Abstract
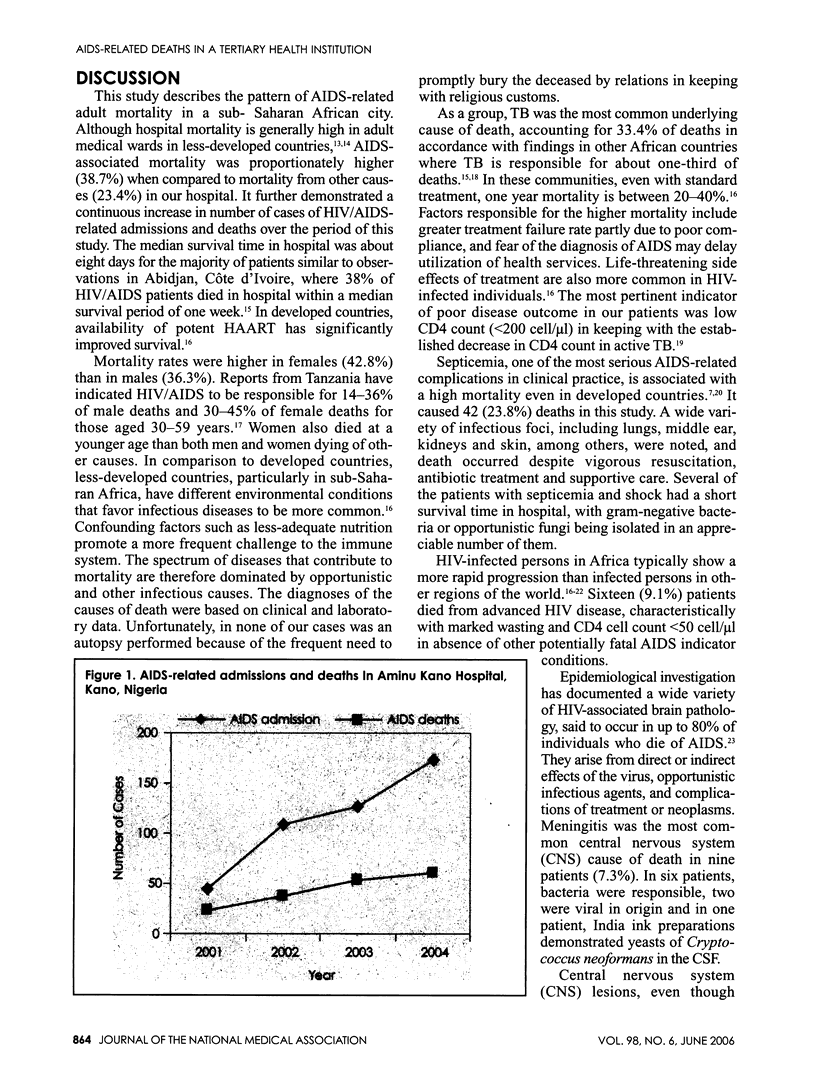
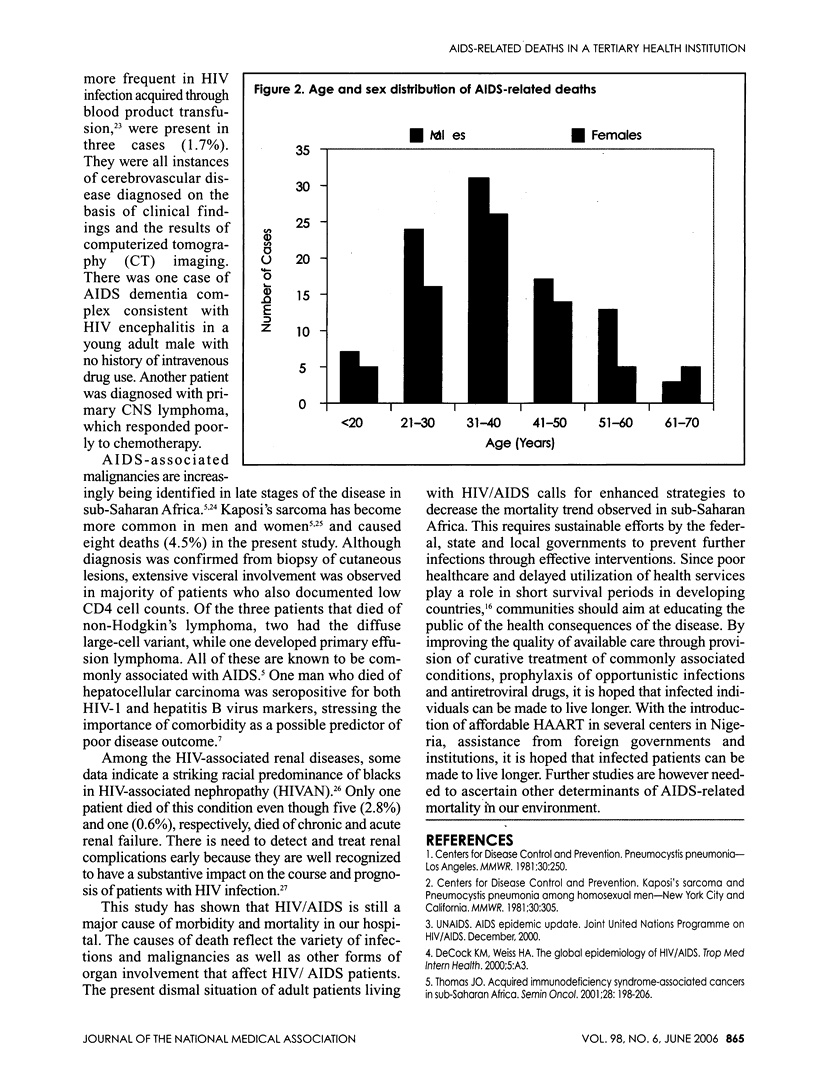
Africa contains 70% of adults and 80% of children living with AIDS in the world and has buried 75% of the 21.8 million worldwide who have died of AIDS since the epidemic began. Nigeria, the most populous country in Africa, has 5.8% of her adult population having HIV infection at the end of 2003. We reviewed the causes of death among AIDS patients in Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital Kano, Nigeria over four years. Four-hundred-fifty-five (9.9%) of the 4,574 adult medical admissions were due to HIV/AIDS-related diagnosis. HIV/AIDS admissions increased progressively from 45 cases in 2001 to 174 in 2004. HIV/AIDS caused 176 deaths over the period giving an HIV-related mortality of 38.7%. This also showed a gradual increase from 24 deaths in 2001 to 61 deaths in 2004. The most common causes of death were tuberculosis (33.4%), septicemia (23.8%), advanced HIV disease (9.1%), meningitis (7.4%), other pulmonary infections (5.1%) and Kaposi's sarcoma (4.5%). The present dismal situation of patients living with HIV/AIDS calls for enhanced strategies to decrease the mortality trend observed. With the introduction of affordable highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in several centers in Nigeria, it is hoped that infected patients can be made to live longer.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal Rajiv. Hypertension and survival in chronic hemodialysis patients--past lessons and future opportunities. Kidney Int. 2005 Jan;67(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed A., Isa M. S., Garba H. A., Kalayi G. D., Muhammad I., Egler L. J. Influence of HIV infection on presentation of Kaposi's sarcoma. Trop Doct. 2001 Jan;31(1):42–45. doi: 10.1177/004947550103100119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anteyi E. A., Idoko J. A., Ukoli C. O., Bello C. S. Clinical pattern of human immunodeficiency virus infection (HIV) in pulmonary tuberculosis patients in Jos, Nigeria. Afr J Med Med Sci. 1996 Dec;25(4):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerma J. T., Nunn A. J., Whitworth J. A. Mortality impact of the AIDS epidemic: evidence from community studies in less developed countries. AIDS. 1998;12 (Suppl 1):S3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Kaposi's sarcoma and Pneumocystis pneumonia among homosexual men--New York City and California. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1981 Jul 3;30(25):305–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Pneumocystis pneumonia--Los Angeles. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1981 Jun 5;30(21):250–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S. Y., Buehler J. W., Lieb L., Beckett G., Conti L., Costa S., Dahan B., Danila R., Fordyce E. J., Hirozawa A. Causes of death among persons reported with AIDS. Am J Public Health. 1993 Oct;83(10):1429–1432. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.10.