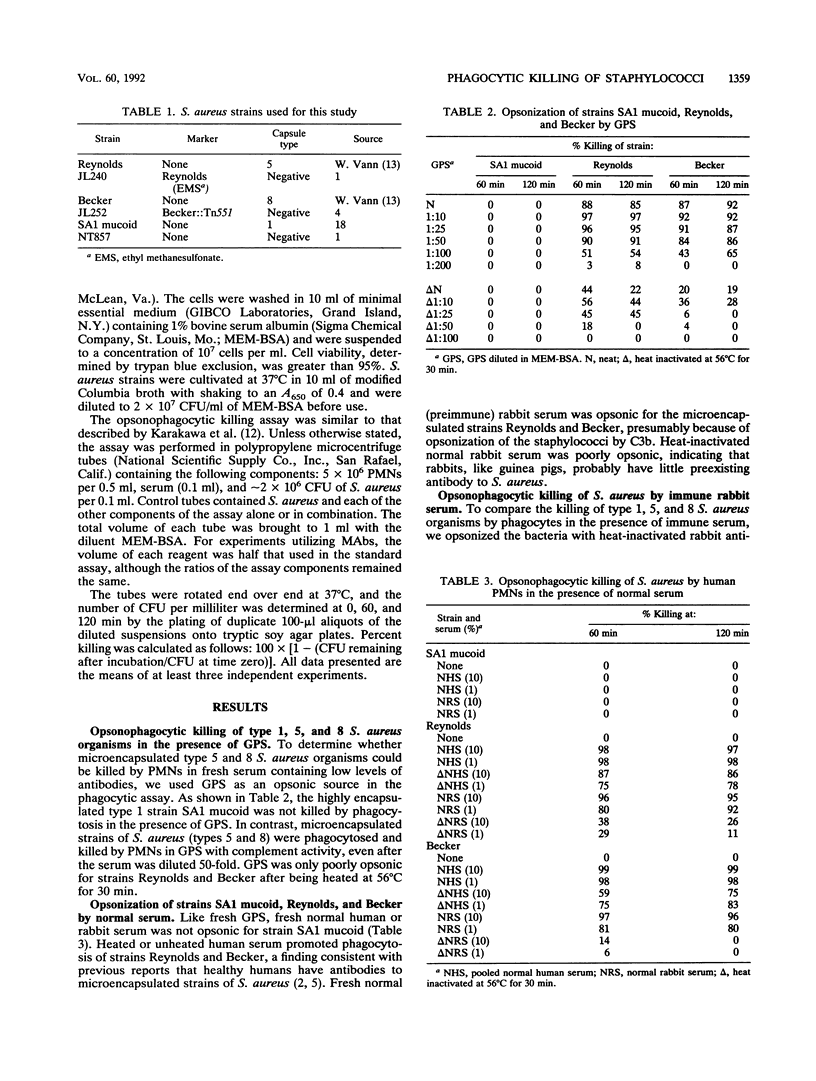
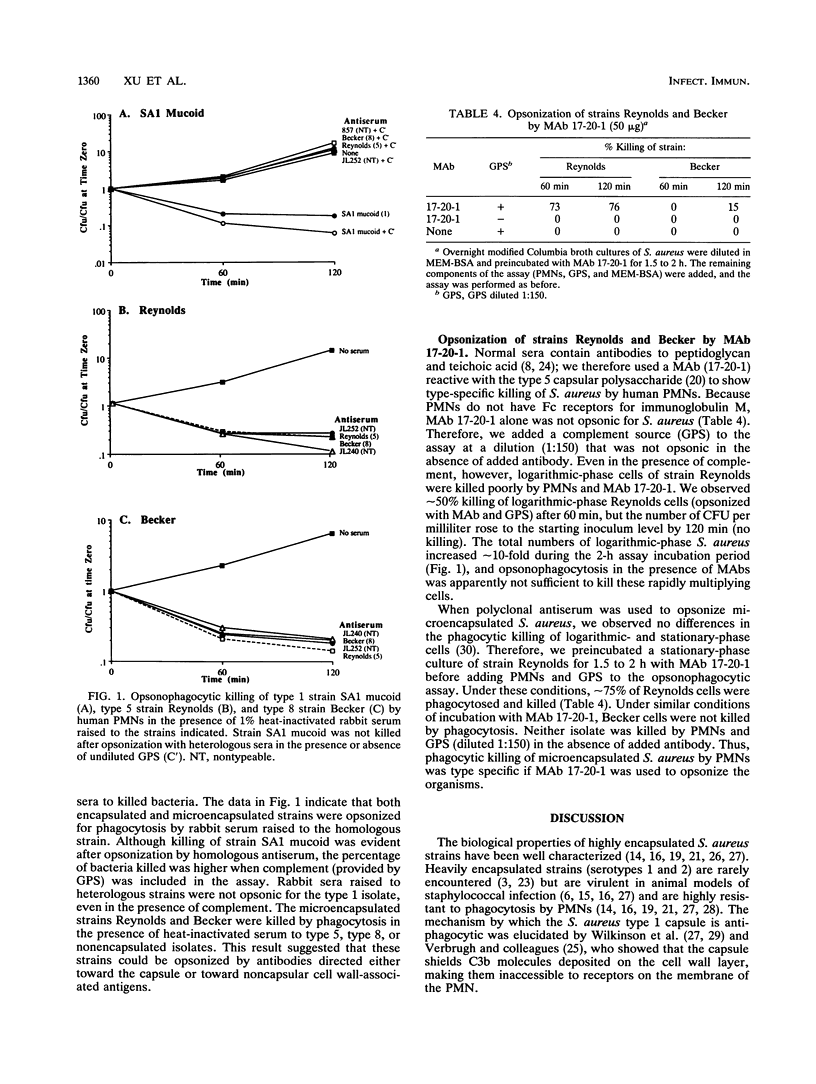
Abstract
Phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) is an important host defense against infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Using an in vitro assay, we compared the opsonic requirements for phagocytic killing of prototype strains of encapsulated (type 1) and microencapsulated (type 5 and type 8) S. aureus by human PMNs. More than 85% of broth-grown, logarithmic-phase type 5 and 8 S. aureus organisms were killed by PMNs incubated with fresh normal human, rabbit, or guinea pig serum with complement activity. Under similar conditions, the highly encapsulated type 1 strain was not killed. Both encapsulated and microencapsulated strains were opsonized for phagocytosis by heat-inactivated serum raised in rabbits to killed bacteria. Opsonization by homologous serum was required for phagocytosis of the type 1 strain. In contrast, microencapsulated type 5 and 8 S. aureus organisms were killed by heat-inactivated rabbit serum raised to type 5, type 8, or nonencapsulated isolates; this result suggested that antibodies to the capsule or to cell wall components other than the capsule could opsonize these organisms for phagocytosis. The specificity of the assay was confirmed with capsule type 5-specific monoclonal antibodies, which were opsonic only for the type 5 S. aureus isolate. These studies indicate that, unlike the highly encapsulated type 1 strain, broth-grown microencapsulated S. aureus strains do not resist opsonophagocytic killing in vitro by normal serum.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albus A., Arbeit R. D., Lee J. C. Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus mutants altered in type 5 capsule production. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1008–1014. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1008-1014.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albus A., Fournier J. M., Wolz C., Boutonnier A., Ranke M., Høiby N., Hochkeppel H., Döring G. Staphylococcus aureus capsular types and antibody response to lung infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2505–2509. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2505-2509.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbeit R. D., Karakawa W. W., Vann W. F., Robbins J. B. Predominance of two newly described capsular polysaccharide types among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;2(2):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A. Determinants of infection in the peritoneal cavity. I. Response to and fate of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus albus in the mouse. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Aug;35:12–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensson B., Boutonnier A., Ryding U., Fournier J. M. Diagnosing Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis by detecting antibodies against S. aureus capsular polysaccharide types 5 and 8. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):530–533. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattom A., Schneerson R., Szu S. C., Vann W. F., Shiloach J., Karakawa W. W., Robbins J. B. Synthesis and immunologic properties in mice of vaccines composed of Staphylococcus aureus type 5 and type 8 capsular polysaccharides conjugated to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2367–2374. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2367-2374.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. P., Bayer A. S., Turner D., Ward J. I. Antibody responses to protein A in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):458–462. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.458-462.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. P., Ward J. I., Bayer A. S. Influence of Staphylococcus aureus antibody on experimental endocarditis in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3030–3034. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3030-3034.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochkeppel H. K., Braun D. G., Vischer W., Imm A., Sutter S., Staeubli U., Guggenheim R., Kaplan E. L., Boutonnier A., Fournier J. M. Serotyping and electron microscopy studies of Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates with monoclonal antibodies to capsular polysaccharide types 5 and 8. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):526–530. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.526-530.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G. Factors relating to the virulence of staphylococci. I. Comparative studies on two colonial variants. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Jun;34:537–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Sutton A., Schneerson R., Karpas A., Vann W. F. Capsular antibodies induce type-specific phagocytosis of capsulated Staphylococcus aureus by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1090–1095. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1090-1095.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Young D. A., Kane J. A. Structural analysis of the cellular constituents of a fresh clinical isolate of Staphylococcus aureus, and their role in the interaction between the organisms and polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the presence of serum factors. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):496–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.496-505.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Betley M. J., Hopkins C. A., Perez N. E., Pier G. B. Virulence studies, in mice, of transposon-induced mutants of Staphylococcus aureus differing in capsule size. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):741–750. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Liu M. J., Parsonnet J., Arbeit R. D. Expression of type 8 capsular polysaccharide and production of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 are associated among vaginal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2612–2615. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2612-2615.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Michon F., Perez N. E., Hopkins C. A., Pier G. B. Chemical characterization and immunogenicity of capsular polysaccharide isolated from mucoid Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2191–2197. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2191-2197.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melly M. A., Duke L. J., Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Biological properties of the encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.389-397.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelles M. J., Niswander C. A., Karakawa W. W., Vann W. F., Arbeit R. D. Reactivity of type-specific monoclonal antibodies with Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates and purified capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.14-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Influence of encapsulation on staphylococcal opsonization and phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):943–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.943-949.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poutrel B., Boutonnier A., Sutra L., Fournier J. M. Prevalence of capsular polysaccharide types 5 and 8 among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from cow, goat, and ewe milk. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.38-40.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Samra Z., Karakawa W. W., Vann W. F., Schneerson R., Malik Z. Encapsulation and capsular types in isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from different sources and relationship to phage types. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):828–834. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.828-834.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peters R., Rozenberg-Arska M., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Antibodies to cell wall peptidoglycan of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with serious staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peterson P. K., Nguyen B. Y., Sisson S. P., Kim Y. Opsonization of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus: the role of specific antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1681–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Maverakis N. H. Capsule production and virulence among strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):221–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Cryptic peptidoglycan and the antiphagocytic effect of the Staphylococcus aureus capsule: model for the antiphagocytic effect of bacterial cell surface polymers. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):502–508. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.502-508.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Sisson S. P., Kim Y., Peterson P. K. Localization of the third component of complement on the cell wall of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M: implications for the mechanism of resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1159-1163.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


