Abstract
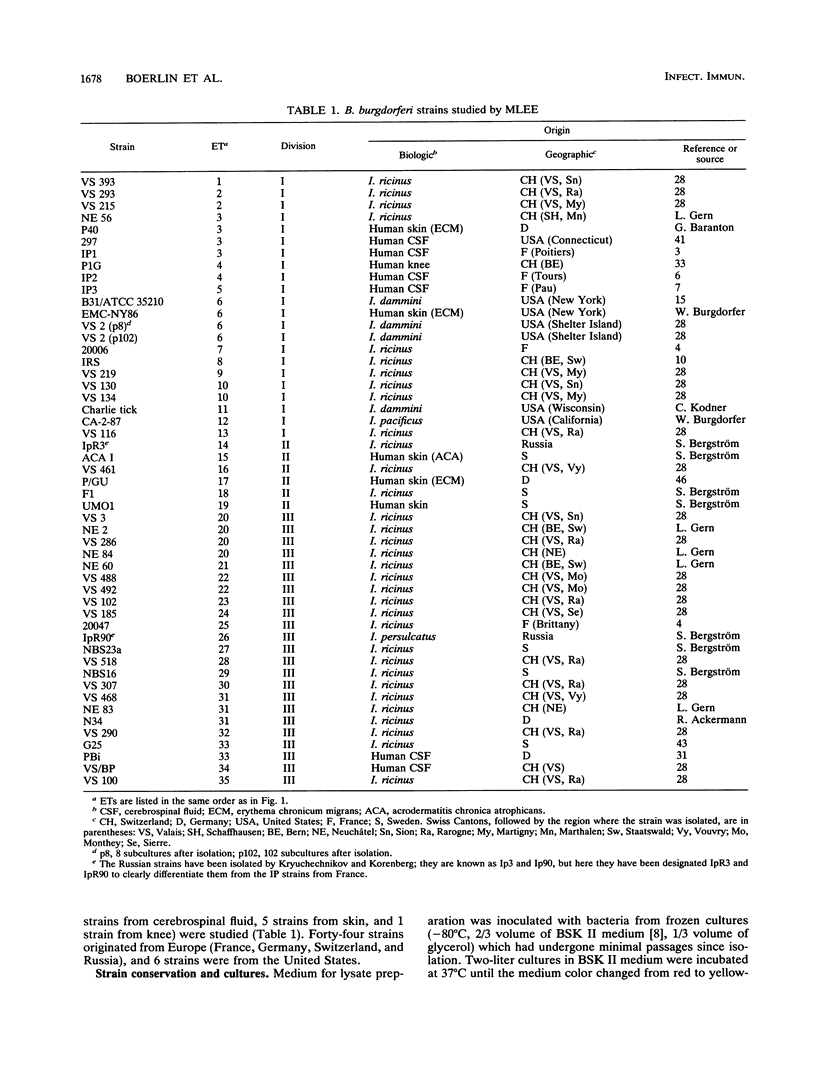
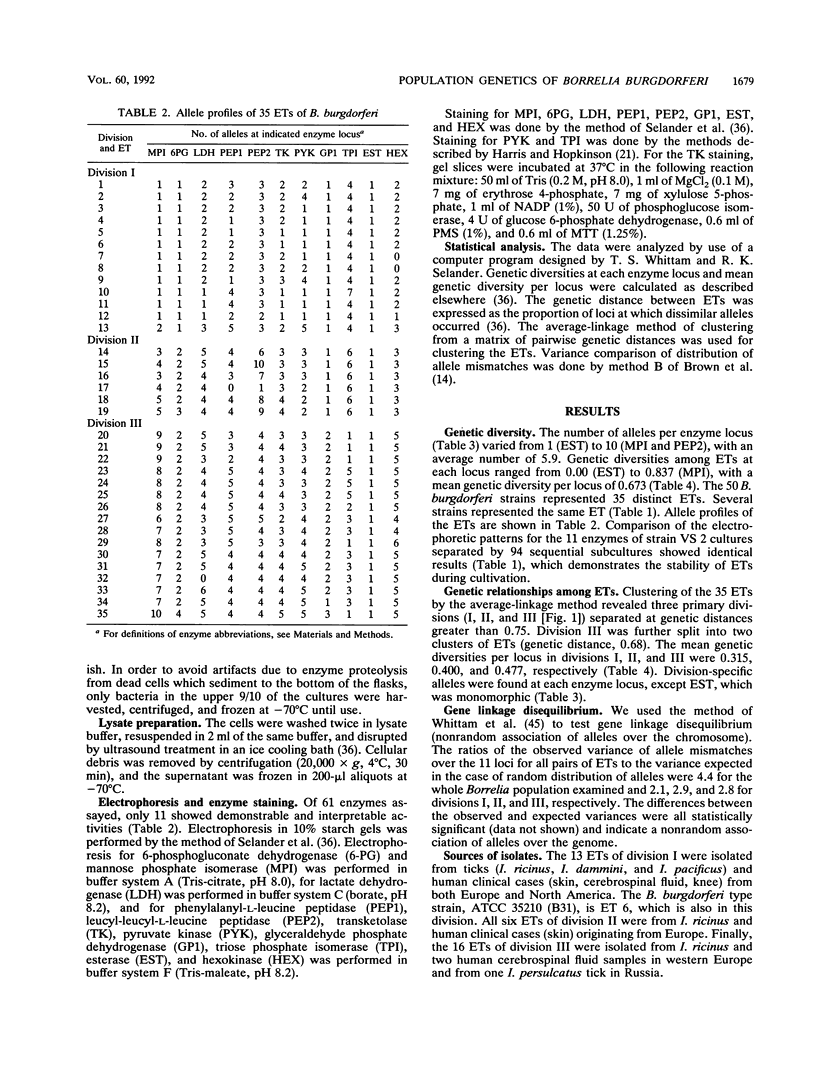
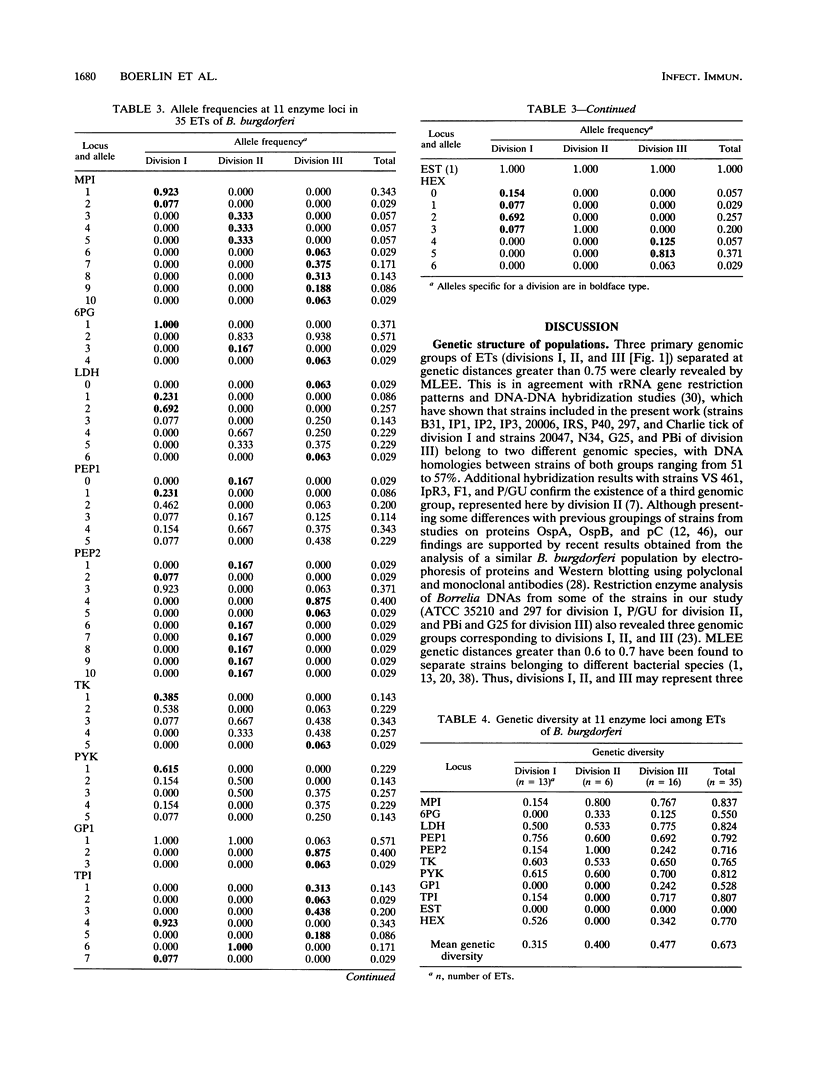
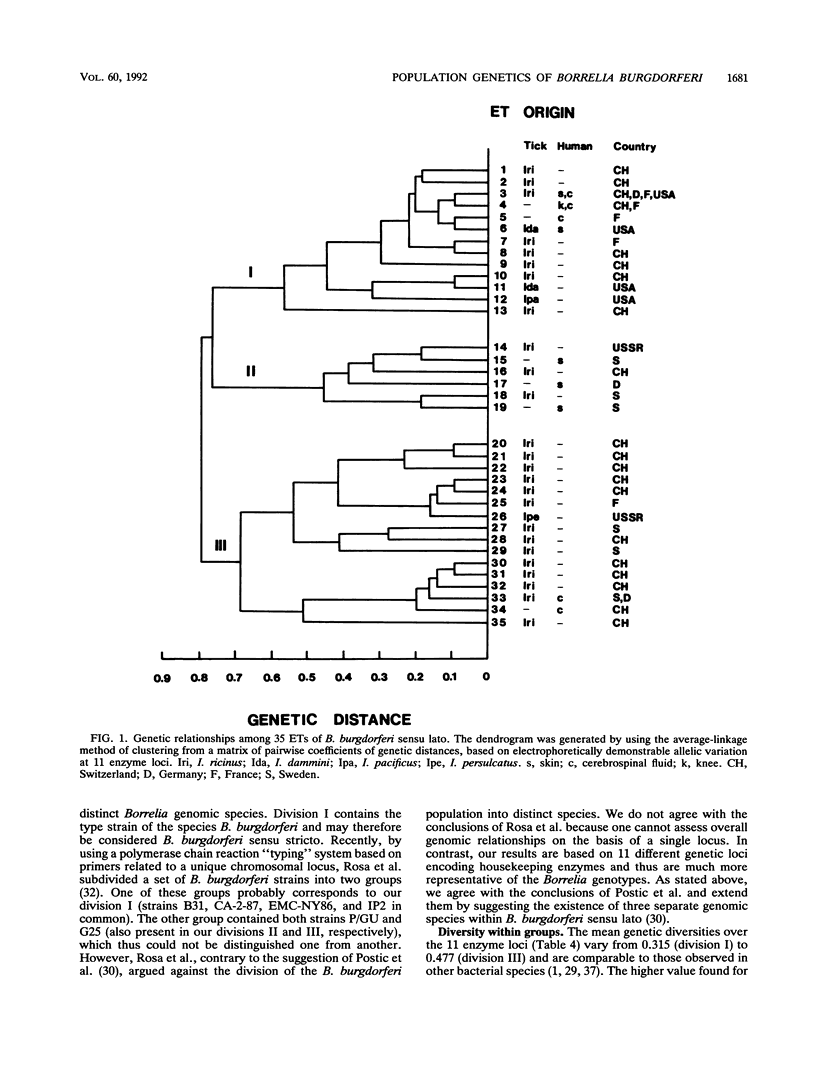
Fifty Borellia burgdorferi strains isolated from humans and ticks in Europe and the United States were analyzed by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Eleven genetic loci were characterized on the basis of the electrophoretic mobilities of their products. Ten loci were polymorphic. The average number of alleles per locus was 5.9, with a mean genetic diversity of 0.673 among electrophoretic types (ETs). The strains were grouped into 35 ETs constituting three main divisions (I, II, and III) separated at a genetic distance greater than 0.75. Divisions I, II, and III contained 13, 6, and 16 ETs, respectively. These findings, together with previous data from DNA hybridization and restriction enzyme analysis of rRNA genes, suggest that divisions I, II, and III may represent three distinct genomic species. All three divisions contained human clinical ETs. However, in division I, which includes the ET of the type strain of B. burgdorferi, the human pathogenic ETs constituted a single clone. The ETs of division I were from west-central Europe and the United States, whereas divisions II and III contained ETs from west-central and northern Europe but not from the United States. Finally, our data show that the genetic structure of B. burgdorferi populations is clonal.