Abstract
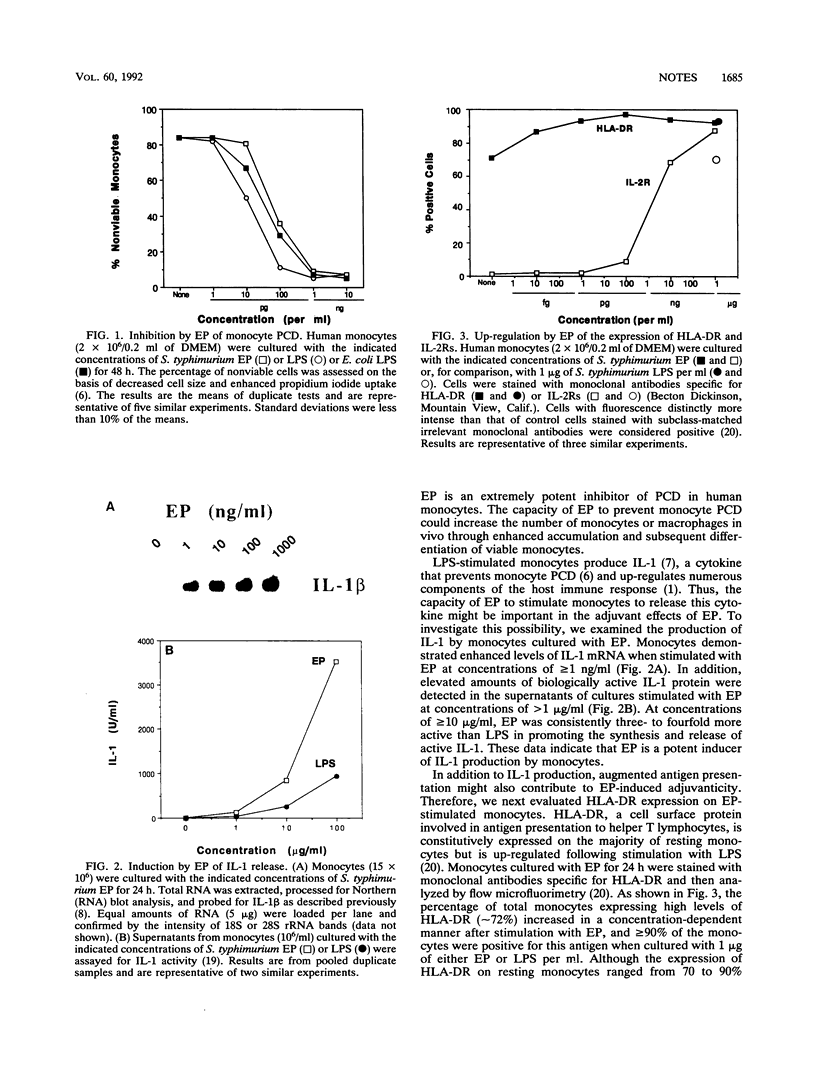
Mononuclear phagocytes are essential for adjuvant activity and polyclonal immunoglobulin synthesis induced by endotoxin-associated protein (EP) from Salmonella spp. To define the mechanisms of EP-mediated immunostimulation, we evaluated monocyte functions central to adjuvanticity following exposure to Salmonella typhimurium EP. In this study, we show that EP promotes the survival of monocytes by blocking programmed cell death (apoptosis), enhancing the production of the immunostimulatory cytokine interleukin-1 (IL-1) and stimulating the increased expression of HLA-DR and IL-2 receptors, which are cell membrane proteins that facilitate antigen presentation and IL-2 regulation, respectively. These results indicate that, like lipopolysaccharide, EP is a potent activator of human monocytes and suggest that EP-induced immunostimulation may be mediated, in part, by enhanced monocyte survival, cytokine release, and receptor expression.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K. I., Lee F., Miyajima A., Miyatake S., Arai N., Yokota T. Cytokines: coordinators of immune and inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe W. F., Yang S. T., Morrison D. C., Betz S. J., Henson P. M. Macrophage stimulation by bacterial lipopolysaccharides. II. Evidence for differentiation signals delivered by lipid A and by a protein rich fraction of lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):557–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman G. W., Sultzer B. M. Characterization of the chemical and physical properties of a novel B-lymphocyte activator, endotoxin protein. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):685–696. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.685-696.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman G. W., Sultzer B. M. Endotoxin protein is a mitogen and polyclonal activator of human B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):713–723. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman G. W., Sultzer B. M. Further studies on the activation of lymphocytes by endotoxin protein. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1329–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Welch G. R., Wahl S. M. Lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and IL-1 beta prevent programmed cell death (apoptosis) in human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1541–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCartney-Francis N., Mizel D., Wong H., Wahl L., Wahl S. TGF-beta regulates production of growth factors and TGF-beta by human peripheral blood monocytes. Growth Factors. 1990;4(1):27–35. doi: 10.3109/08977199009011007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Farrar J. J., Michalek S. M., Mergenhagen S. E., Rosenstreich D. L. Cellular requirements for lipopolysaccharide adjuvanticity. A role for both T lymphocytes and macrophages for in vitro responses to particulate antigens. J Exp Med. 1979 Apr 1;149(4):793–807. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staber F. G., Habild W. F., Morrison D. C., Tarcsay L. Hemopoietic effects in mice of a lipid A-associated protein. Exp Hematol. 1981 Mar;9(3):264–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Castagna R. The activation of C3H/HeJ cells by certain types of lipopolysaccharides. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;256:149–157. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-5140-6_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Craig J. P., Castagna R. The adjuvant effect of pertussis endotoxin protein in modulating the immune response to cholera toxoid in mice. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;61:225–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Goodman G. W. Endotoxin protein: a B-cell mitogen and polyclonal activator of C3H/HeJ lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):821–827. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang J. C., Wang C. S., Alaupovic P. Degradative effect of phenol on endotoxin and lipopolysaccharide preparations from Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):786–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.786-795.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Wong H. L., Dougherty S., McCartney-Francis N., Wahl L. M., Ellingsworth L., Schmidt J. A., Hall G., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor-beta is a potent immunosuppressive agent that inhibits IL-1-dependent lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3026–3032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., McCartney-Francis N., Hunt D. A., Smith P. D., Wahl L. M., Katona I. M. Monocyte interleukin 2 receptor gene expression and interleukin 2 augmentation of microbicidal activity. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1342–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wober W., Alaupović P. Studies on the protein moiety of endotoxin from gram-negative bacteria. Characterization of the protein moiety isolated by phenol treatment of endotoxin from Serratia marcescens 08 and Escherichia coli 0 141:K85(B). Eur J Biochem. 1971 Apr;19(3):340–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]