Abstract
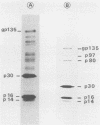
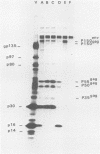
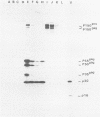
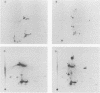
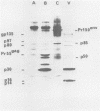
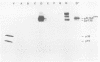
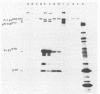
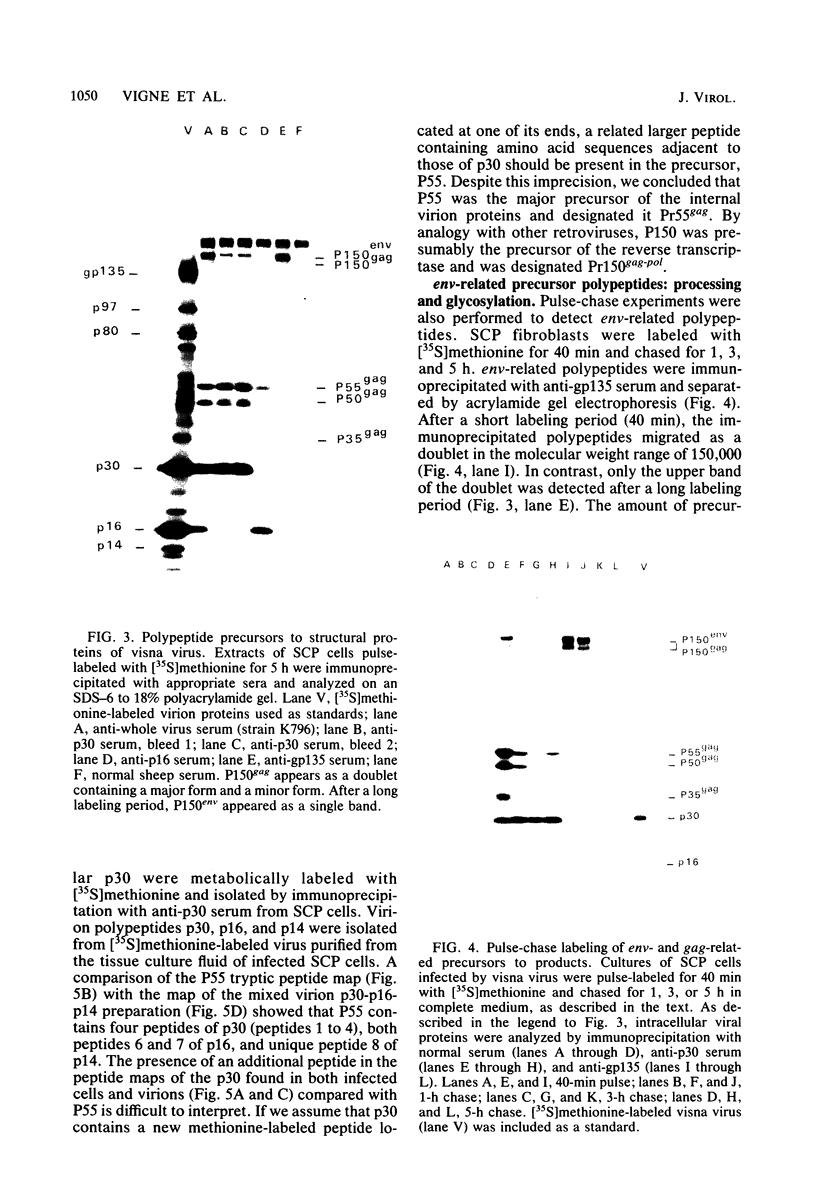
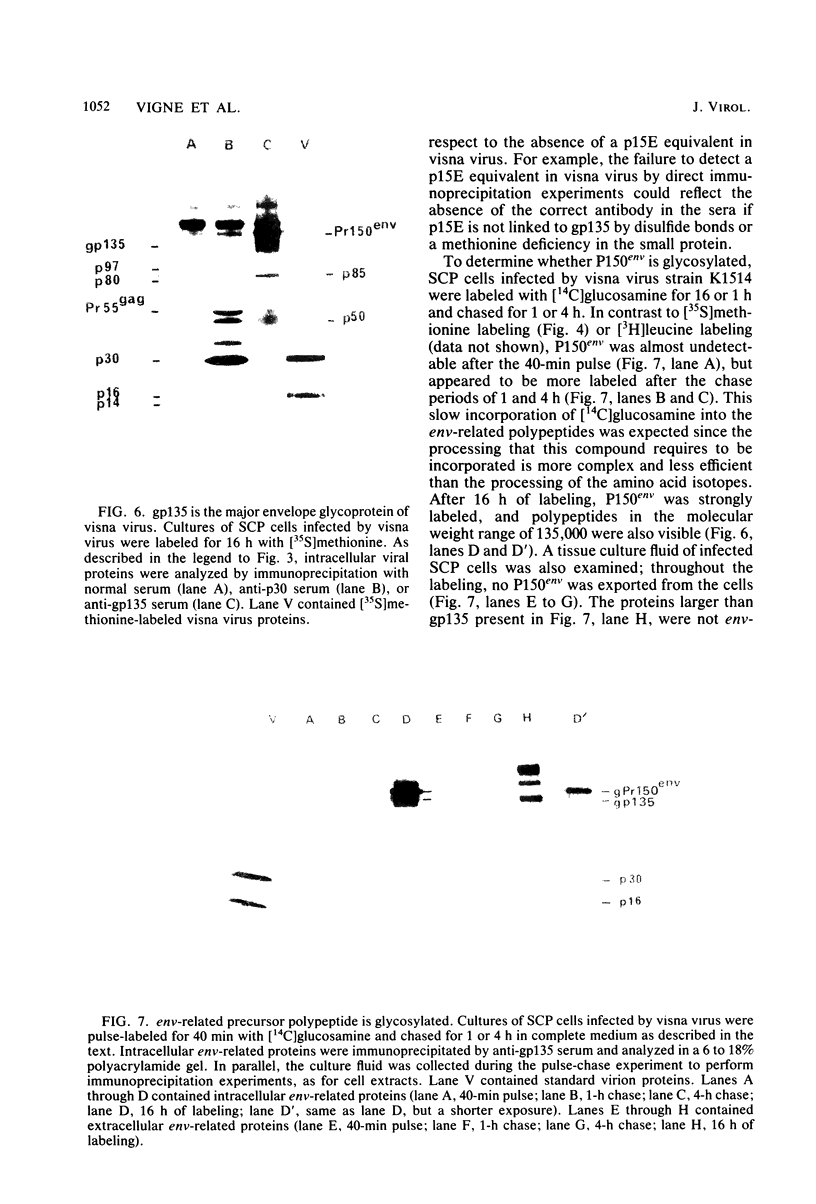
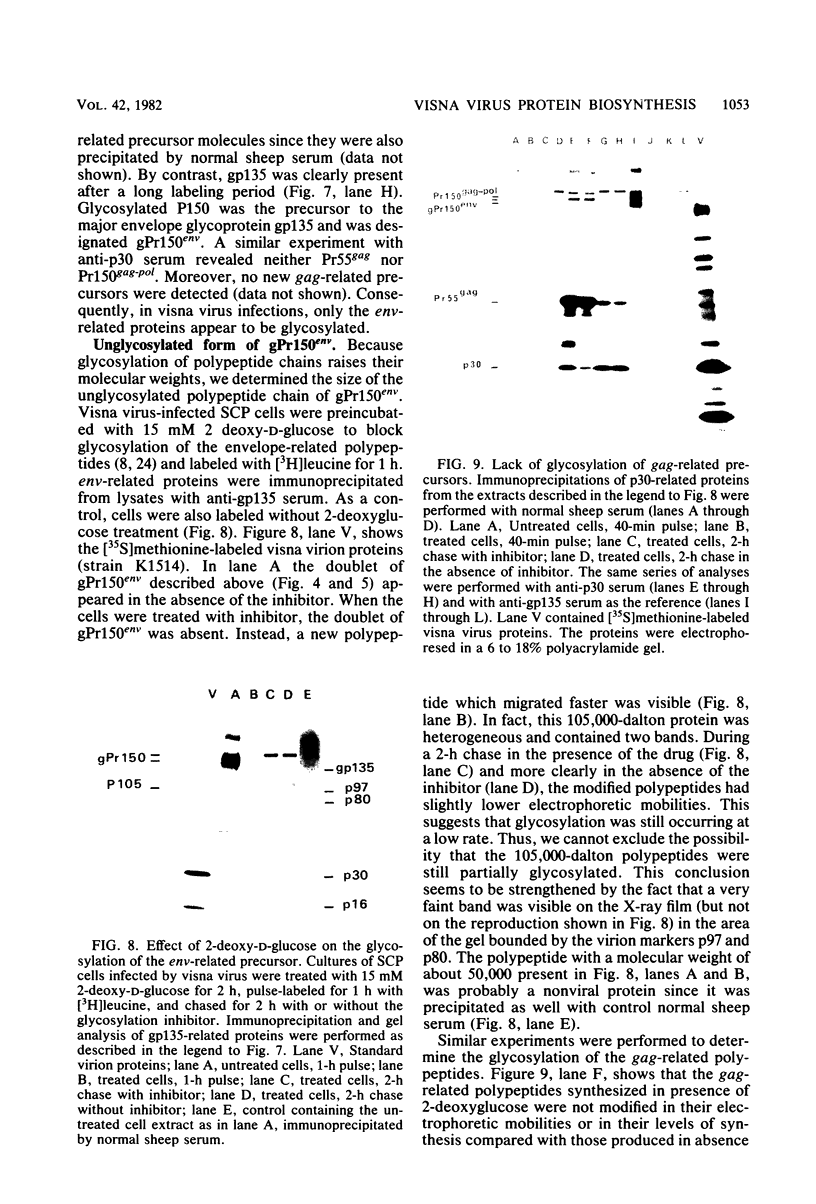
Visna virus is a retrovirus which replicates in fibroblast-like cells of the sheep choroid plexus through a lytic cycle. Visna virions contain three major low-molecular-weight proteins (p30, p16, and p14) which, together with the genomic RNA and several molecules of reverse transcriptase, constitute the core structure of the virions. The core is surrounded by an envelope containing a major glycoprotein (gp135). By analogy with the oncoviruses, these three groups of structural proteins (i.e., the internal proteins, the envelope glycoprotein, and the reverse transcriptase) are probably encoded by the gag, env, and pol genes, respectively. To elucidate the genetic organization of the visna virus genome and its expression, we studied the synthesis of viral proteins in infected sheep choroid plexus cells. Intracellular viral proteins were detected by immunoprecipitation of pulse-labeled cell extracts with monospecific sera raised against p30, p16, and gp135 and resolution of the proteins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Immunoprecipitation with anti-p30 and anti-p16 sera allowed the characterization of the 55,000-dalton polypeptide precursor to internal virion proteins p30, p16, and p14 (Pr55gag). Tryptic peptide mapping confirmed the precursor-product relationship between Pr55gag and the three internal proteins. In addition, a gag-related polypeptide of 150,000 daltons was also detected. This polypeptide, which was less abundant than Pr55gag, is a likely precursor to the viral reverse transcriptase (Pr150gag-pol). Pr55gag and Pr150gag-pol are not glycosylated. The precursor related to major envelope protein gp135 is a glycosylated polypeptide with an average molecular weight of 150,000 (gPr150env). Pulse-chase experiments indicated that gPr150env matures into glycoprotein gp135 intracellularly; however, gp135 was