Abstract
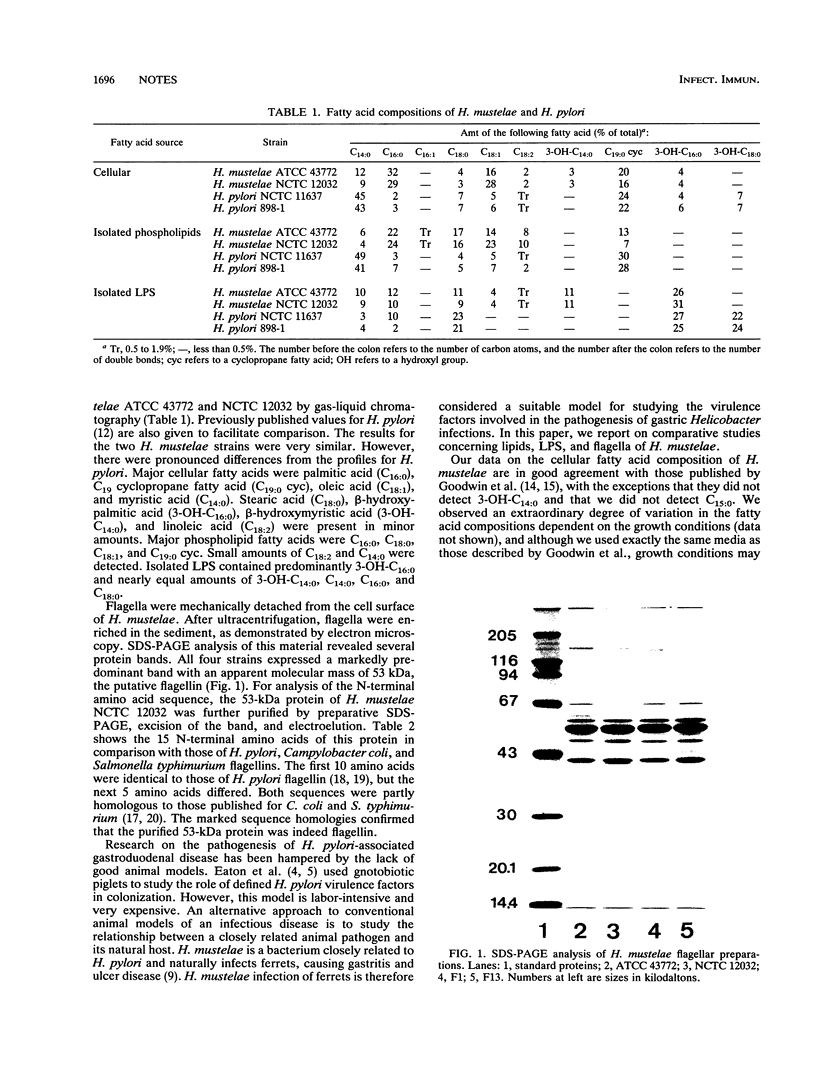
The fatty acid compositions of Helicobacter mustelae whole cells, isolated phospholipids, and isolated lipopolysaccharides were analyzed by gas-liquid chromatography. Major phospholipid fatty acids were C16:0, C18:0, C18:1, and C19:0 cyc. In isolated lipopolysaccharides, 3-OH-C16:0, 3-OH-C14:0, C14:0, C16:0, and C18:0 were found. The lipid composition of H. mustelae thus showed pronounced differences from that of H. pylori. Flagella were purified by mechanical shearing and centrifugation steps. In all H. mustelae strains, the flagellin had an apparent molecular mass of 53 kDa and was thus the same size as H. pylori flagellin. The flagellin of strain NCTC 12032 was further purified and subjected to N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis. The first 10 amino acids were identical to those of H. pylori flagellin, but the next 5 were different. Significant homology was also found with flagellins of other bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dick J. D. Helicobacter (Campylobacter) pylori: a new twist to an old disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:249–269. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Brooks C. L., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Essential role of urease in pathogenesis of gastritis induced by Helicobacter pylori in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2470-2475.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Campylobacter pylori virulence factors in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1119–1125. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1119-1125.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Cabot E. B., Taylor N. S., Laraway R. Gastric colonization by Campylobacter pylori subsp. mustelae in ferrets. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2994–2996. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2994-2996.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Correa P., Taylor N. S., Lee A., Otto G., Murphy J. C., Rose R. Helicobacter mustelae-associated gastritis in ferrets. An animal model of Helicobacter pylori gastritis in humans. Gastroenterology. 1990 Aug;99(2):352–361. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91016-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Otto G., Taylor N. S., Rosenblad W., Murphy J. C. Helicobacter mustelae-induced gastritis and elevated gastric pH in the ferret (Mustela putorius furo). Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1875–1880. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1875-1880.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geis G., Leying H., Suerbaum S., Mai U., Opferkuch W. Ultrastructure and chemical analysis of Campylobacter pylori flagella. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):436–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.436-441.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geis G., Leying H., Suerbaum S., Opferkuch W. Unusual fatty acid substitution in lipids and lipopolysaccharides of Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):930–932. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.930-932.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Martin H. H. Phospholipid and lipopolysaccharide in Proteus mirabilis and its stable protoplast L-form. Difference in content and fatty acid composition. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 16;67(2):487–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., McConnell W., McCulloch R. K., McCullough C., Hill R., Bronsdon M. A., Kasper G. Cellular fatty acid composition of Campylobacter pylori from primates and ferrets compared with those of other campylobacters. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):938–943. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.938-943.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The covalent structure of the phase-1 flagellar filament protein of Salmonella typhimurium and its comparison with other flagellins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostrzynska M., Betts J. D., Austin J. W., Trust T. J. Identification, characterization, and spatial localization of two flagellin species in Helicobacter pylori flagella. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):937–946. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.937-946.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Harris L. A., Trust T. J. Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter flagellins. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5072–5077. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5072-5077.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. R., Fox J. G., Leunk R. D. Comparison of isolates of Helicobacter pylori and Helicobacter mustelae. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):395–397. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.395-397.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C. Bacterial endotoxins and pathogenesis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S733–S747. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto G., Fox J. G., Wu P. Y., Taylor N. S. Eradication of Helicobacter mustelae from the ferret stomach: an animal model of Helicobacter (Campylobacter) pylori chemotherapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1232–1236. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson W. L. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 11;324(15):1043–1048. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104113241507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda S., Miwatani T., Fujino T. Antigens of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. II. Existence of two different subunits in the flagella of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and their characterization. Biken J. 1970 Dec;13(4):241–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekmann J., Wenzel H. R., Schröder W., Tschesche H. Characterization and sequence determination of six aprotinin homologues from bovine lungs. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 Mar;369(3):157–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



