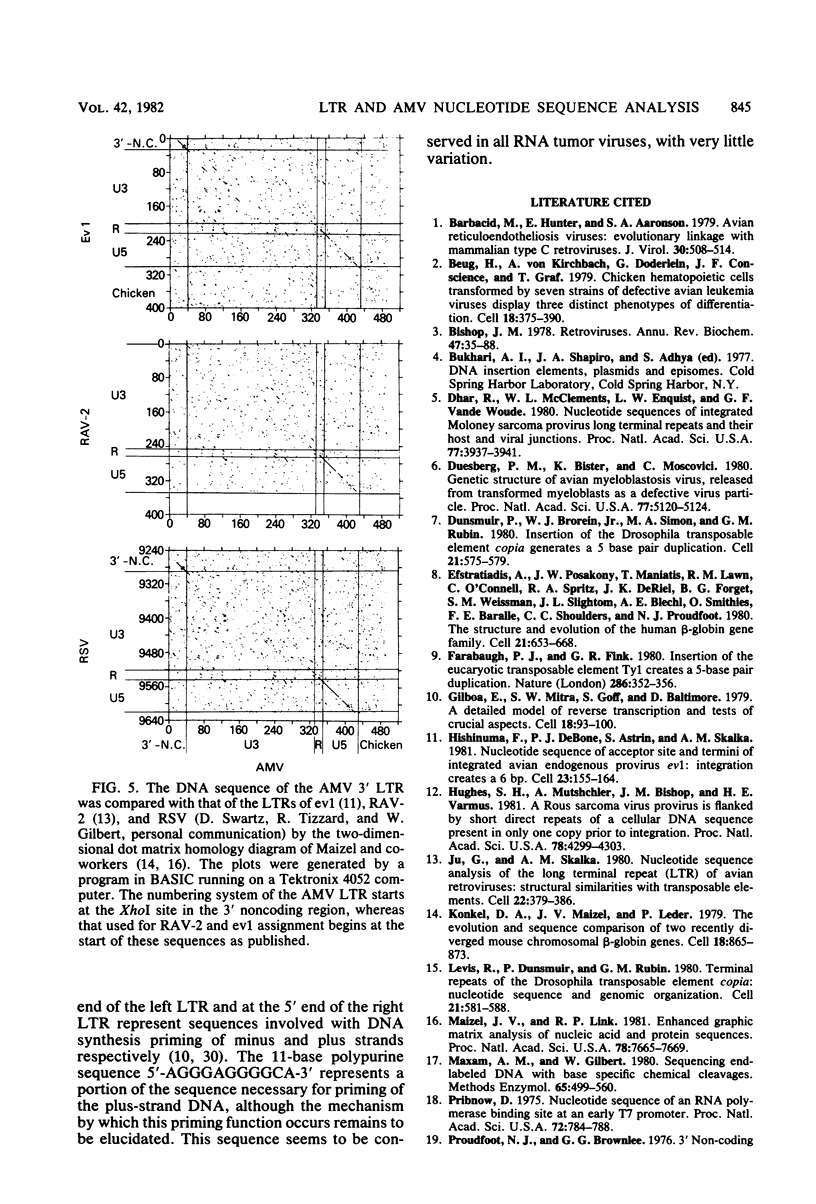
The nucleotide sequence of the integrated avian myeloblastosis virus long terminal repeat has been determined. The sequence is 385 base pairs long and is present at both ends of the viral DNA. The cell-virus junctions at each end consist of a 6-base-pair direct repeat of cell DNA next to the inverted repeat of viral DNA. The long terminal repeat also contains promoter-like sequences, an mRNA capping site, and polyadenylation signals. Several features of this long terminal repeat suggest a structural and functional similarity with sequences of transposable and other genetic elements. Comparison of these sequences with long terminal repeats of other avian retroviruses indicates that there is a great variation in the 3' unique sequence (U3), whereas the 5' specific sequences (U5) and the R region are highly conserved.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M., Hunter E., Aaronson S. A. Avian reticuloendotheliosis viruses: evolutionary linkage with mammalian type C retroviruses. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):508–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.508-514.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:35–88. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., McClements W. L., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequences of integrated Moloney sarcoma provirus long terminal repeats and their host and viral junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Bister K., Moscovici C. Genetic structure of avian myeloblastosis virus, released from transformed myeloblasts as a defective virus particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5120–5124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmuir P., Brorein W. J., Jr, Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. Insertion of the Drosophila transposable element copia generates a 5 base pair duplication. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):575–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90495-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Fink G. R. Insertion of the eukaryotic transposable element Ty1 creates a 5-base pair duplication. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):352–356. doi: 10.1038/286352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa E., Mitra S. W., Goff S., Baltimore D. A detailed model of reverse transcription and tests of crucial aspects. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hishinuma F., DeBona P. J., Astrin S., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence of acceptor site and termini of integrated avian endogenous provirus ev1: integration creates a 6 bp repeat of host DNA. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Mutschler A., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. A Rous sarcoma virus provirus is flanked by short direct repeats of a cellular DNA sequence present in only one copy prior to integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4299–4303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the long terminal repeat (LTR) of avian retroviruses: structural similarities with transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):379–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel D. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The evolution and sequence comparison of two recently diverged mouse chromosomal beta--globin genes. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):865–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Terminal repeats of the Drosophila transposable element copia: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90496-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Lenk R. P. Enhanced graphic matrix analysis of nucleic acid and protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7665–7669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site at an early T7 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):784–788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. L., Korn L. J. Computer analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):595–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Smith M. J., Canaani E., Robbins K. C., Tronick S. R., Zain S., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the transforming region and large terminal redundancies of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5234–5238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Farabaugh P. J., Chaleff D. T., Fink G. R. The origins of gene instability in yeast. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1375–1380. doi: 10.1126/science.6251544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R. A., Chirikjian J. G., Papas T. S. Analysis of avian myeloblastosis viral RNA and in vitro synthesis of proviral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2057–2061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Mizutani S., Temin H. M. Sequence of retrovirus provirus resembles that of bacterial transposable elements. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):550–554. doi: 10.1038/285550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Baluda M. A. Identification of the avian myeloblastosis virus genome. I. Identification of restriction endonuclease fragments associated with acute myeloblastic leukemia. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):317–324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.317-324.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Briskin M. J., Hillyard R. L., Baluda M. A. Identification of the avian myeloblastosis virus genome. II. Restriction endonuclease analysis of DNA from lambda proviral recombinants and leukemic myeoblast clones. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):325–336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.325-336.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Komaromy M. C., Baluda M. A. Identification of a proviral genome associated with avian myeloblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):3004–3008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll E., Billeter M. A., Palmenberg A., Weissmann C. Avian myeloblastosis virus RNA is terminally redundant: implications for the mechanism of retrovirus replication. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):57–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., DeLorbe W. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of cloned unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: viral DNA contains direct and inverted repeats similar to those in transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):124–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Identification of a functional promoter in the long terminal repeat of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90555-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