never preponderant in cell extracts. The non-glycosylated from of gPr150env, which accumulated in the presence of 2-deoxy-d-glucose, appeared as a polypeptide of about 100,000 daltons. These results indicated that visna virus codes for the largest non-glycosylated env-related precursor among all of the retroviruses and therefore probably contains the largest env gene.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcement L. J., Karshin W. L., Naso R. B., Jamjoom G., Arlinghaus R. B. Biosynthesis of Rauscher leukemia viral proteins: presence of p30 and envelope p15 sequences in precursor polypeptides. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90504-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Tumor viruses: 1974. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1187–1200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. gag Gene of mammalian type-C RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):554–559. doi: 10.1038/262554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K. L., Faras A. J., Hasse A. T., Duesberg P. H., Maisel J. E. Genomic complexities of murine leukemia and sarcoma, reticuloendotheliosis, and visna viruses. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):525–537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.525-537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Atterwill M. Composition, arrangement and cleavage of the mouse mammary tumor virus polyprotein precursor Pr77gag and p110gag. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):1003–1012. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Atterwill M. Polyproteins related to the major core protein of mouse mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):660–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.660-672.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggelmann H. Biosynthesis of an unglycosylated envelope glycoprotein of Rous sarcoma virus in the presence of tunicamycin. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):799–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.799-804.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresler S., Ruta M., Murray M. J., Kabat D. Glycoprotein encoded by the Friend spleen focus-forming virus. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):564–575. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.564-575.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Dresler S., Kabat D. Synthesis and glycosylation of polyprotein precursors to the internal core proteins of Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):865–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.865-874.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi P., Brahic M., Vigne R., Tamalet J. Characterization of visna virus mRNA. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):25–30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.25-30.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi P., Vigne R., Quérat G., Jouanny C., Sauze N. Intracellular ribonucleoprotein complexes of visna virus are infectious. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1057–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1057-1066.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Baringer J. R. The structural polypeptides of RNA slow viruses. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T. The slow infection caused by visna virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;72:101–156. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66289-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. H., Genovese M., Thormar H. Multiple activities of DNA polymerase from visna virus. Prep Biochem. 1973;3(6):525–539. doi: 10.1080/00327487308061535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. H., Papini M. Evidence for two forms of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in Visna virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 27;561(2):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. H., Thormar H. Precipitation of visna viral proteins by immune sera of rabbits and sheep. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):536–539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.536-539.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. C., Jr, Arlinghaus R. B. Tryptic peptide analyses of polypeptides generated by premature termination of cell-free protein synthesis allow a determination of the Rauscher leukemia virus gag gene order. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):929–935. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.929-935.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racevskis J., Sarkar N. H. Synthesis and processing of precursor polypeptides to murine mammary tumor virus structural proteins. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):374–383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.374-383.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. K., Stephenson J. R. Intracistronic mapping of the murine type C viral gag gene by use of conditional lethal replication mutants. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Long C. W., Oroszlan S., Arthur L., Fine D. L. Isolation of separate precursor polypeptides for the mouse mammary tumor virus glycoproteins and nonglycoproteins. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. V., Stowring L., Haase A. T., Narayan O., Vigne R. Antigenic variation in visna virus. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. Z., Strand M., August J. T. High molecular weight precursor polypeptides to structural proteins of Rauscher murine leukemia virus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 15;107(4):459–477. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowring L., Haase A. T., Charman H. P. Serological definition of the lentivirus group of retroviruses. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):523–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.523-528.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne R., Brahic M., Filippi P., Tamalet J. Complexity and polyadenylic acid content of visna virus 60-70S RNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):386–395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.386-395.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne R., Filippi P., Brahic M., Tamalet J. Absence of circularly permuted and largely redundant sequences in the genome of visna virus. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):543–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.543-550.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne R., Neil J. C., Breitman M. L., Vogt P. K. Recovered src genes are polymorphic and contain host markers. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):71–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]