Abstract
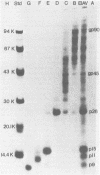
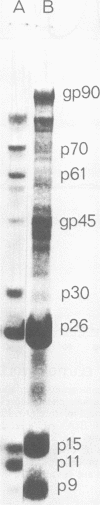
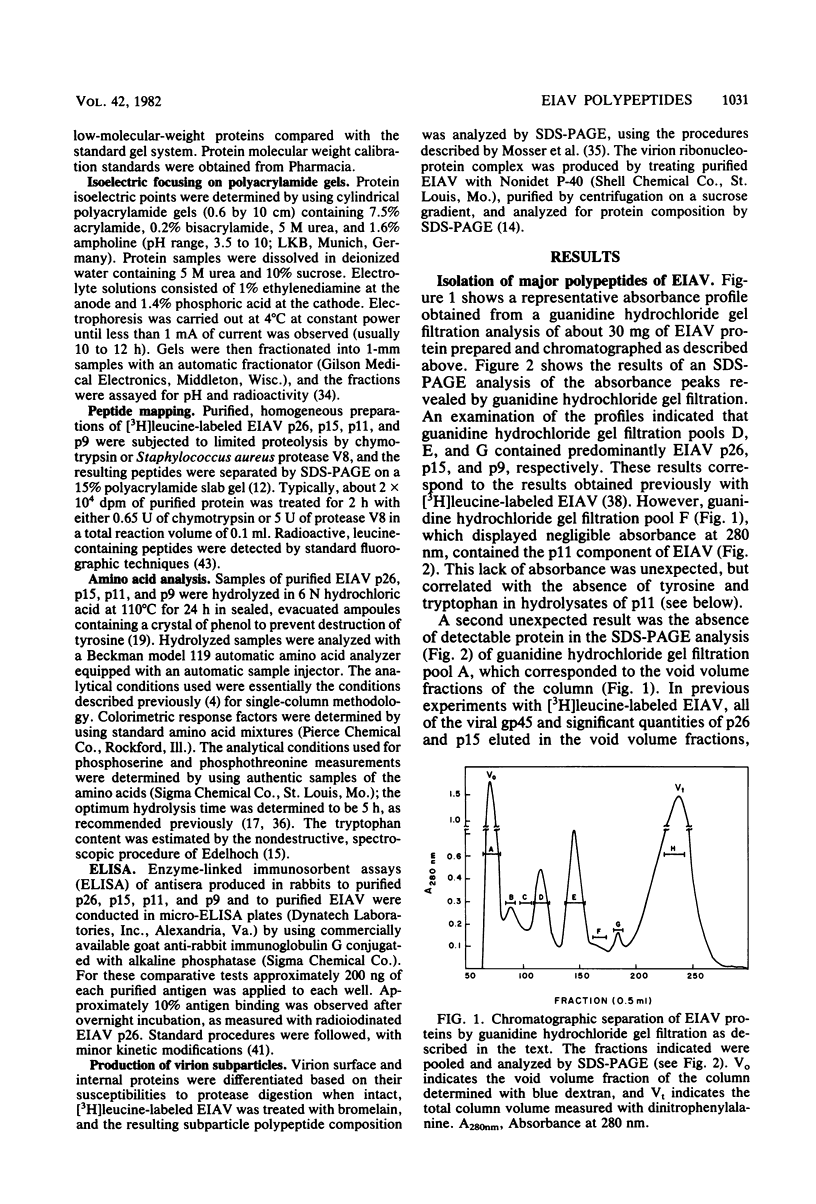
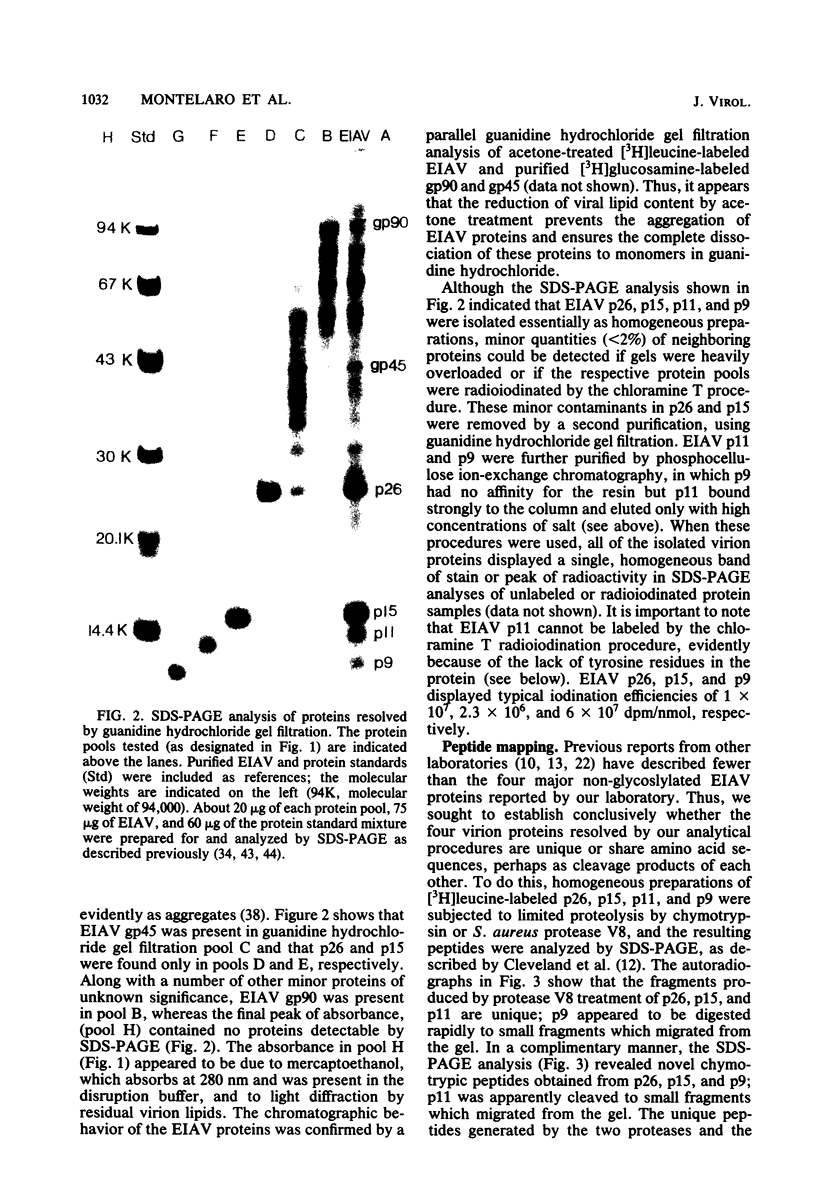
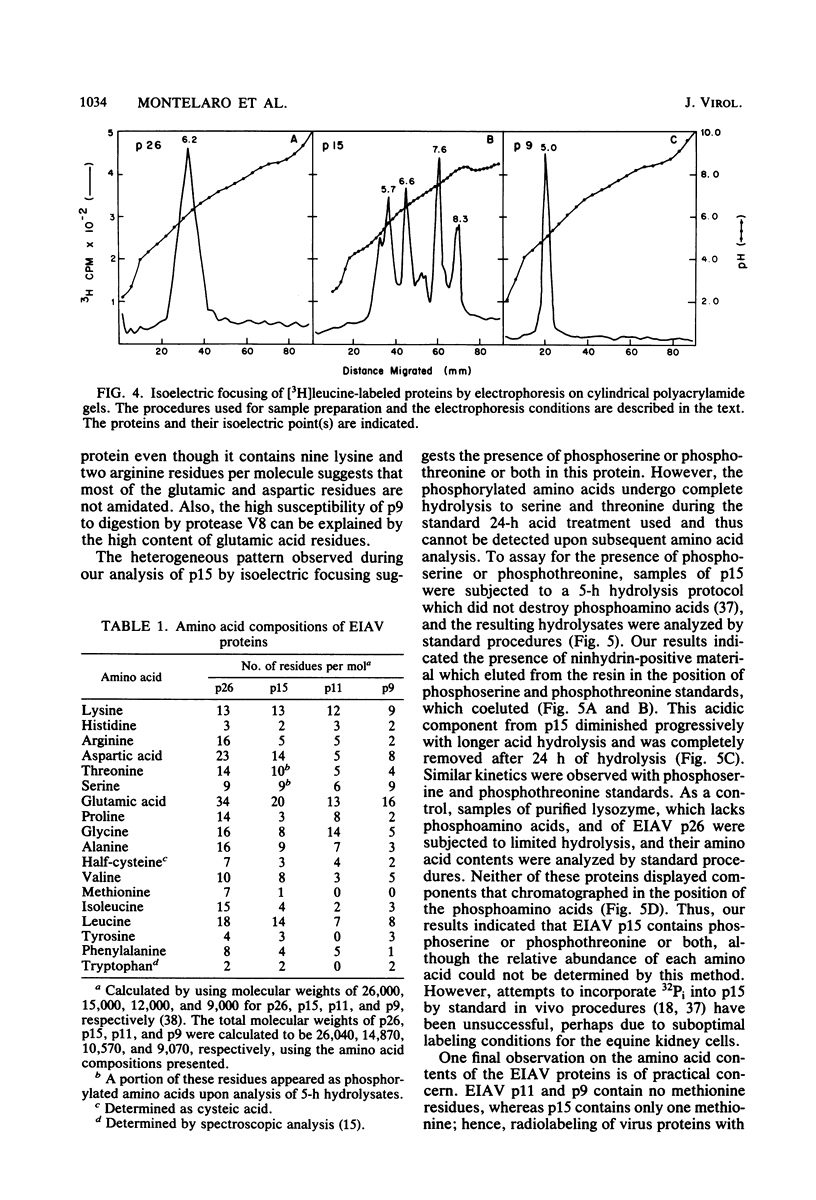
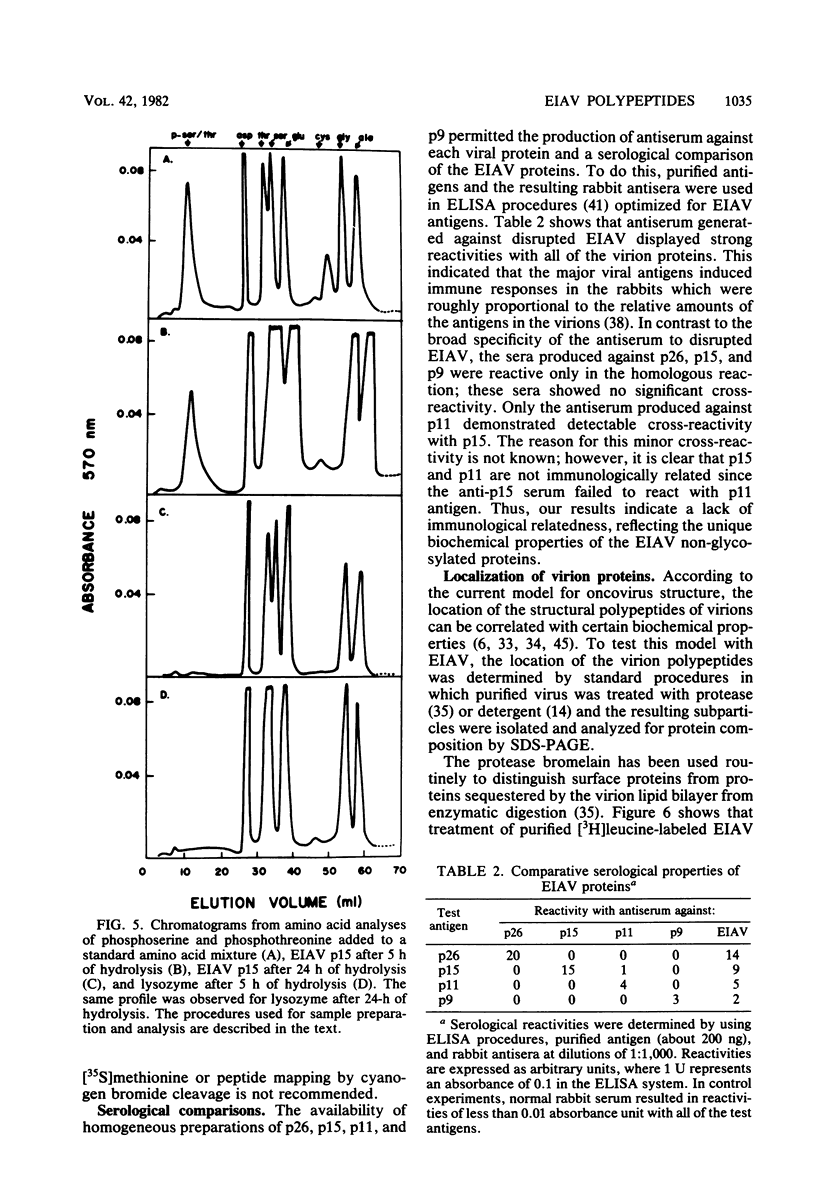
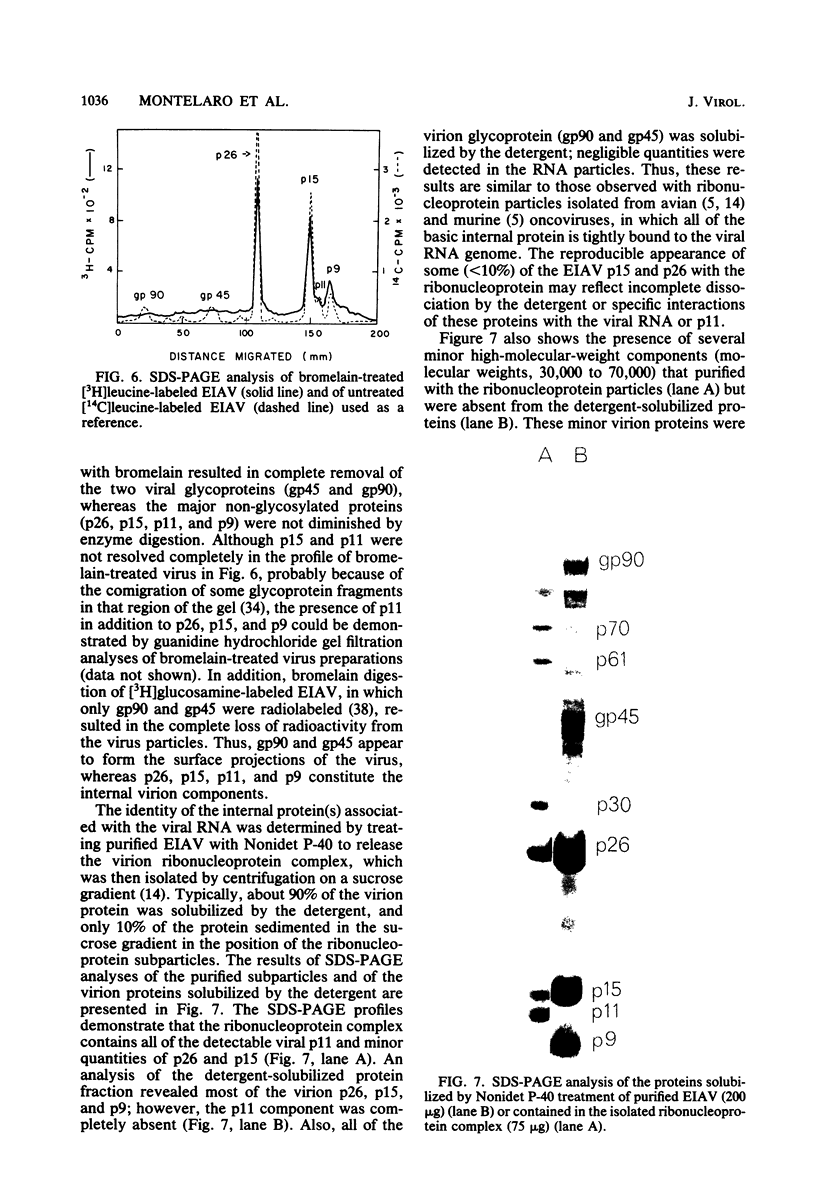
We describe procedures for the large-scale production of equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV) and for the isolation of the four major non-glycosylated virion proteins, designated p26, p15, p11, and p9. Comparisons of the purified proteins by peptide mapping procedures and by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays demonstrated the unrelatedness of the four proteins. The characteristic properties of each purified protein were examined by determining isoelectric points and amino acid compositions. We found that EIAV p26 and p9 focus at pI values of 6.2 and 5.0, respectively, and that these proteins contain no unusual amino acids. In contrast, EIAV p15 reproducibly displayed a heterogeneous isoelectric focusing pattern, with major pI values ranging from 5.7 to 8.3. This charge variation evidently correlated with different levels of phosphorylated serine or threonine or both, which could be detected by an amino acid analysis of purified p15. EIAV p11 apparently focused at a pI of greater than 10, reflecting its high content of basic amino acids. Moreover, localization experiments indicated that all four nonglycosylated proteins constitute the internal components of the virus, with all of the virion p11 closely associated with the viral RNA genome. Thus, our results demonstrated that EIAV, a lentivirus, contains structural polypeptides which are analogous to the structural polypeptides described previously in prototype C oncoviruses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amborski G. F., Jeffers G., Amborski R. L., Issel C. J. Equine infectious anemia virus: development of a simple reproducible method for titrating infectivity of the cell-adapted strain. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Feb;40(2):302–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer B. G., Crawford T. B., McGuire T. C., Frazier M. E. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase associated with equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.16-22.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barta V., Issel C. J. Simple method for preparation of specific antisera against viral proteins: rabbit antisera against equine infectious anemia virus proteins p26 and p16. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Nov;39(11):1856–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi D. P., Montelaro R. C., Frank H., Schäfer W. Assembly of type C oncornaviruses: a model. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):183–186. doi: 10.1126/science.202022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi D. P. Structural components of rna tumor viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1974;19:315–359. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60663-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M., Frenzel B. Isolation of a glycoprotein and two structural proteins of Maedi-Visna virus. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charman H. P., Bladen S., Gilden R. V., Coggins L. Equine infectious anemia virus: evidence favoring classification as a retravirus. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):1073–1079. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.1073-1079.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charman H., Long C., Coggins L. Specificity of response to viral proteins in horses infected with equine infectious anemia virus. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):472–478. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.472-478.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheevers W. P., Ackley C. M., Crawford T. B. Structural proteins of equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):997–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.997-1001.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Rueckert R. R. Properties of a ribonucleoprotein particle isolated from Nonidet P-40-treated Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1010–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1010-1020.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. W., Bolognesi D. P. Isolation of proteins by gel filtration in 6M guanidinium chloride: application to RNA tumor viruses. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jan;57(1):108–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Pal B. K., Roy-Burman P. RNA tumour virus phosphoproteins: evidence for virus specificity of phosphorylation. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):459–469. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A. C., Green R. W., Bolognesi D. P., Vanaman T. C. Comparative chemical properties of avian oncornavirus polypeptides. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Jr, Hanna M. G., Schafer W., Hunsmann G., Bolognesi D. P., HUPER G. Polypeptides of mammalian oncornaviruses. III. Localization of p 15 and reactivity with natural antibody. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90370-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Hardy W., Jr, Tress E., Fleissner E. Chromatographic separation and antigenic analysis of proteins of the oncornaviruses. V. Identification of a new murine viral protein, p15(E). J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):53–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.53-61.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki R., Green R. W., Bolognesi D. P. The structural polypeptides of equine infections anemia virus. Intervirology. 1978;9(5):286–294. doi: 10.1159/000148946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issel C. J., Coggins L. Equine infectious anemia: current knowledge. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1979 Apr 1;174(7):727–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Kobayashi K., Fukunaga Y. Antigenic drift of equine infectious anemia virus in chronically infected horses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;41(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01249923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Kobayashi K., Fukunaga Y. Serological comparison among various strains of equine infectious anemia virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;34(3):202–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01242993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. H. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of visna virus polypeptides isolated by agarose gel chromatography. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):207–214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.207-214.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmquist W. A., Barnett D., Becvar C. S. Production of equine infectious anemia antigen in a persistently infected cell line. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;42(4):361–370. doi: 10.1007/BF01250717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnel M. B., Katada M., McConnell S., Moore R. Demonstration of equine infectious anemia virus in primary leukocyte cultures by electron microscopy. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Dec;38(12):2067–2069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., Bolognesi D. P. Structure and morphogenesis of type-C retroviruses. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;28:63–89. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60646-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., Sullivan S. J., Bolognesi D. P. An analysis of type-C retrovirus polypeptides and their associations in the virion. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., West M., Issel C. J. High-performance gel permeation chromatography of proteins in denaturing solvents and its application to the analysis of enveloped virus polypeptides. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 1;114(2):398–406. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90501-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser A. G., Montelaro R. C., Rueckert R. R. Proteins of Rous-associated virus type 61: polypeptide stoichiometry and evidence that glycoprotein gp35 is not a cleavage product of gp85. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):10–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.10-19.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal B. K., Roy-Burman P. Phosphoproteins: structural components of oncornaviruses. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):540–549. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.540-549.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh B., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. Equine infectious anemia virus, a putative lentivirus, contains polypeptides analogous to prototype-C oncornaviruses. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):520–525. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Simek S., Ryder O. A., Coggins L. Detection of proviral DNA in horse cells infected with equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):577–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.577-583.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W., Hunsmann G., Moennig V., Noranha F., Bolognesi D. P., Green R. W., Hüper G. Polypeptides of mammalian oncornaviruses. II Characterization of murine leukemia virus polypeptide (p 15) bearing interspecies reactivity. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):48–59. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90369-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schetters H., Hehlmann R., Erfle V., Ramanarayanan M. Detection and quantification of type C viral proteins in tissues and sera with an enzyme immunoassay. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):972–980. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.972-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. V., Stowring L., Haase A. T., Narayan O., Vigne R. Antigenic variation in visna virus. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shealy D. J., Mosser A. G., Rueckert R. R. Novel p19-related protein in Rous-associated virus type 61: implications for avian gag gene order. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):431–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.431-437.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shealy D. J., Rueckert R. R. Proteins of Rous-associated virus 61, an avian retrovirus: common precursor for glycoproteins gp85 and gp35 and use of pactamycin to map translational order of proteins in the gag, pol, and env genes. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):380–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.380-388.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Reynolds R. K., Devare S. G., Reynolds F. H. Biochemical and immunological properties of gag genecoded structural proteins of endogenous tyep C RNA tumor viruses of diverse mammalian species. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7818–7825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowring L., Haase A. T., Charman H. P. Serological definition of the lentivirus group of retroviruses. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):523–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.523-528.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., August J. T. Structural proteins of oncogenic ribonucleic acid viruses. Interspec II, a new interspecies antigen. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5627–5633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland F., Matheka H. D., Coggins L., Hatner D. Electron microscopic studies on equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV). Brief report. Arch Virol. 1977;55(4):335–340. doi: 10.1007/BF01315055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]