Abstract
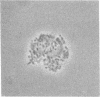
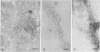
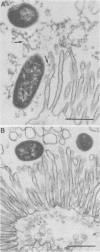
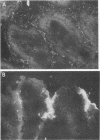
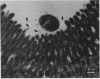
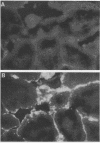
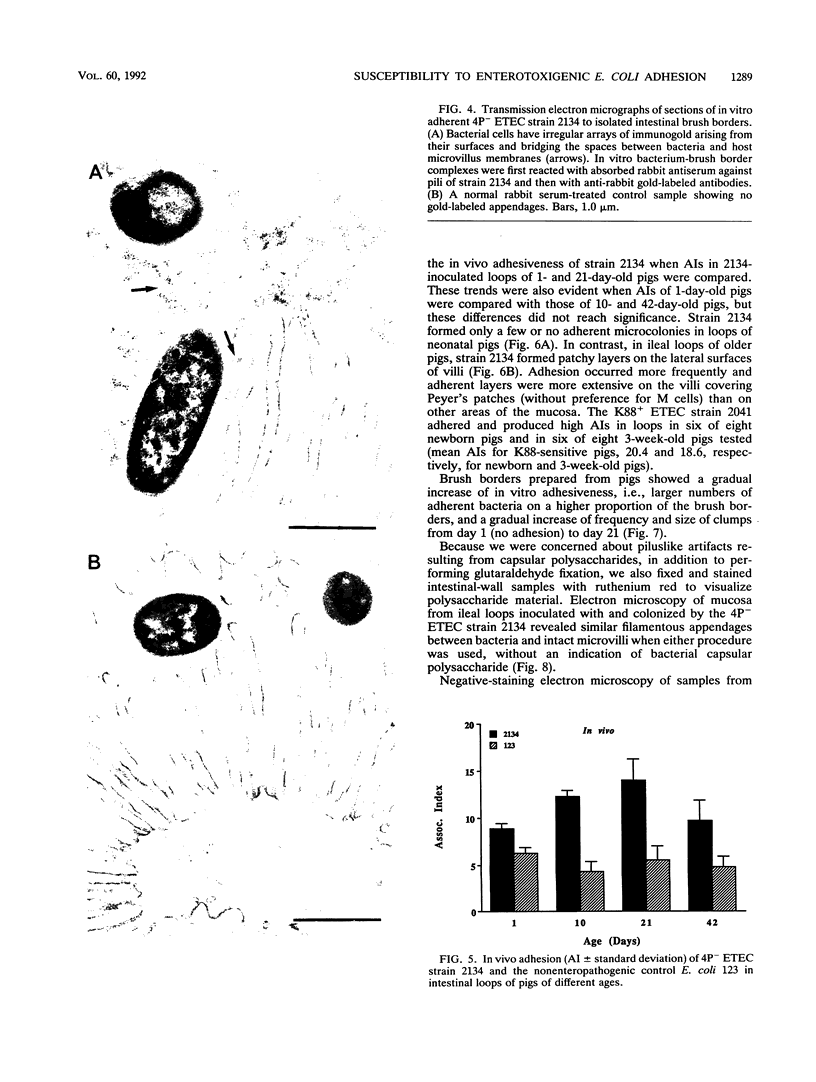
Two porcine isolates of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) (serogroup O157 and O141) derived from fatal cases of postweaning diarrhea and lacking K88, K99, F41, and 987P pili (4P- ETEC) were tested for adhesiveness to small-intestinal epithelia of pigs of different ages. Neither strain adhered to isolated intestinal brush borders of newborn (1-day-old) pigs in the presence of mannose. However, mannose-resistant adhesion occurred when brush borders from 10-day- and 3- and 6-week-old pigs were used. Electron microscopy revealed that both strains produced fine (3.5-nm) and type 1 pili at 37 degrees C but only type 1 pili at 18 degrees C. Mannose-resistant in vitro adhesion to brush borders of older pigs correlated with the presence of fine pili. These strains produced predominantly fine pili in ligated intestinal loops of both older and newborn pigs, but adherence was greater in loops in older pigs. Immunoelectron microscopic studies, using antiserum raised against piliated bacteria and absorbed with nonpiliated bacteria, of samples from brush border adherence studies revealed labelled appendages between adherent bacteria and intestinal microvilli. Orogastric inoculation of pigs weaned at 10 and 21 days of age indicated significantly (P less than 0.001) higher levels of adhesion by the ETEC to the ileal epithelia of older pigs than to that of younger ones. We suggest that small-intestinal adhesion and colonization by these ETEC isolates is dependent on receptors that develop progressively with age during the first 3 weeks after birth. Furthermore, our data are consistent with the hypothesis that the fine pili described mediate intestinal adhesion by the 4P- ETEC strains studied.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertschinger H. U., Bachmann M., Mettler C., Pospischil A., Schraner E. M., Stamm M., Sydler T., Wild P. Adhesive fimbriae produced in vivo by Escherichia coli O139:K12(B):H1 associated with enterotoxaemia in pigs. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Nov;25(2-3):267–281. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Inman L. R. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 in the rabbit: the peyer's patch as the initial site of attachment and colonization. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):440–446. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Boedeker E. C. Rabbit mucosal receptors for an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain: appearance of bacterial receptor activity at weaning. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):821–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A. Comparison of receptors for 987P pili of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in the small intestines of neonatal and older pig. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4030–4035. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4030-4035.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Isaacson R. E. Purification and characterization of a receptor for the 987P pilus of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):98–105. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.98-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominick M. A., Schmerr M. J., Jensen A. E. Expression of type 1 pili by Escherichia coli strains of high and low virulence in the intestinal tract of gnotobiotic turkeys. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jan;46(1):270–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother J. M., Larivière S., Lallier R. New fimbrial antigen F165 from Escherichia coli serogroup O115 strains isolated from piglets with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.10-15.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Veldkamp J., Jansen W. H. Improved minca medium for the detection of K99 antigen in calf enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):676–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.676-678.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E. K99 surface antigen of Escherichia coli: purification and partial characterization. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):272–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.272-279.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennan R. M., Monckton R. P. Adhesive fimbriae associated with porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of the O141 serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2006–2011. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2006-2011.