Abstract
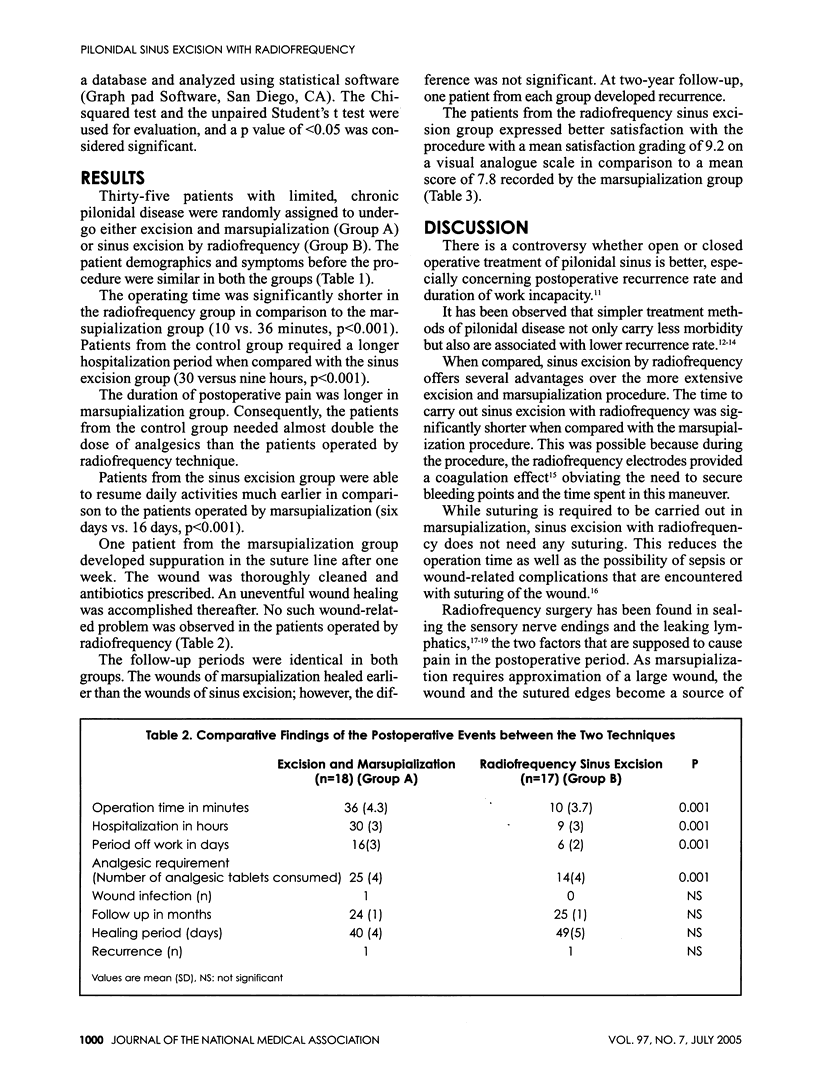
BACKGROUND: A number of techniques have been described for treatment of patients with sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus disease. The author reports his experience in the surgical management of pilonidal sinus using radiofrequency sinus excision technique. The results are compared with those obtained after excision and marsupialization procedure. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Seventeen patients were operated by radiofrequency sinus excision and 18 with excision and marsupialization. An Ellman radiofrequency device was used. The two groups were matched for age, gender and presentation symptoms. The median follow-up was two years. The patient's satisfaction on the outcome of the procedure was also evaluated. RESULTS: In the radiofrequency sinus excision group, we found on average a shorter operation time (10 vs. 36 minutes, p < 0.001), shorter hospitalization (nine vs. 30 hours, p < 0.001), significantly less postoperative pain, fewer cumulatve requests for analgesia by the patients (14 vs. 25 tablets, p < 0.001), and earlier return to work (six vs. 16 days, p < 0.001) The wounds with marsupialization did heal faster than those with sinus excision; however, the difference was not significant. At two year follow-up, one patient from each group had a recurrence. CONCLUSION: This pilot study shows that this new technique can be performed as a day care surgery. With reduced postoperative pain and early resumption to work, patient satisfaction is better in comparison to excision and marsupialization technique.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. H., Barcia P. J. Pilonidal sinus disease. The conservative approach. Arch Surg. 1994 Sep;129(9):914–919. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420330028006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aydede H., Erhan Y., Sakarya A., Kumkumoglu Y. Comparison of three methods in surgical treatment of pilonidal disease. ANZ J Surg. 2001 Jun;71(6):362–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchateau J., De Mol J., Bostoen H., Allegaert W. Pilonidal sinus. Excision--marsupialization--phenolization? Acta Chir Belg. 1985 Sep-Oct;85(5):325–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filingeri V., Gravante G., Baldessari E., Casciani C. U. Radiofrequency fistulectomy vs. diathermic fistulotomy for submucosal fistulas: a randomized trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2004 May-Jun;8(3):111–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. N., Gazelle G. S., Dawson S. L., Rittman W. J., Mueller P. R., Rosenthal D. I. Tissue ablation with radiofrequency: effect of probe size, gauge, duration, and temperature on lesion volume. Acad Radiol. 1995 May;2(5):399–404. doi: 10.1016/s1076-6332(05)80342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunawardhana P. A., Deen K. I. Comparison of hydrogen peroxide instillation with Goodsall's rule for fistula-in-ano. ANZ J Surg. 2001 Aug;71(8):472–474. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1622.2001.02169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull Tracy L., Wu James. Pilonidal disease. Surg Clin North Am. 2002 Dec;82(6):1169–1185. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(02)00062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst D. W. The evolution of management of pilonidal sinus disease. Can J Surg. 1984 Nov;27(6):603–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain S. A., Hussain S. Incisions with knife or diathermy and postoperative pain. Br J Surg. 1988 Dec;75(12):1179–1180. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800751211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isbister W. H., Prasad J. Pilonidal disease. Aust N Z J Surg. 1995 Aug;65(8):561–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1995.tb01695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karydakis G. E. New approach to the problem of pilonidal sinus. Lancet. 1973 Dec 22;2(7843):1414–1415. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92803-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. C., Ho Y. H., Seow C. F., Eu K. W., Nyam D. Pilonidal disease in Singapore: clinical features and management. Aust N Z J Surg. 2000 Mar;70(3):196–198. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1622.2000.01785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masala Salvatore, Roselli Mario, Massari Francesco, Fiori Roberto, Ursone Antonio, Fossile Emanuela, Laudisi Anastasia, Simonetti Giovanni. Radiofrequency Heat Ablation and Vertebroplasty in the treatment of neoplastic vertebral body fractures. Anticancer Res. 2004 Sep-Oct;24(5B):3129–3133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meban S., Hunter E. Outpatient treatment of pilonidal disease. Can Med Assoc J. 1982 Apr 15;126(8):941–941. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel T., Dörner A., Cramer J. Exzision und offene Wundbehandlung des Sinus pilonidalis. Rezidivrate und Dauer der Arbeitsunfähigkeit. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1997 Nov 21;122(47):1447–1451. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1047784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miocinović M., Horzić M., Bunoza D. The treatment of pilonidal disease of the sacrococcygeal region by the method of limited excision and open wound healing. Acta Med Croatica. 2000;54(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz H. H., Marti J., Sitges A. Pilonidal sinus: a claim for simple track incision. Dis Colon Rectum. 1977 May-Jun;20(4):325–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02586431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen Sven, Koch Rainer, Stelzner Sigmar, Wendlandt Thomas-Peter, Ludwig Klaus. Primary closure techniques in chronic pilonidal sinus: a survey of the results of different surgical approaches. Dis Colon Rectum. 2002 Nov;45(11):1458–1467. doi: 10.1007/s10350-004-6451-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saidi M. H., Setzler F. D., Jr, Sadler R. K., Farhart S. A., Akright B. D. Comparison of office loop electrosurgical conization and cold knife conization. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 1994 Feb;1(2):135–139. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)80777-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafik A. Electrocauterization in the treatment of pilonidal sinus. Int Surg. 1996 Jan-Mar;81(1):83–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak H., Brooks V. L., Nussbaum M., Friedman I. Treatment of chronic pilonidal disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1996 Oct;39(10):1136–1139. doi: 10.1007/BF02081415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terk Alyssa R., Levine Steven B. Radiofrequency volume tissue reduction of the tonsils: case report and histopathologic findings. Ear Nose Throat J. 2004 Aug;83(8):572, 574, 576-8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieger K. Komplikationer efter operation for cystis pilonidalis. Oplaeg til ny debat om en "kostbar" sygdom. Ugeskr Laeger. 1999 Nov 1;161(44):6056–6058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva J. H. Pilonidal cyst: cause and treatment. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000 Aug;43(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1007/BF02236564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