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aeschbacher M., Piffaretti J. C. Population genetics of human and animal enteric Campylobacter strains. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1432–1437. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1432-1437.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranton G., Perolat P., Dufresne Y., Postic D., Quentin R., Fouquet B. Isolement de Borrelia burgdorferi du liquide céphalorachidien d'un malade traité par la pénicilline. Presse Med. 1989 Mar 25;18(12):637–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Schrumpf M. E. Polymorphisms of major surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerlin P., Rocourt J., Piffaretti J. C. Taxonomy of the genus Listeria by using multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;41(1):59–64. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. H., Feldman M. W., Nevo E. Multilocus Structure of Natural Populations of HORDEUM SPONTANEUM. Genetics. 1980 Oct;96(2):523–536. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Péter O., Aeschlimann A. Erythema chronicum migrans--a tickborne spirochetosis. Acta Trop. 1983 Mar;40(1):79–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Lane R. S., Barbour A. G., Gresbrink R. A., Anderson J. R. The western black-legged tick, Ixodes pacificus: a vector of Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Sep;34(5):925–930. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekonenko E. J., Steere A. C., Berardi V. P., Kravchuk L. N. Lyme borreliosis in the Soviet Union: a cooperative US-USSR report. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):748–753. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S., Kilian M., Selander R. K. Genetic relationships among the oral streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5247–5257. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5247-5257.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B., Perng G. C., Johnson R. C. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):636–639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.636-639.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. F., Wilson M. L., Spielman A. Mice as reservoirs of the Lyme disease spirochete. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Mar;34(2):355–360. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Schlievert P. M., Chow A. W., Ewan P., Kreiswirth B. N., Rosdahl V. T., Naidu A. S., Witte W., Selander R. K. A single clone of Staphylococcus aureus causes the majority of cases of toxic shock syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piffaretti J. C., Kressebuch H., Aeschbacher M., Bille J., Bannerman E., Musser J. M., Selander R. K., Rocourt J. Genetic characterization of clones of the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postic D., Edlinger C., Richaud C., Grimont F., Dufresne Y., Perolat P., Baranton G., Grimont P. A. Two genomic species in Borrelia burgdorferi. Res Microbiol. 1990 May;141(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Schierz G. European Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from humans and ticks culture conditions and antibiotic susceptibility. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):112–118. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Hogan D., Schwan T. G. Polymerase chain reaction analyses identify two distinct classes of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):524–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.524-532.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidli J., Hunziker T., Moesli P., Schaad U. B. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from joint fluid three months after treatment of facial palsy due to Lyme borreliosis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):905–906. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Levin B. R. Genetic diversity and structure in Escherichia coli populations. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6999623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiernstedt G. Tick-borne Borrelia infection in Sweden. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1985;45:1–70. doi: 10.3109/inf.1985.17.suppl-45.01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod A. R., Johnson R. C. Lyme disease and migrating birds in the Saint Croix River Valley. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):1921–1924. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1921-1924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Ochman H., Selander R. K. Multilocus genetic structure in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


