Abstract
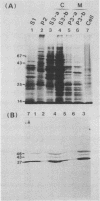
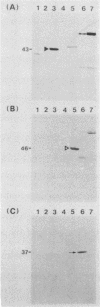
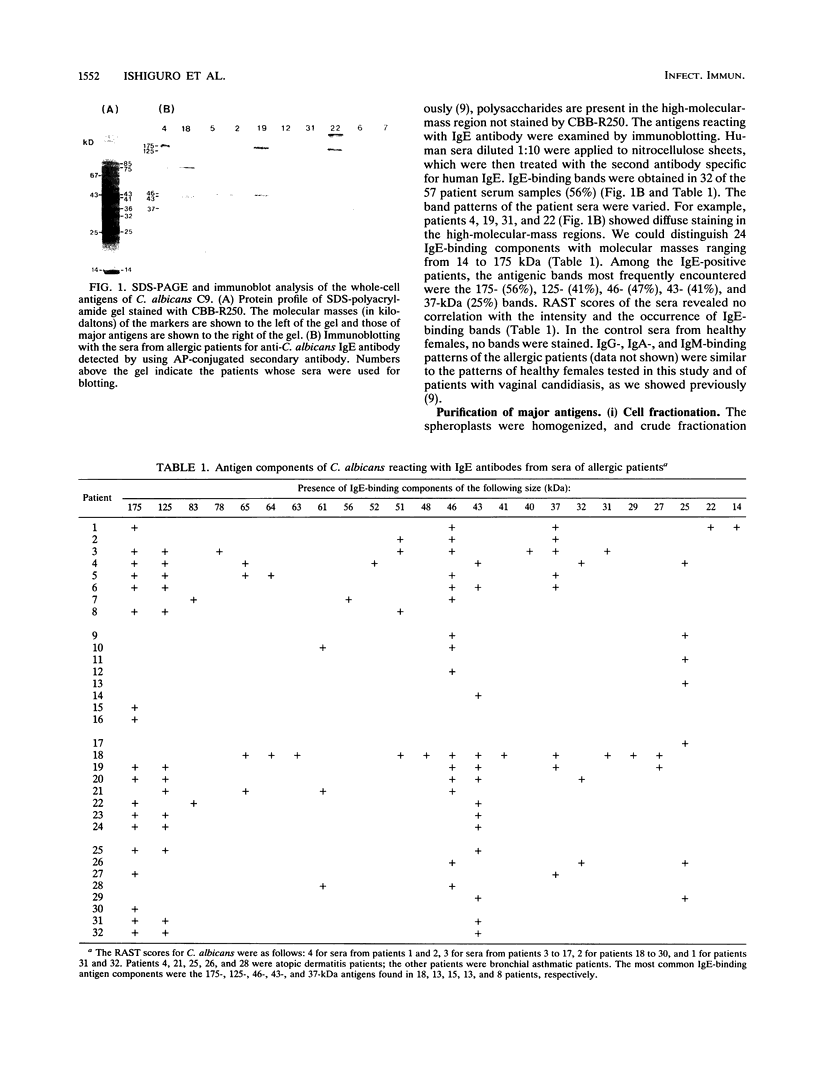
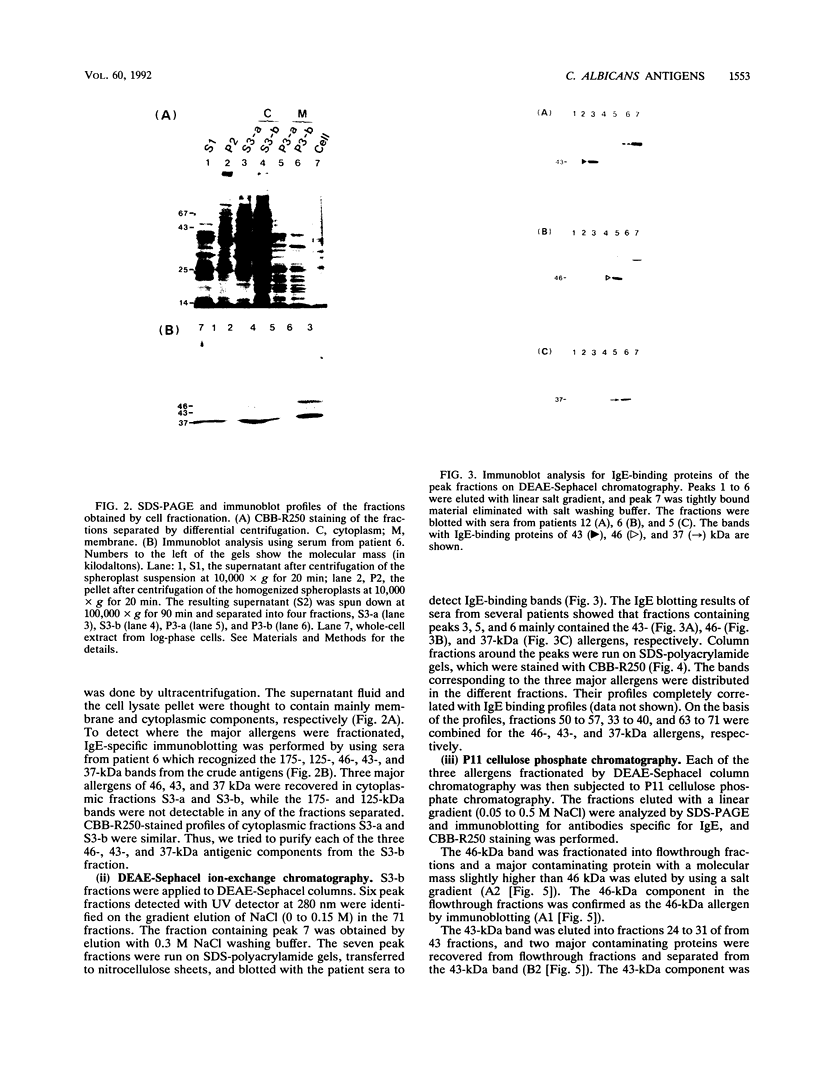
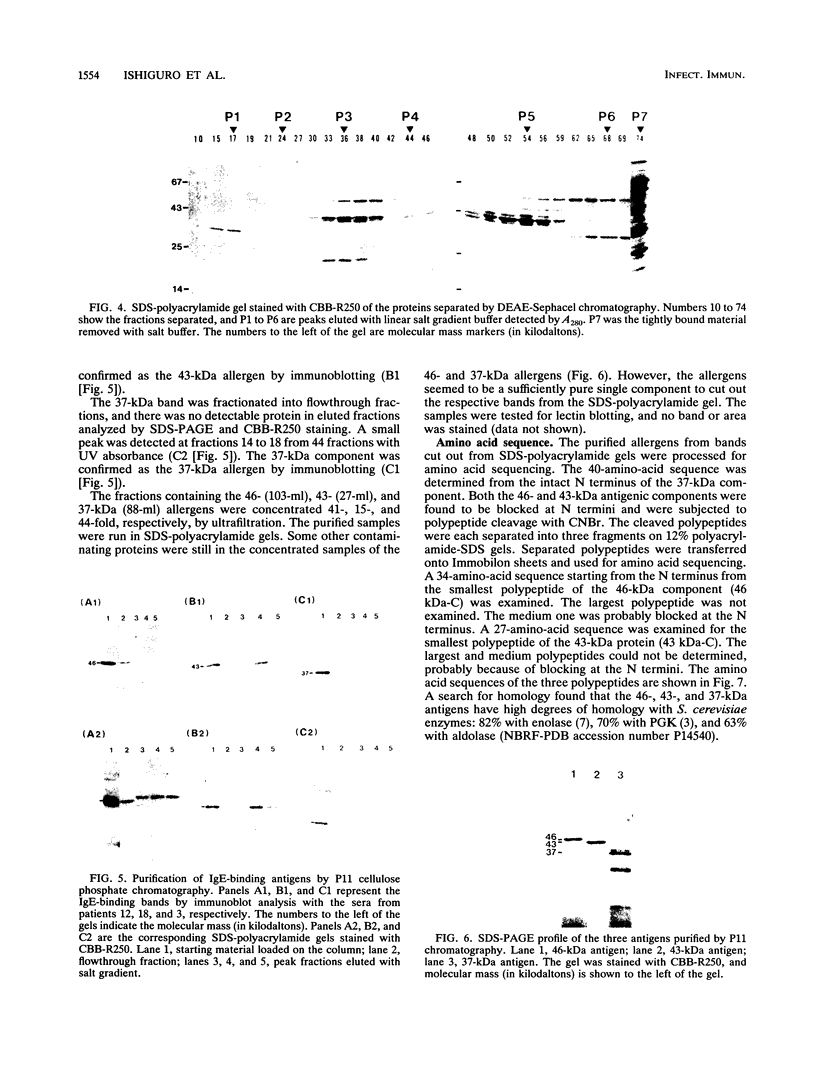
Candida albicans antigens which reacted with immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies of 57 allergic patients were detected by immunoblotting. Of the various antigens, the 175-, 125-, 46-, 43-, and 37-kDa antigenic components reacted most frequently with the patient sera. To purify the major antigens, C. albicans cells were fractionated. The 46-, 43-, and 37-kDa antigens were recovered in cytoplasmic fractions, but the 175- and 125-kDa antigens were not recovered in any fraction. The 46-, 43-, and 37-kDa antigens were purified from cytoplasmic fractions by DEAE and P11 ion-exchange chromatography. Antigens were isolated by cutting bands out of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. The purified components confirmed by immunoblotting were next processed for amino acid sequencing. Parts of the sequences of the 46-, 43-, and 37-kDa antigens had significant levels of homology with Saccharomyces cerevisiae glycolytic enzyme enolase, phosphoglycerate kinase, and aldolase, respectively. Rabbit IgG antibodies prepared against the 46- and 43-kDa antigens strongly cross-reacted with the homologous proteins of S. cerevisiae. However, S. cerevisiae enolase and phosphoglycerate kinase did not cross-react with IgE of patient sera. This result suggests that IgE antibodies against only small parts of their epitopes are elevated in the allergic patients. Since enolase is reported to be a major antigen for systemic candidiasis, this enzyme may be the immunodominant protein in both allergies and fungal infections.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashman R. B., Papadimitriou J. M., Ott A. K., Warmington J. R. Antigens and immune responses in Candida albicans infection. Immunol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;68(Pt 1):1–13. doi: 10.1038/icb.1990.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldo B. A., Baker R. S. Inhalant allergies to fungi: reactions to bakers' yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and identification of bakers' yeast enolase as an important allergen. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;86(2):201–208. doi: 10.1159/000234572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Roberts N. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Fothergill L. A. Conservation of high efficiency promoter sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2625–2637. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklyn K. M., Warmington J. R., Ott A. K., Ashman R. B. An immunodominant antigen of Candida albicans shows homology to the enzyme enolase. Immunol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;68(Pt 3):173–178. doi: 10.1038/icb.1990.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. A GTP-binding protein required for secretion rapidly associates with secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):753–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Holland J. P. Isolation and identification of yeast messenger ribonucleic acids coding for enolase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and phosphoglycerate kinase. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4900–4907. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Holland J. P., Thill G. P., Jackson K. A. The primary structures of two yeast enolase genes. Homology between the 5' noncoding flanking regions of yeast enolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1385–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Hershey J. W. A sensitive immunoblotting method for measuring protein synthesis initiation factor levels in lysates of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12836–12839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaguchi S., Homma M., Tanaka K. Variation in the electrophoretic karyotype analysed by the assignment of DNA probes in Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Dec;136(12):2433–2442. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-12-2433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Lehman D., Good C., Magee P. T. Genetic evidence for role of extracellular proteinase in virulence of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):571–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.571-575.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longbottom J. L., Brighton W. D., Edge G., Pepys J. Antibodies mediating type I skin test reactions to polysaccharide and protein antigens of Candida albicans. Clin Allergy. 1976 Jan;6(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning-Zweerink M., Maloney C. S., Mitchell T. G., Weston H. Immunoblot analyses of Candida albicans-associated antigens and antibodies in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.46-52.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. B., Brandt M. E., Buckley H. R. Enolase activity associated with a C. albicans cytoplasmic antigen. Yeast. 1989 Apr;5(Spec No):S231–S239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. C., Burnie J. P., Tabaqchali S. Immunoblot analysis of the serological response in systemic candidosis. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1415–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91618-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. C., Burnie J. P., Tabaqchali S. Isolation of immunodominant antigens from sera of patients with systemic candidiasis and characterization of serological response to Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):230–237. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.230-237.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul T. R., Smith S. N., Brown M. R. Effect of iron depletion on cell-wall antigens of Candida albicans. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Feb;28(2):93–100. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-2-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savolainen J., Viander M., Einarsson R., Koivikko A. Immunoblotting analysis of concanavalin A-isolated allergens of Candida albicans. Allergy. 1990 Jan;45(1):40–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1990.tb01082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savolainen J., Viander M., Koivikko A. Distribution of watersoluble antigens and allergens of Candida albicans in blastospore cell extract fractions. Allergy. 1990 Jan;45(1):47–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1990.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savolainen J., Viander M., Koivikko A. IgE-, IgA- and IgG-antibody responses to carbohydrate and protein antigens of Candida albicans in asthmatic children. Allergy. 1990 Jan;45(1):54–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1990.tb01084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen H. D., Choo K. B., Tang R. B., Lee C. F., Yeh J. Y., Han S. H. Allergenic components of Candida albicans identified by immunoblot analysis. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989 Mar;19(2):191–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1989.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Largen M. T., Zweibel S. M., Buckley H. R. Identification and molecular weight characterization of antigens from Candida albicans that are recognized by human sera. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):715–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.715-721.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Hathorn J. W., Sobel J. D., Merz W. G., Sanchez V., Maret S. M., Buckley H. R., Pfaller M. A., Schaufele R., Sliva C. Detection of circulating candida enolase by immunoassay in patients with cancer and invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 11;324(15):1026–1031. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104113241504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]