Abstract
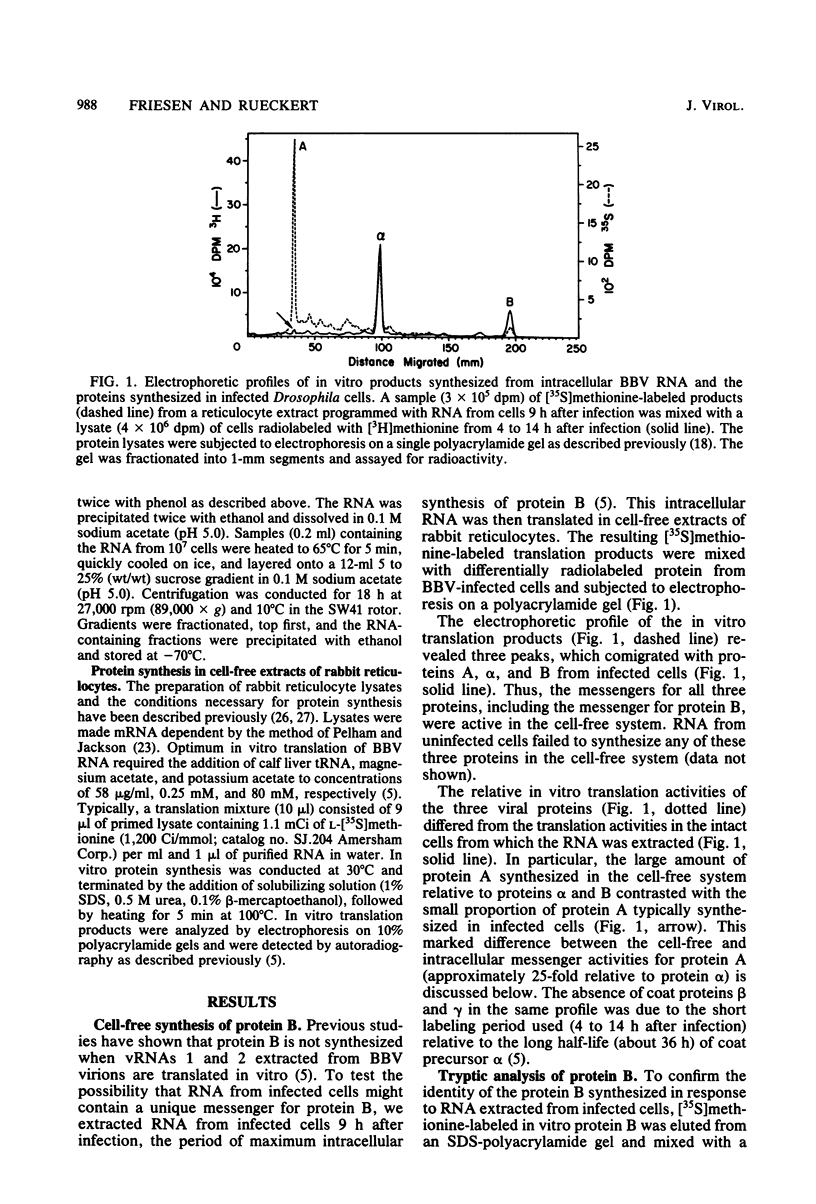
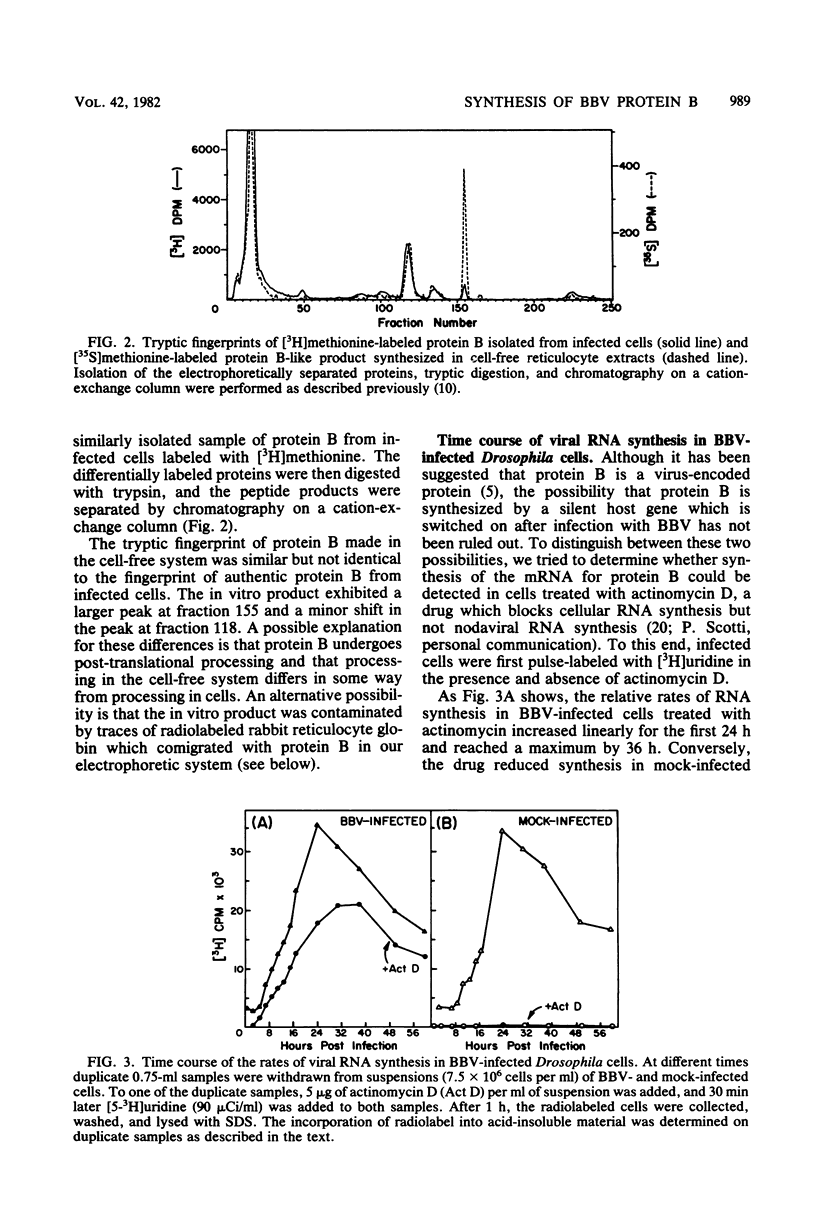
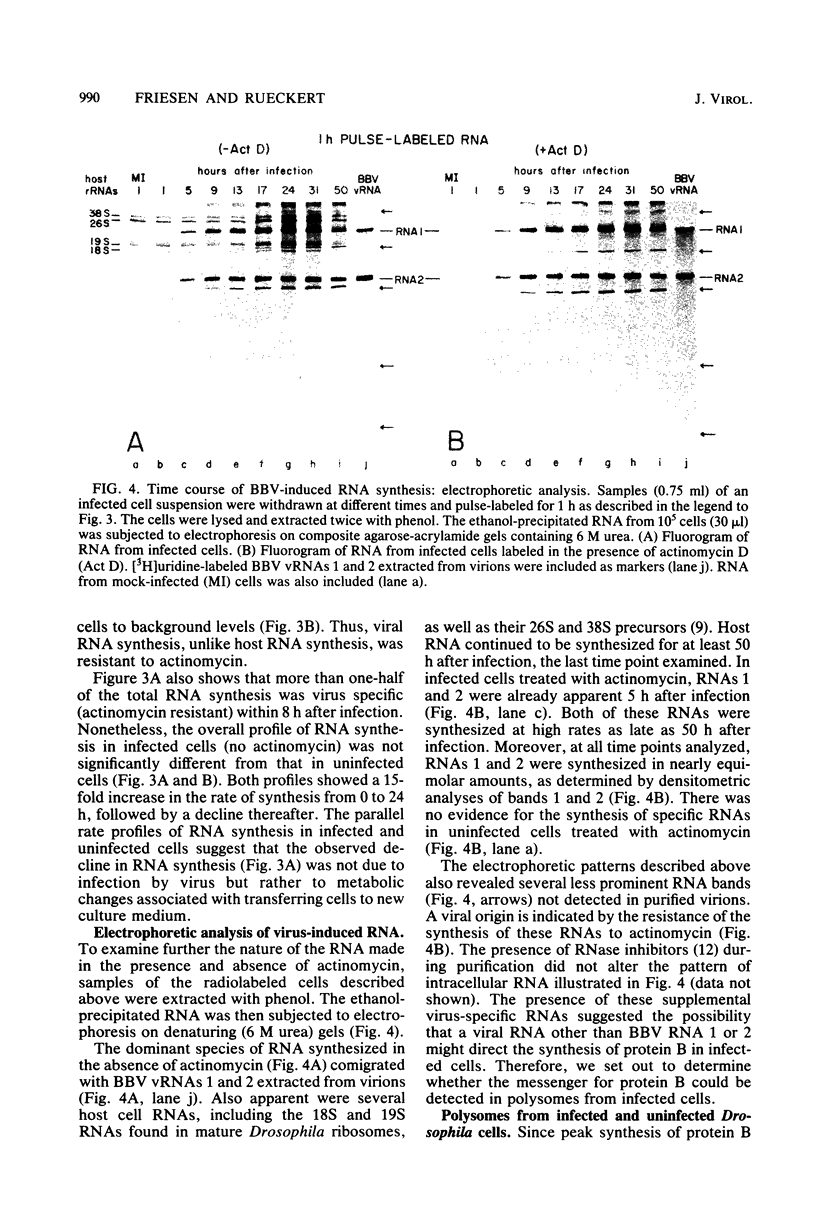
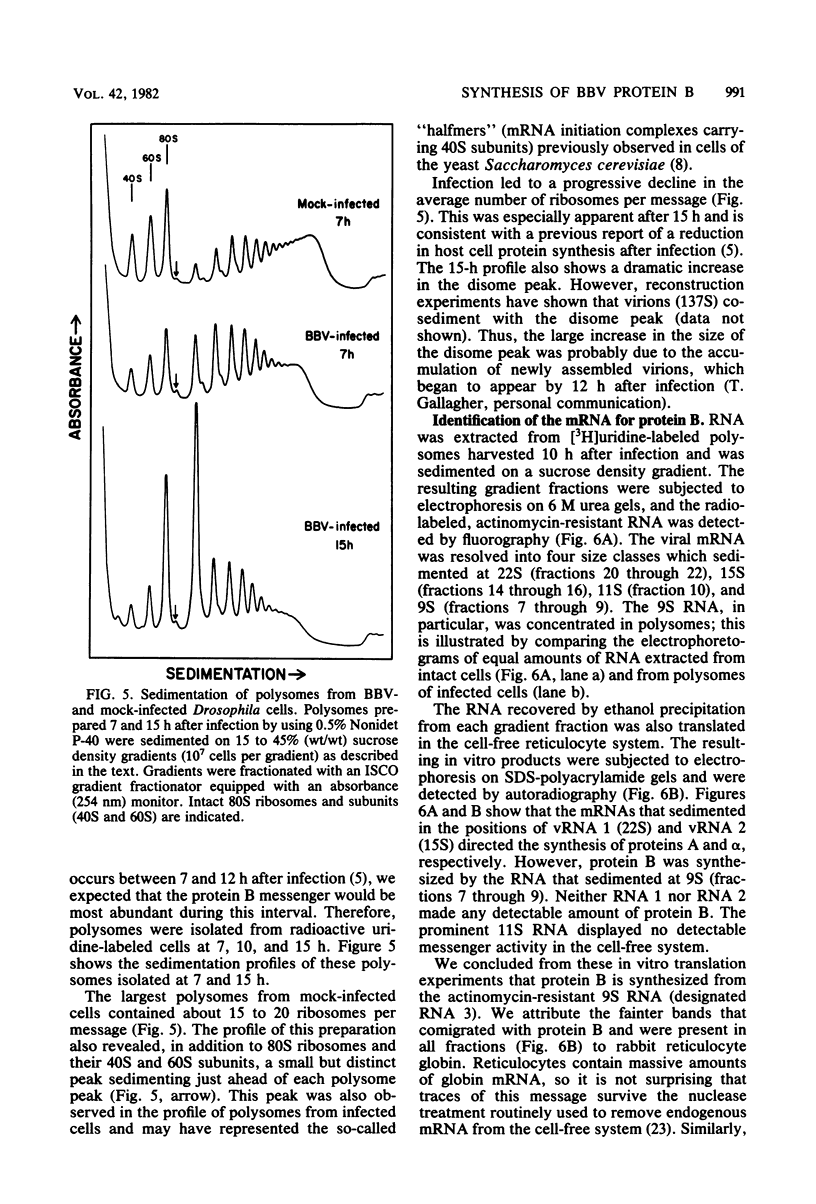
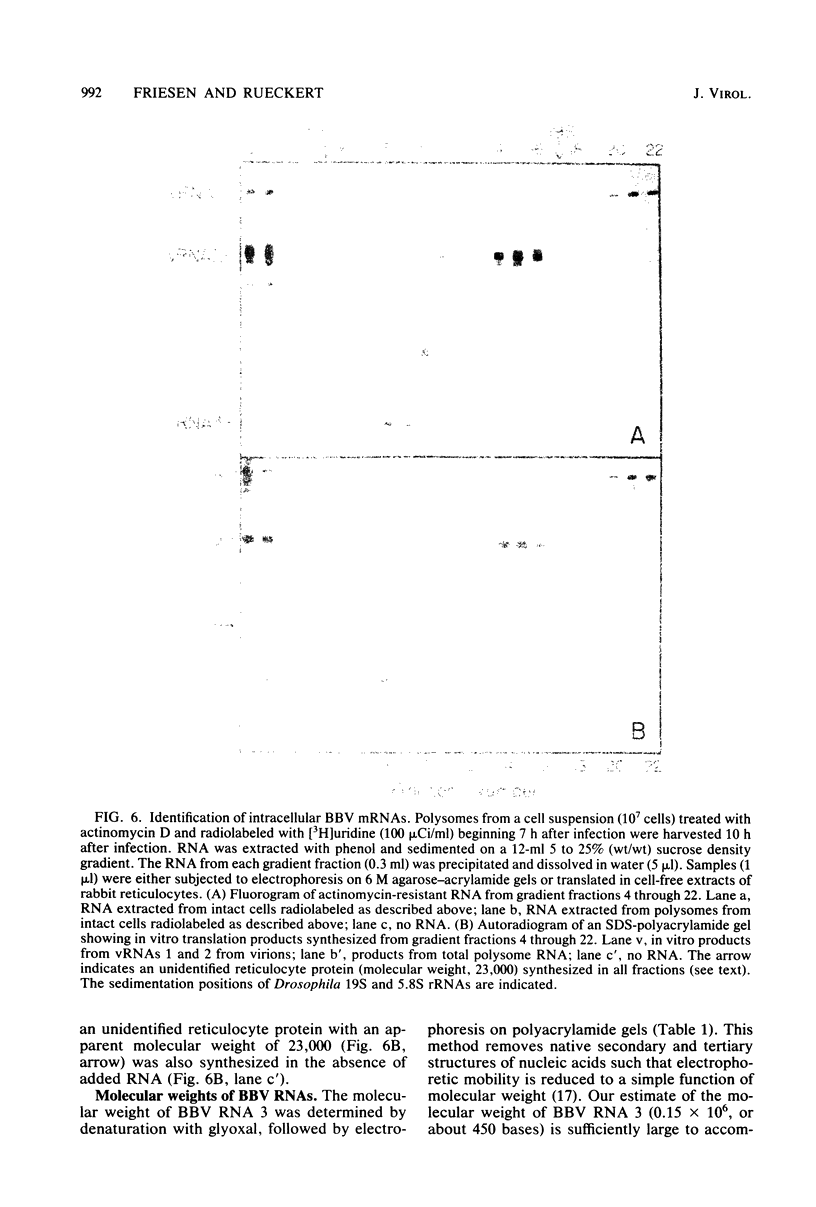
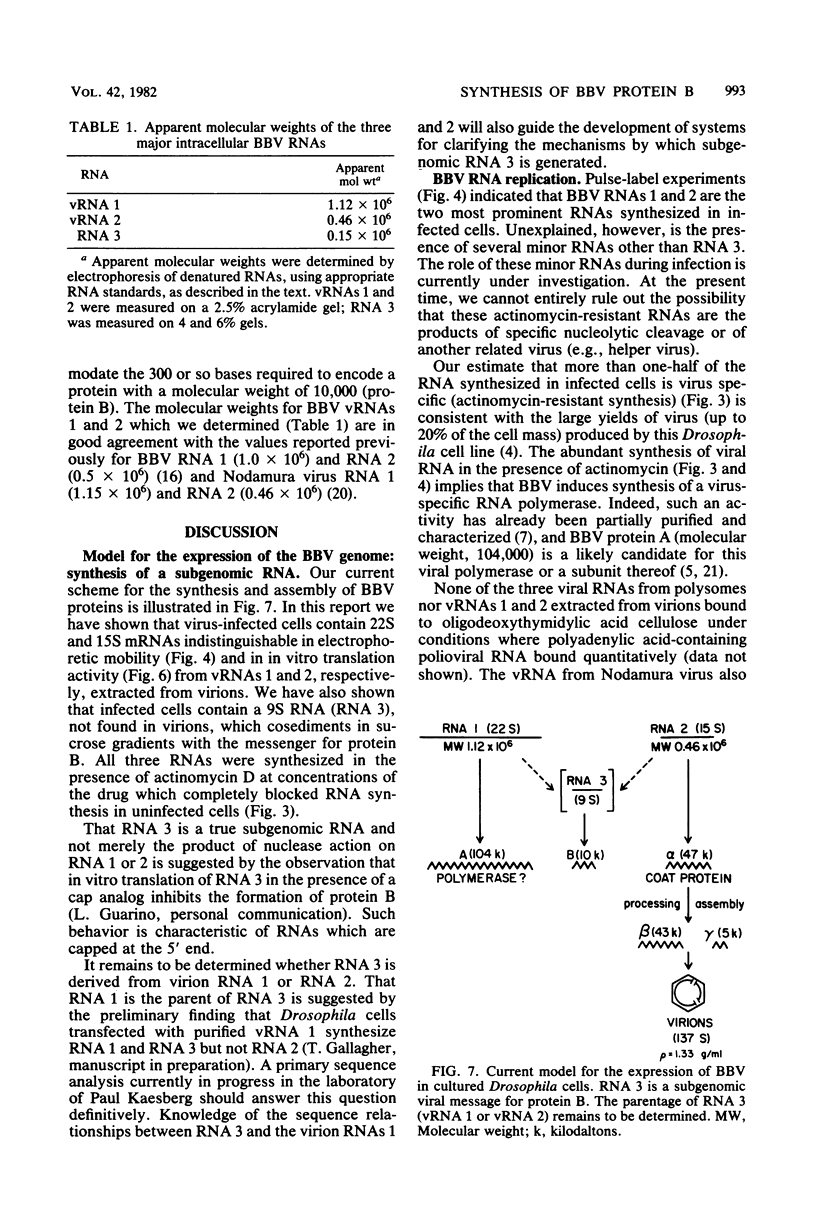
Black beetle virus induces the synthesis of three new proteins, protein A (molecular weight, 104,000), protein α (molecular weight, 47,000), and protein B (molecular weight, 10,000), in infected Drosophila cells. Two of these proteins, A and α, are known to be encoded by black beetle virus RNAs 1 and 2, respectively, extracted from virions. We found that RNA extracted from infected cells directed the synthesis of all three proteins when it was added to a cell-free protein-synthesizing system. When polysomal RNA was fractionated on a sucrose density gradient, the messengers for proteins A and α cosedimented with viral RNAs 1 (22S) and 2 (15S), respectively. However, the messenger for protein B was a 9S RNA (RNA 3) not found in purified virions. Like the synthesis of viral RNAs 1 and 2, intracellular synthesis