Abstract
Injection of type 6b pneumococci into pigs results in a sharp rise in levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in blood, with an average peak value of 7,700 U/ml at 4 h and mortality in five of seven of these animals. Pretreatment at -24 h with the monocyte activator MTP-PE prevents this strong increase in IL-6 (peak value, 1,000 U/ml) and reduces mortality to zero of six animals. This suggests that MTP-PE, in addition to activating monocytes, protects animals by preventing the harmful increase of cytokines such as IL-6.
Full text
PDF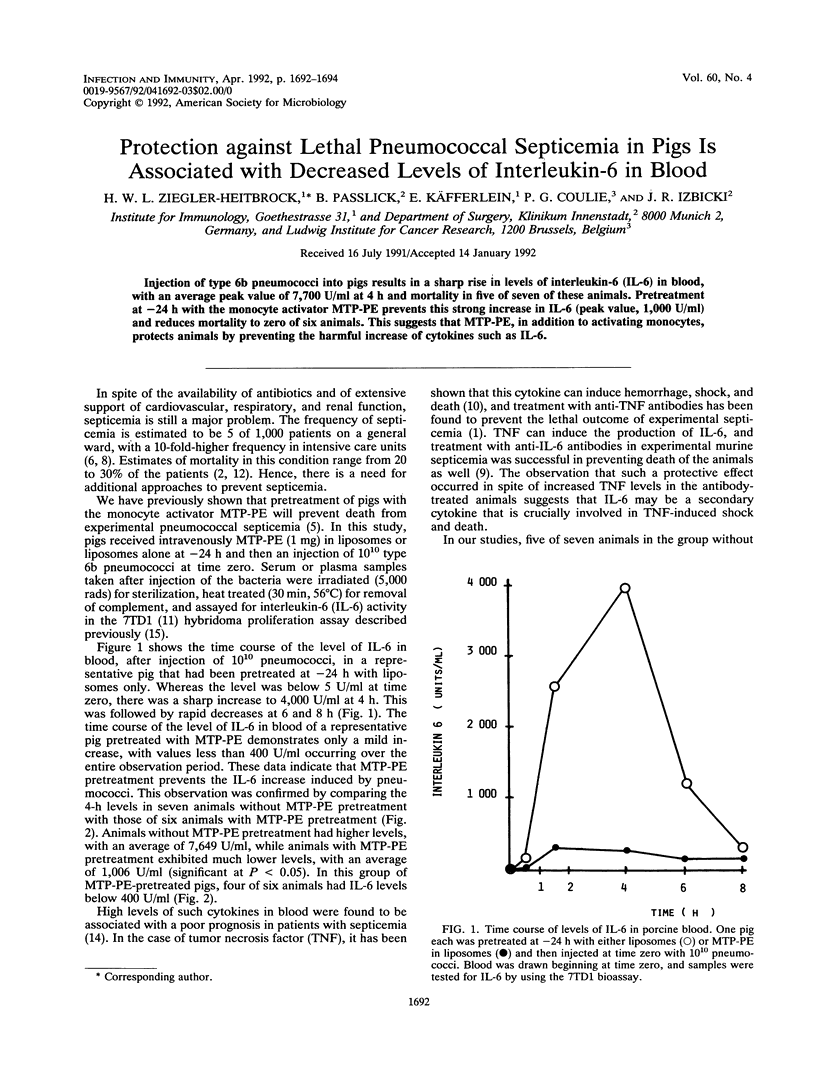
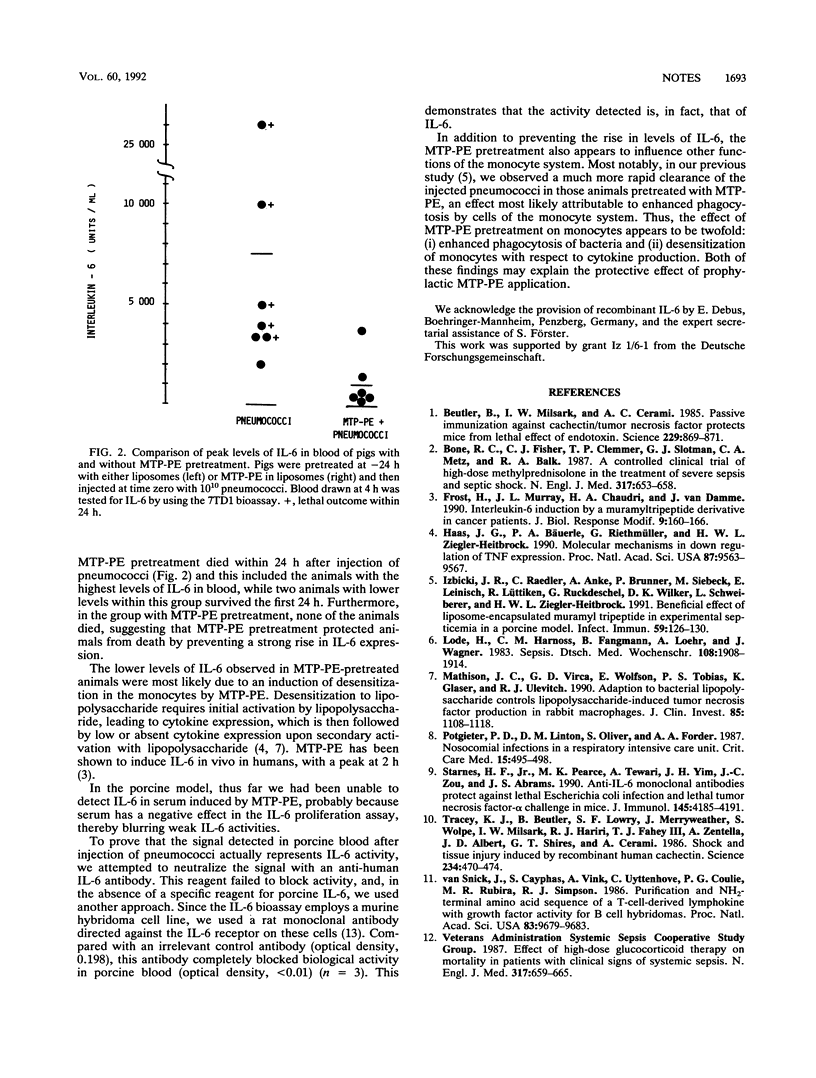

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Fisher C. J., Jr, Clemmer T. P., Slotman G. J., Metz C. A., Balk R. A. A controlled clinical trial of high-dose methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):653–658. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost H., Murray J. L., Chaudri H. A., Van Damme J. Interleukin-6 induction by a muramyltripeptide derivative in cancer patients. J Biol Response Mod. 1990 Apr;9(2):160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas J. G., Baeuerle P. A., Riethmüller G., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W. Molecular mechanisms in down-regulation of tumor necrosis factor expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9563–9567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izbicki J. R., Raedler C., Anke A., Brunner P., Siebeck M., Leinisch E., Lüttiken R., Ruckdeschel G., Wilker D. K., Schweiberer L. Beneficial effect of liposome-encapsulated muramyl tripeptide in experimental septicemia in a porcine model. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):126–130. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.126-130.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H., Harnoss C. M., Fangmann B., Loehr A., Wagner J. Sepsis. Aetiologie, Epidemiologie, Klinik und Prognose bei 446 Patienten. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1983 Dec 16;108(50):1908–1914. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1069849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Virca G. D., Wolfson E., Tobias P. S., Glaser K., Ulevitch R. J. Adaptation to bacterial lipopolysaccharide controls lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in rabbit macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1108–1118. doi: 10.1172/JCI114542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potgieter P. D., Linton D. M., Oliver S., Forder A. A. Nosocomial infections in a respiratory intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 1987 May;15(5):495–498. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198705000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes H. F., Jr, Pearce M. K., Tewari A., Yim J. H., Zou J. C., Abrams J. S. Anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies protect against lethal Escherichia coli infection and lethal tumor necrosis factor-alpha challenge in mice. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Coulie P. G., Rubira M. R., Simpson R. J. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a T-cell-derived lymphokine with growth factor activity for B-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9679–9683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink A., Coulie P., Warnier G., Renauld J. C., Stevens M., Donckers D., Van Snick J. Mouse plasmacytoma growth in vivo: enhancement by interleukin 6 (IL-6) and inhibition by antibodies directed against IL-6 or its receptor. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):997–1000. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Ströbel M., Kieper D., Fingerle G., Schlunck T., Petersmann I., Ellwart J., Blumenstein M., Haas J. G. Differential expression of cytokines in human blood monocyte subpopulations. Blood. 1992 Jan 15;79(2):503–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