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., McConnell M. M., Rowe B., McNeish A. S. Adhesion and ultrastructural properties of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli producing colonization factor antigens III and IV. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3364–3371. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3364-3371.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leite D. S., Yano T., Pestana de Castro A. F. Production, purification and partial characterization of a new adhesive factor (F42) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from pigs. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 May-Jun;139(3):295–306. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lintermans P. F., Pohl P., Bertels A., Charlier G., Vandekerckhove J., Van Damme J., Schoup J., Schlicker C., Korhonen T., De Greve H. Characterization and purification of the F17 adhesin on the surface of bovine enteropathogenic and septicemic Escherichia coli. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Nov;49(11):1794–1799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Kohler E. M., Schneider R. A., Whipp S. C. Prevalence of pilus antigens, enterotoxin types, and enteropathogenicity among K88-negative enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from neonatal pigs. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):222–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.222-230.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Sorensen D. K., Sautter J. H. Experimental enteric colibacillosis in piglets. Can J Comp Med. 1968 Jul;32(3):493–497. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Casey T. A., Moon H. W. Phenotype and genotype of Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with postweaning diarrhea in Hungary. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):651–653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.651-653.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E. Colonization of porcine intestine by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: selection of piliated forms in vivo, adhesion of piliated forms to epithelial cells in vitro, and incidence of a pilus antigen among porcine enteropathogenic E. coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):344–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.344-352.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Sugimoto C., Isayama Y., Kashiwazaki M. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli isolated from piglets with neonatal and post-weaning diarrhea in Japan. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Apr;13(4):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Serology of Escherichia coli fimbriae. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:80–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Pierce N. F., Apple R. T., Cray W. C., Jr M cell transport of Vibrio cholerae from the intestinal lumen into Peyer's patches: a mechanism for antigen sampling and for microbial transepithelial migration. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1108–1118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters J. E., Charlier G. J., Halen P. H. Pathogenicity of attaching effacing enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from diarrheic suckling and weanling rabbits for newborn rabbits. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):690–696. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.690-696.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runnels P. L., Moon H. W., Schneider R. A. Development of resistance with host age to adhesion of K99+ Escherichia coli to isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):298–300. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.298-300.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento J. I., Casey T. A., Moon H. W. Postweaning diarrhea in swine: experimental model of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;49(7):1154–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A., Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to pig intestinal brush borders: the existence of two pig phenotypes. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):405–411. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlind O., Thafvelin B., Möllby R. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli strains isolated from Swedish piglets with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):879–884. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.879-884.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. A., Francis D. H. Fimbriae and enterotoxins associated with Escherichia coli serogroups isolated from pigs with colibacillosis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Feb;47(2):213–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]