Abstract
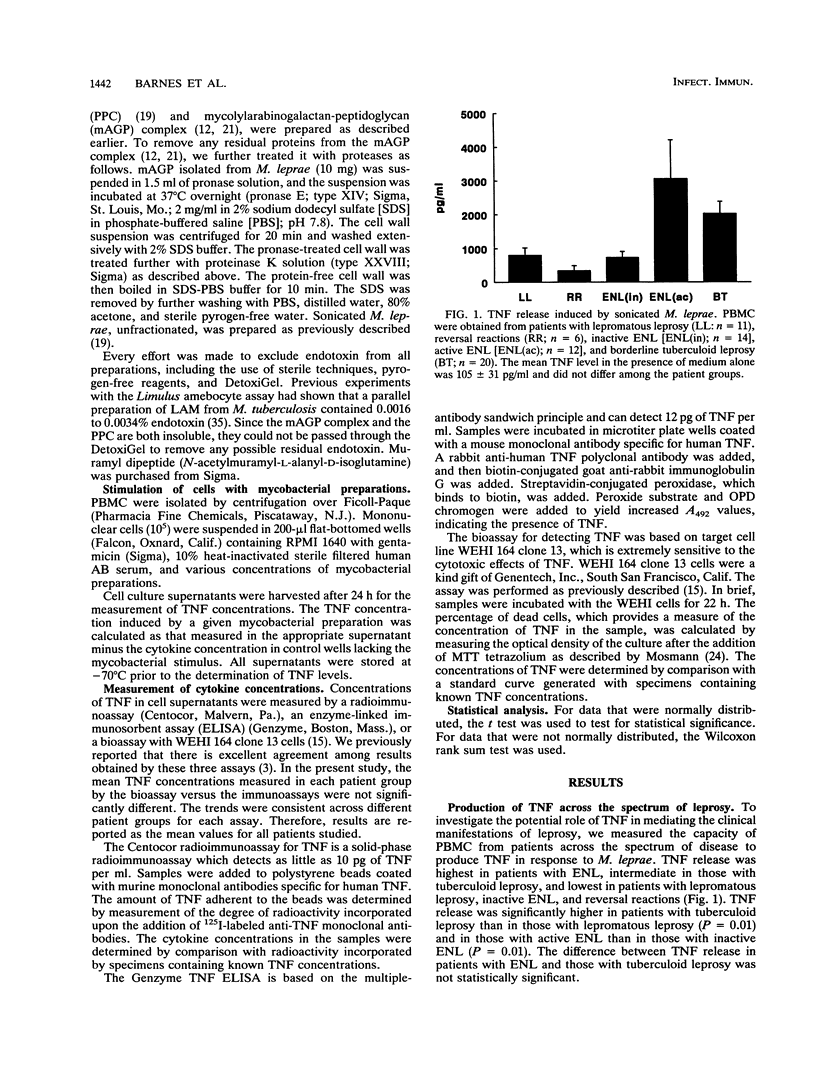
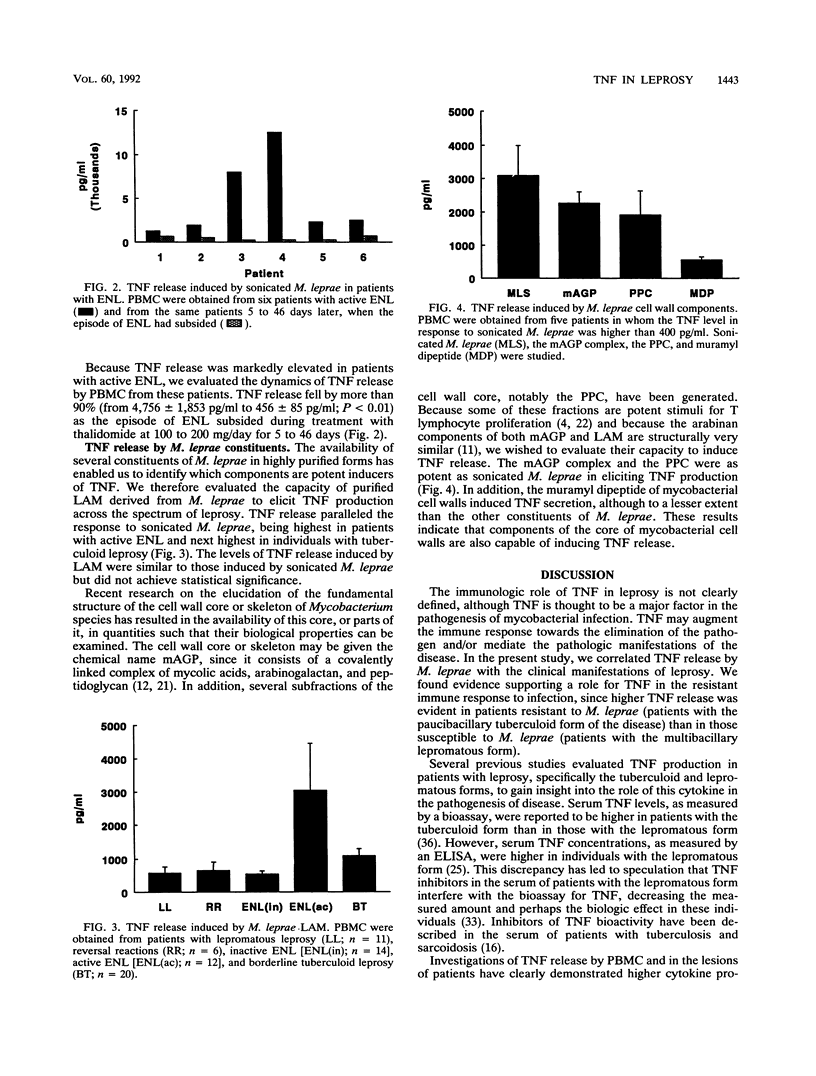
The spectrum of host responses to Mycobacterium leprae provides a model for investigating the role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of mycobacterial disease. Of particular interest is tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a cytokine which may have both antimycobacterial and immunopathologic effects. To evaluate the potential role of TNF in leprosy, we measured TNF production in response to M. leprae and its defined constituents by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients across the spectrum of disease. The levels of TNF induced through the stimulation of cells with M. leprae or its dominant "lipopolysaccharide," lipoarabinomannan, were higher in patients with the tuberculoid form of the disease than in those with the lepromatous form. In patients with erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL), a reactional state of lepromatous leprosy, the levels of TNF release by peripheral blood mononuclear cells were higher than in any other form of the disease. Treatment of ENL patients with thalidomide reduced TNF secretion by more than 90%. The mycolylarabinogalactan-peptidoglycan complex of Mycobacterium species, the protein-peptidoglycan complex, and muramyl dipeptide all elicited significant TNF release. Therefore, TNF release appears to be triggered by at least two major cell wall structural constituents of M. leprae, lipoarabinomannan and segments of the cell wall skeleton. The prominent TNF release in patients with the paucibacillary tuberculoid form of the disease compared with that in patients with the multibacillary lepromatous form suggests that this cytokine contributes to a resistant immune response to mycobacterial infection. However, the marked TNF release in patients with ENL indicates that TNF may also mediate immunopathologic effects, such as fever and tissue damage.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams L. B., Franzblau S. G., Vavrin Z., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Krahenbuhl J. L. L-arginine-dependent macrophage effector functions inhibit metabolic activity of Mycobacterium leprae. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1642–1646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnoldi J., Gerdes J., Flad H. D. Immunohistologic assessment of cytokine production of infiltrating cells in various forms of leprosy. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):749–753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Fong S. J., Brennan P. J., Twomey P. E., Mazumder A., Modlin R. L. Local production of tumor necrosis factor and IFN-gamma in tuberculous pleuritis. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Mehra V., Hirschfield G. R., Fong S. J., Abou-Zeid C., Rook G. A., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J., Modlin R. L. Characterization of T cell antigens associated with the cell wall protein-peptidoglycan complex of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2656–2662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnetson R. S., Bjune G., Pearson J. M., Kronvall G. Cell mediated and humoral immunity in "reversal reactions". Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1976 Jan-Jun;44(1-2):267–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorvatn B., Barnetson R. S., Kronvall G., Zubler R. H., Lambert P. H. Immune complexes and complement hypercatabolism in patients with leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Dec;26(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjune G., Barnetson R. S., Ridley D. S., Kronvall G. Lymphocyte transformation test in leprosy; correlation of the response with inflammation of lesions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):85–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D., Bozic C. M., McNeil M., Brennan P. J. Structural features of the arabinan component of the lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9652–9660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffe M., Brennan P. J., McNeil M. Predominant structural features of the cell wall arabinogalactan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as revealed through characterization of oligoglycosyl alditol fragments by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and by 1H and 13C NMR analyses. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6734–6743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Gutman R. A. Renal manifestations of leprosy: glomerulonephritis, a complication of erythema nodosum leprosum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1973 Jul;22(4):496–502. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1973.22.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley N., Lambert C., McNicol M., Johnson N., Rook G. A. An inhibitor of the toxicity of tumour necrosis factor in the serum of patients with sarcoidosis, tuberculosis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jun;80(3):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T., Myrvang B., Samuel D. R., Ross W. F., Lofgren M. Mechanism of "reactions" in borderline tuberculoid (BT) leprosy. A preliminary report. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1973;236(0):45–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Crawford R. M., Hockmeyer J. T., Meltzer M. S., Nacy C. A. Leishmania major amastigotes initiate the L-arginine-dependent killing mechanism in IFN-gamma-stimulated macrophages by induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4290–4297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., McNeil M., Modlin R. L., Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Brennan P. J. Isolation and characterization of the highly immunogenic cell wall-associated protein of Mycobacterium leprae. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2864–2872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil M., Daffe M., Brennan P. J. Evidence for the nature of the link between the arabinogalactan and peptidoglycan of mycobacterial cell walls. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18200–18206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Torigian V. K., Mandich D., Reichel M., Young S. M., Salgame P., Convit J., Hunter S. W., McNeil M. Characterization of Mycobacterium leprae cell wall-associated proteins with the use of T lymphocyte clones. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2873–2878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Taverne J., Mehlert A., Bate C. A., Brealey R. J., Meager A., Rook G. A., Playfair J. H. Lipoarabinomannan from Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces the production of tumour necrosis factor from human and murine macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):240–245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisa P., Gennene M., Söder O., Ottenhoff T., Hansson M., Kiessling R. Serum tumor necrosis factor levels and disease dissemination in leprosy and leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):988–991. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. H., Levan N. E. Variations in dinitrochlorobenzene responsivity in untreated leprosy: evidence of a beneficial role for anergy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1980 Jun;48(2):120–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. H., Taylor C. R. Serum and tissue lysozyme in leprosy. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):847–856. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.847-856.