of RNA 3 was not affected by the drug actinomycin D at concentrations which blocked synthesis of host cell RNA. This indicated that RNA 3 is a virus-specific subgenomic RNA and, therefore, that protein B is a virus-encoded protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Desselberger U., Palese P. Molecular weights of RNA segments of influenza A and B viruses. Virology. 1978 Jul 15;88(2):394–399. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Rueckert R. R. Synthesis of Black Beetle Virus Proteins in Cultured Drosophila Cells: Differential Expression of RNAs 1 and 2. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):876–886. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.876-886.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P., Scotti P., Longworth J., Rueckert R. Black beetle virus: propagation in Drosophila line 1 cells and an infection-resistant subline carrying endogenous black beetle virus-related particles. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):741–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.741-747.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Hruby D. E., Ball L. A., Kaesberg P. Translation of black beetle virus RNA and heterologous viral RNAs in cell-free lysates derived from Drosophila melanogaster. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):500–505. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.500-505.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Kaesberg P. Isolation and Characterization of an RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from Black Beetle Virus-Infected Drosophila melanogaster Cells. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):379–386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.379-386.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helser T. L., Baan R. A., Dahlberg A. E. Characterization of a 40S ribosomal subunit complex in polyribosomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae treated with cycloheximide. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;1(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R., Jourdan R., Jacq B. Late steps in the maturation of Drosophila 26 S ribosomal RNA: generation of 5-8 S and 2 S RNAs by cleavages occurring in the cytoplasm. J Mol Biol. 1976 Feb 15;101(1):85–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew O. M., Pallansch M. A., Omilianowski D. R., Rueckert R. R. Changes in three of the four coat proteins of oral polio vaccine strain derived from type 1 poliovirus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.256-263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane L. C., Kaesberg P. Multiple genetic components in bromegrass mosaic virus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 14;232(28):40–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio232040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel J., Penman S. hnRNA size and processing as related to different DNA content in two dipterans: Drosophila and Aedes. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel J., Spradling A., Penman S. Methods with insect cells in suspension culture. II. Drosophila melanogaster. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;10:195–208. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60738-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longworth J. F., Carey G. P. A small RNA virus with a divided genome from Heteronychus arator (F.) [Coleoperai Scarabaeidae]. J Gen Virol. 1976 Oct;33(1):31–40. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longworth J. F. Small isometric viruses of invertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1978;23:103–157. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medappa K. C., McLean C., Rueckert R. R. On the structure of rhinovirus 1A. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. F., Brown F. Absence of poly (A) from the infective RNA of Nodamura virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jan;30(1):137–140. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. F., Brown F. Further physicochemical characterization of Nodamura virus. Evidence that the divided genome occurs in a single component. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):83–95. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER I. DIFFERENTIATION OF LARVAL DROSOPHILA EYE-ANTENNAL DISCS IN VITRO. J Exp Zool. 1964 Jun;156:91–103. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401560107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. Cell lines derived from late embryonic stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1972 Apr;27(2):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Kew O., Pallansch M., Rueckert R., Kaesberg P. Cell-free synthesis and processing of the proteins of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Zimmern D., Rueckert R. R., Kaesberg P. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in reticulocyte lysates: kinetic analysis of the formation of virion proteins and a protein required for processing. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):472–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.472-480.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W. Two groups of small stable RNAs. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):296–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]