Abstract
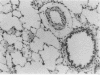
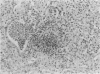
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an important nosocomial pathogen causing severe pulmonary infections. The majority of clinical Klebsiella isolates produce a high-molecular-weight capsular polysaccharide (CPS) which is one of the dominant virulence factors. In the present study, we examined the potency of a murine immunoglobulin M monoclonal antibody (MAb) with specificity to Klebsiella type 2 CPS to protect rats against experimental Klebsiella pneumonia. The MAb did not prevent the invasion of virulent bacteria into the interalveolar space. However, the resolution of infection was accelerated in MAb-treated animals. This was demonstrated by (i) less severe weight loss and (ii) markedly reduced inflammatory reactions in the lung. The elimination of bacteria was significantly increased not only in the lungs but also in the livers of antibody-treated rats. This was reflected by reduced levels of circulating, soluble CPS and MAb-bound CPS. A mixture of human MAbs with specificity to CPS of clinically important Klebsiella serotypes may prove to be a useful tool for the prevention or supportive treatment of Klebsiella pneumonia.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAER H., EHRENWORTH L. The pathogenicity of Klebsiella pneumoniae for mice: the relationship to the quantity and rate of production of type-specific capsular polysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):713–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.713-717.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATSHON B. A., BAER H., SHAFFER M. F. Immunologic paralysis produced in mice by Klebsiella pneumoniae type 2 polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1963 Jan;90:121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., O'Keefe P., Tally F. P., Louie T. J., Gorbach S. L. Bacteriology of hospital-acquired pneumonia. Arch Intern Med. 1986 May;146(5):868–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Forman C., Horowitz J. C., Volanakis J. E., Benjamin W. H., Jr, McDaniel L. S., Eldridge J., Brooks J. Antipneumococcal effects of C-reactive protein and monoclonal antibodies to pneumococcal cell wall and capsular antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1457–1464. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1457-1464.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun-Buisson C., Legrand P., Philippon A., Montravers F., Ansquer M., Duval J. Transferable enzymatic resistance to third-generation cephalosporins during nosocomial outbreak of multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Lancet. 1987 Aug 8;2(8554):302–306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90891-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan C. S., Reynolds K. L., Brenner E. R. Analysis of 1,186 episodes of gram-negative bacteremia in non-university hospitals: the effects of antimicrobial therapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):629–638. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter J. L. Klebsiella pulmonary infections: occurrence at one medical center and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jul-Aug;12(4):672–682. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.4.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong K. T., Huston M. Implications of endotoxin contamination in the evaluation of antibodies to lipopolysaccharides in a murine model of gram-negative sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):713–719. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Drennan D. P. Pneumococcal pneumonia: capsular polysaccharide antigenemia and antibody responses. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Mar;84(3):254–260. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-3-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A., Allen J. R., Burke J., Ducel G., Harris A., John J., Johnson D., Lew M., MacMillan B., Meers P. Nosocomial infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: review of recent trends. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S837–S845. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Immunization against fatal experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):403–407. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.403-407.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenico P., Johanson W. G., Jr, Straus D. C. Lobar pneumonia in rats produced by clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):327–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.327-335.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García de la Torre M., Romero-Vivas J., Martínez-Beltrán J., Guerrero A., Meseguer M., Bouza E. Klebsiella bacteremia: an analysis of 100 episodes. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):143–150. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hector R. F., Collins M. S., Pennington J. E. Treatment of experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia with a human IgM monoclonal antibody. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):483–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis W. R., Munn V. P., Highsmith A. K., Culver D. H., Hughes J. M. The epidemiology of nosocomial infections caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Control. 1985 Feb;6(2):68–74. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700062639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay S. J. Nosocomial pneumonia. The challenge of a changing clinical spectrum. Postgrad Med. 1983 Aug;74(2):221-5, 228-9, 232-5. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1983.11698392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn F. W., Jones J. M. Latex agglutination tests for detection of Candida antigens in sera of patients with invasive candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):579–585. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F. W., Williamson R., Tran Van Nhieu G., Carlet J., Acar J. F., Gutmann L. Dissemination of the novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase CTX-1, which confers resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins, and its inhibition by beta-lactamase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H., Antal M., Krcméry V. Imipenem and ceftazidime resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Jan;19(1):136–138. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.1.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. B., Bruderer U., Senyk G., Pitt T. L., Larrick J. W., Cryz S. J., Jr Human monoclonal antibodies specific for capsular polysaccharides of Klebsiella recognize clusters of multiple serotypes. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3160–3164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. B., Fürer E., Schürch U., Cross A. S., Larrick J. W., Cryz S. J., Jr Human monoclonal antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa type-specific lipopolysaccharides, toxin A and Klebsiella capsular polysaccharides. Dev Biol Stand. 1990;71:121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of S. Minnesota. I. Protection against challenge with heterologous gram-negative bacilli. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):601–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Scott G., Kearney J. F., Briles D. E. Monoclonal antibodies against protease-sensitive pneumococcal antigens can protect mice from fatal infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):386–397. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr Changing etiology of nosocomial bacteremia and fungemia and other hospital-acquired infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7 (Suppl 3):S357–S370. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.supplement_3.s357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Small G. J., Lostrom M. E., Pier G. B. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibody therapy for experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.239-244.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podschun R., Heineken P., Ullmann U., Sonntag H. G. Comparative investigations of Klebsiella species of clinical origin: plasmid patterns, biochemical reactions, antibiotic resistances and serotypes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Sep;262(3):335–345. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. Significance of circulating capsular antigen in Klebsiella infections. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1543–1548. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1543-1548.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A. T., Bayston K. F., Cohen J. Prophylactic and therapeutic effects of a monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in experimental gram-negative shock. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):421–427. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. C., Atkisson D. L., Garner C. W. Importance of a lipopolysaccharide-containing extracellular toxic complex in infections produced by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):787–795. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.787-795.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. C. Production of an extracellular toxic complex by various strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):44–48. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.44-48.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann M., Cryz S. J., Jr, Sadoff J. C., Cross A. S. A murine monoclonal antibody against Klebsiella capsular polysaccharide is opsonic in vitro and protects against experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. Microb Pathog. 1988 Sep;5(3):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann M., Müller-Leutloff Y., Hofstaetter T., Seiler F. R., Hahn H. Experimental Klebsiella septicemia in mice: treatment with specific antibodies from the rabbit alone and in combination with gentamicin. Infection. 1985 Jan-Feb;13(1):29–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01643618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokochi T., Nakashima I., Kato N. Effect of capsular polysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae on the differentiation and functional capacity of macrophages cultured in vitro. Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Oct 20;21(10):601–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokochi T., Nakashima I., Kato N. Further studies on generation of macrophages in in vitro cultures of mouse spleen cells and its inhibition by the capsular polysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol Immunol. 1979;23(6):487–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1979.tb00488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]