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S. Histological classification and the immunological spectrum of leprosy. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51(5):451–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S. Reactions in leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1969 Apr;40(2):77–81. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19690016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio E. P., Sarno E. N., Galilly R., Cohn Z. A., Kaplan G. Thalidomide selectively inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha production by stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):699–703. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarno E. N., Grau G. E., Vieira L. M., Nery J. A. Serum levels of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta during leprosy reactional states. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Apr;84(1):103–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K. W., Raine C. S. Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro. Ann Neurol. 1988 Apr;23(4):339–346. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Adams L. B., Krahenbuhl J. L. Inhibition of interferon-gamma-mediated activation in mouse macrophages treated with lipoarabinomannan. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Apr;80(1):141–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb06454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva C. L., Foss N. T. Tumor necrosis factor in leprosy patients. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):787–790. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stach J. L., Strobel M., Fumoux F., Bach J. F. Defect in the generation of cytotoxic T cells in lepromatous leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):633–640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan L., Sano S., Pirmez C., Salgame P., Mueller C., Hofman F., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Modlin R. L. Expression of adhesion molecules in leprosy lesions. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4154–4160. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4154-4160.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima T., Ueta C., Tsuyuguchi I., Kishimoto S. Production of tumor necrosis factor alpha by monocytes from patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3286–3292. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3286-3292.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson B. M., Mundy G. R., Chambers T. J. Tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta induce osteoblastic cells to stimulate osteoclastic bone resorption. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):775–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. S., Amir-Tahmasseb M., Ellner J. J. Induction of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor by mycobacterial proteins: the monocyte western blot. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3348–3352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. F., Turk J. L., Wemambu S. N. Mechanisms of reactions in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1971 Apr-Jun;39(2):417–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wemambu S. N., Turk J. L., Waters M. F., Rees R. J. Erythema nodosum leprosum: a clinical manifestation of the arthus phenomenon. Lancet. 1969 Nov 1;2(7627):933–935. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura M., Uyemura K., Deans R. J., Weinberg K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Modlin R. L. Defining protective responses to pathogens: cytokine profiles in leprosy lesions. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):277–279. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