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinque P., Scarpellini P., Vago L., Linde A., Lazzarin A. Diagnosis of central nervous system complications in HIV-infected patients: cerebrospinal fluid analysis by the polymerase chain reaction. AIDS. 1997 Jan;11(1):1–17. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199701000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cock K. M., Weiss H. A. The global epidemiology of HIV/AIDS. Trop Med Int Health. 2000 Jul;5(7):A3–A9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3156.2000.00590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy V., Msellati P., Lepage P., Batungwanayo J., Hitimana D. G., Taelman H., Bogaerts J., Boineau F., Van de Perre P., Simonon A. Four years of natural history of HIV-1 infection in african women: a prospective cohort study in Kigali (Rwanda), 1988-1993. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995 Aug 1;9(4):415–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas S. B., Hounnou A., Peacock C., Beaumel A., Djomand G., N'Gbichi J. M., Yeboue K., Hondé M., Diomande M., Giordano C. The mortality and pathology of HIV infection in a west African city. AIDS. 1993 Dec;7(12):1569–1579. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199312000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D., Maude G. H., Malamba S. S., Okongo M. J., Wagner H. U., Mulder D. W., Whitworth J. A. HIV-1 disease progression and AIDS-defining disorders in rural Uganda. Lancet. 1997 Jul 26;350(9073):245–250. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)01474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogun S. A., Adelowo O. O., Familoni O. B., Adefuye O. B., Alebiosu C., Jaiyesimi A. E. A., Fakoya E. A. O., Odusan B., Odusoga O. L., Ola O. O. Spectrum and outcome of clinical diseases in adults living with AIDS at the Ogun State University Teaching Hospital. East Afr Med J. 2003 Oct;80(10):513–517. doi: 10.4314/eamj.v80i10.8753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogun S. A., Adelowo O. O., Familoni O. B., Jaiyesimi A. E., Fakoya E. A. Pattern and outcome of medical admissions at the Ogun State University Teaching Hospital, Sagamu--a three year review. West Afr J Med. 2000 Oct-Dec;19(4):304–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer R. W., Bloch A. B., Larkin C., Vasudavan V., Seligman S., Dehovitz J. D., DiFerdinando G., Stoneburner R., Cauthen G. Predictors of survival in HIV-infected tuberculosis patients. AIDS. 1996 Mar;10(3):269–272. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199603000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated cancers in Sub-Saharan Africa. Semin Oncol. 2001 Apr;28(2):198–206. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(01)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner Neil J., Goodman Jeffrey W., Kimmel Paul L. The HIV-associated renal diseases: current insight into pathogenesis and treatment. Kidney Int. 2003 May;63(5):1618–1631. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



