Abstract
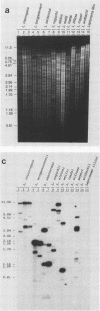
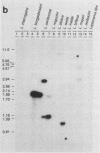
The presence of multiple DNA elements in pathogenic members of the family Leptospiraceae, similar to the sphA sphingomyelinase gene from Leptospira borgpetersenii, was demonstrated by low-stringency hybridization experiments. These DNA elements were designated putative sphingomyelinase genes. Grouping of strains by similarity of hybridization patterns corresponds to the species subdivision of the family Leptospiraceae on the basis of genetic characteristics. Therefore, hybridization with the sphA gene can be used as a taxonomic tool. These hybridization experiments indicate the presence of two groups of genetically related pathogenic Leptospira species.
Full text
PDF
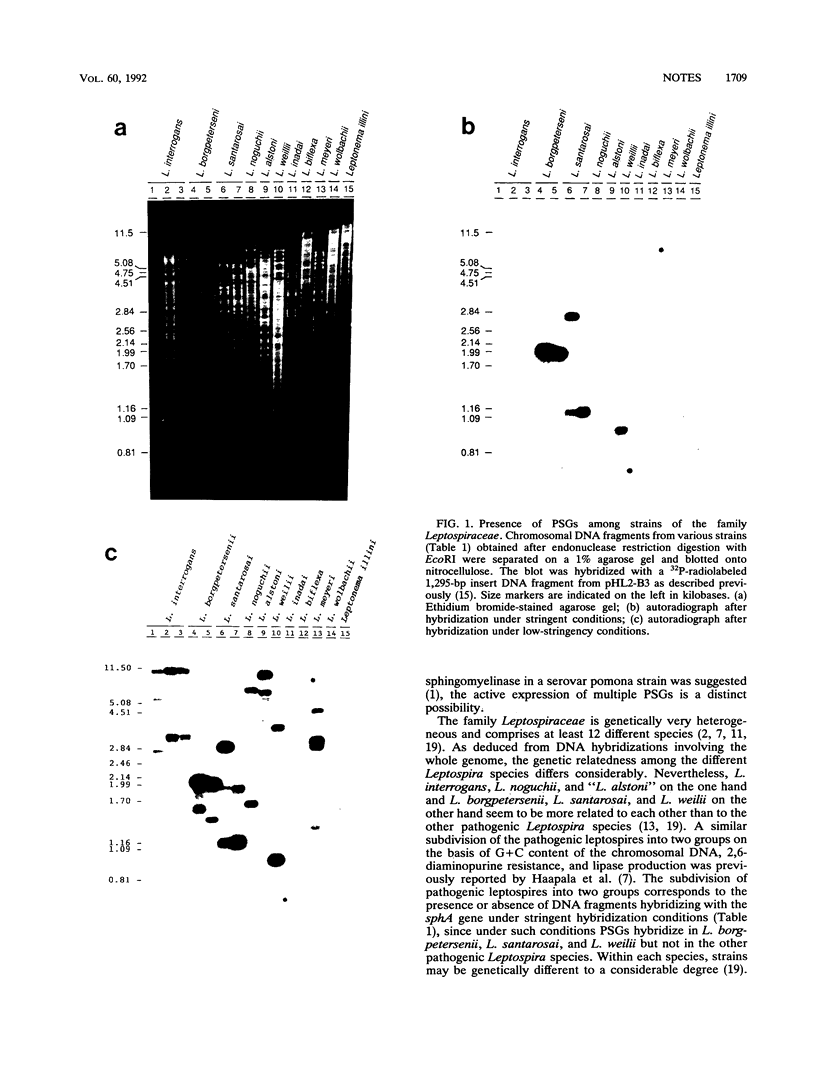

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheimer A. W., Bey R. F. Copurification of Leptospira interrogans serovar pomona hemolysin and sphingomyelinase C. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):262–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.262-264.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dain A. A., Rozinov M. N., Gol'tsmaier T. A., Gershanovich V. N., Chernukha Iu G. Klonirovanie i ékspressiia gena gemolizina Leptospira pomona pomona v Escherichia coli. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1985 Jul;(7):7–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diesch S. L., McCulloch W. F., Braun J. L., Ellinghausen H. C., Jr Leptospires isolated from frog kidneys. Nature. 1966 Feb 26;209(5026):939–940. doi: 10.1038/209939a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Mifuchi I., Yanagihara Y. Cloning of genes for a hemolytic factor of Leptospira interrogans serovar autumnalis strain Congo 21-543. Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34(10):879–883. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1990.tb01066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapala D. K., Rogul M., Evans L. B., Alexander A. D. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition and homology studies of Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):421–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.421-428.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B., Thiermann A. B., Foley J. Genetic and antigenic differences of serologically indistinguishable leptospires of serovar hardjo. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2094–2097. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2094-2097.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paster B. J., Dewhirst F. E., Weisburg W. G., Tordoff L. A., Fraser G. J., Hespell R. B., Stanton T. B., Zablen L., Mandelco L., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6101–6109. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6101-6109.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérolat P., Grimont F., Regnault B., Grimont P. A., Fournié E., Thevenet H., Baranton G. rRNA gene restriction patterns of Leptospira: a molecular typing system. Res Microbiol. 1990 Feb;141(2):159–171. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90025-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadass P., Jarvis B. D., Corner R. J., Cinco M., Marshall R. B. DNA relatedness among strains of Leptospira biflexa. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;40(3):231–235. doi: 10.1099/00207713-40-3-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P., Steere A. C., Kornblatt A. N., Kaufmann A. F., Moss C. W., Johnson R. C., Hovind-Hougen K., Brenner D. J. Newly recognized Leptospira species ("Leptospira inadai" serovar lyme) isolated from human skin. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):484–486. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.484-486.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segers R. P., van der Drift A., de Nijs A., Corcione P., van der Zeijst B. A., Gaastra W. Molecular analysis of a sphingomyelinase C gene from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2177–2185. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2177-2185.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Gerritsen M. J., Korver H., Schoone G. J., Kroon C. C., Terpstra W. J. Characterization of serovars of the genus Leptospira by DNA hybridization with hardjobovis and icterohaemorrhagiae recombinant probes with special attention to serogroup sejroe. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):1042–1048. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.1042-1048.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Zaal J., Schoone G. J., Terpstra W. J. DNA hybridization with hardjobovis-specific recombinant probes as a method for type discrimination of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):567–574. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-3-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Bolin C. A. Nucleic acid probe characterizes Leptospira interrogans serovars by restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Sep;24(3-4):355–366. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90183-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Bolin C. A. Repetitive sequence element cloned from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo type hardjo-bovis provides a sensitive diagnostic probe for bovine leptospirosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2495–2500. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2495-2500.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Real G., Segers R. P., van der Zeijst B. A., Gaastra W. Cloning of a hemolysin gene from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2588–2590. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2588-2590.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]