Abstract
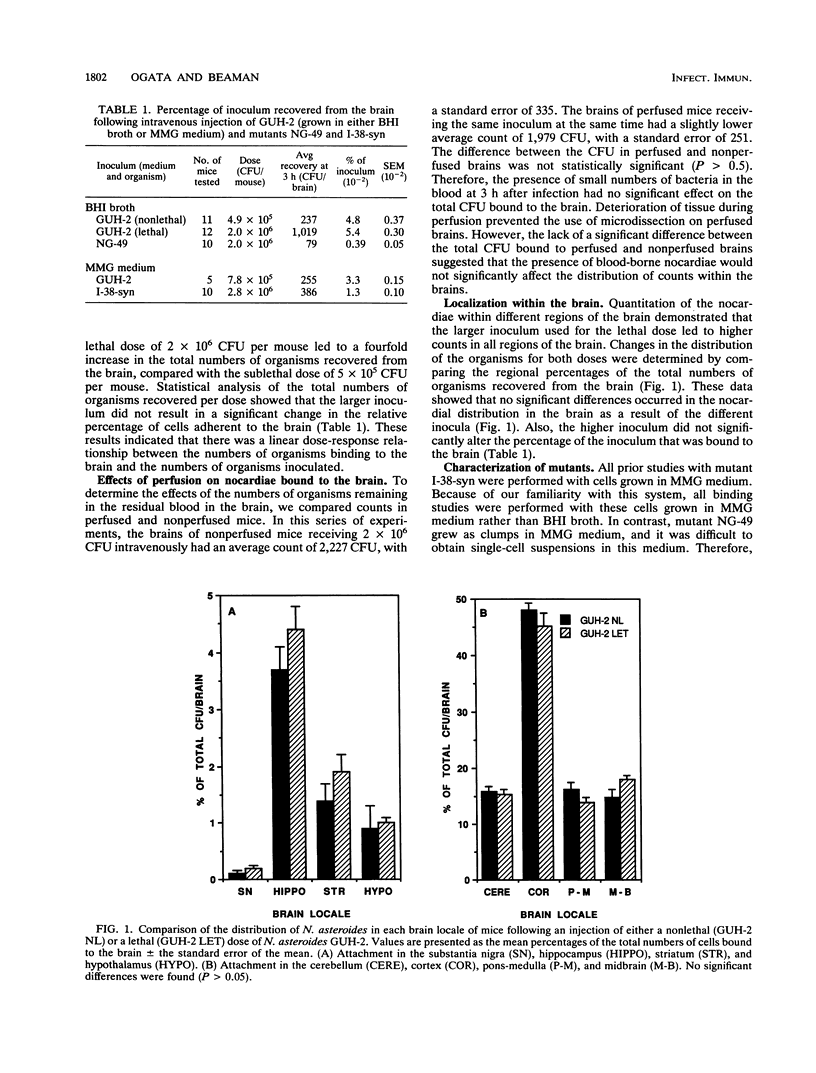
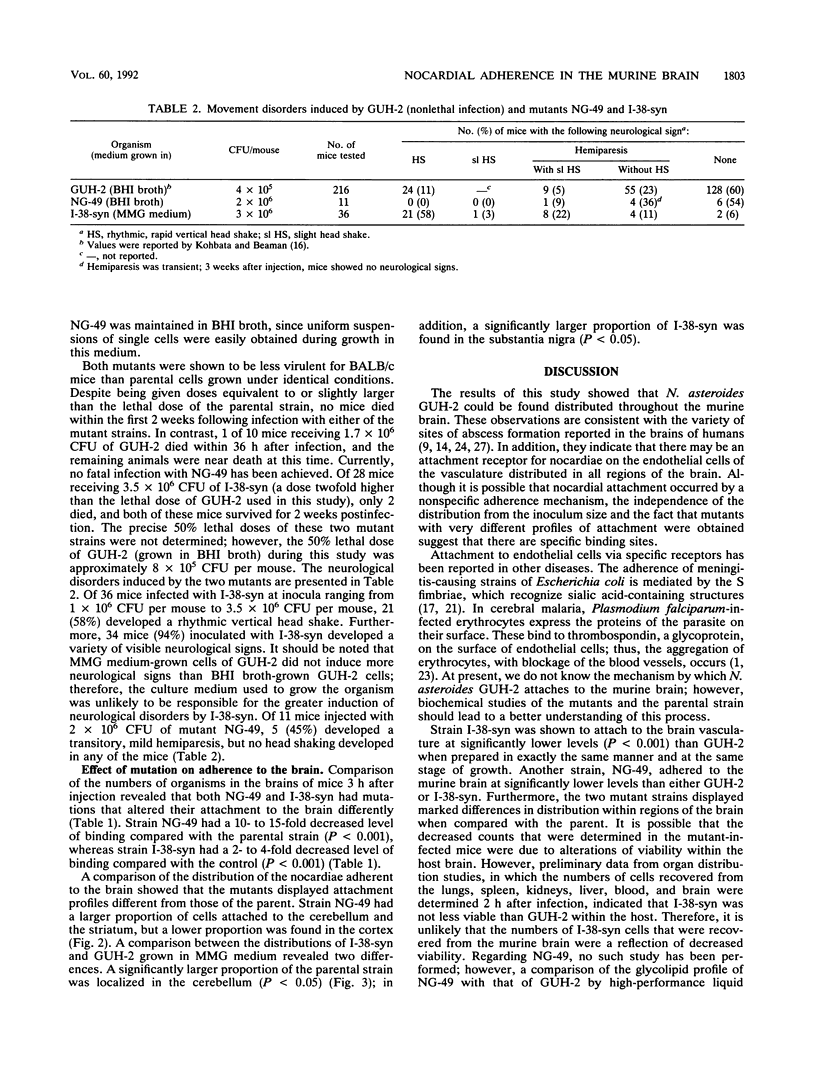
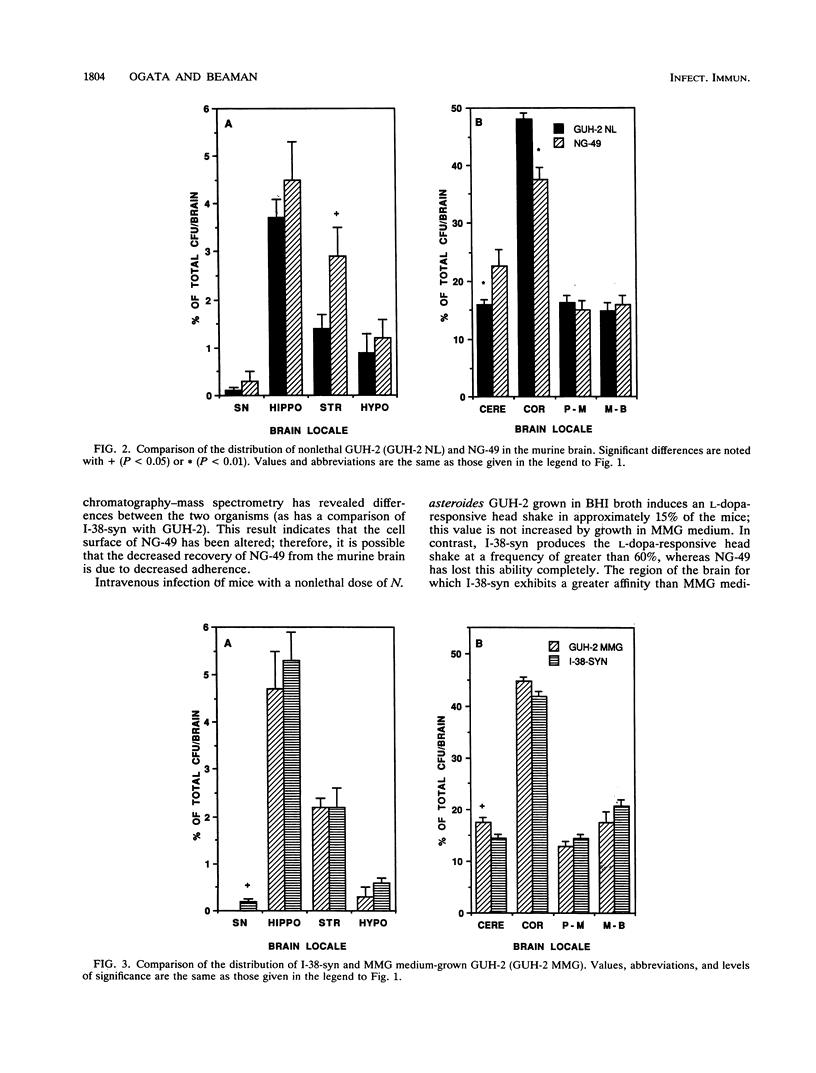
Nonlethal infection of BALB/c mice with Nocardia asteroides GUH-2 (GUH-2) produces a variety of neurological signs, including an L-dopa-responsive movement disorder in 10 to 15% of the infected population. To study nocardial interactions with the brain, we characterized the attachment of GUH-2 within specific regions through the use of microdissection. Following an intravenous injection of a single-cell suspension of log-phase GUH-2, viable cells were recovered from all regions of the brain, and the distribution of the nocardiae was independent of the size of the inoculum. In addition, two mutants of GUH-2 were found to possess significantly altered binding characteristics with regard to both the percentage of the inoculum bound per brain and the relative distribution of adherence to regions of the brain, when compared with the parental strain. These results indicated that GUH-2 bound throughout the murine brain and suggested that GUH-2 utilized specific receptors to facilitate this attachment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AJAX E. T. ACQUIRED DYSLEXIA; A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF TWO CASES. Arch Neurol. 1964 Jul;11:66–72. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460190070005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa M. Human cerebral malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jul;39(1):3–10. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Burnside J., Edwards B., Causey W. Nocardial infections in the United States, 1972-1974. J Infect Dis. 1976 Sep;134(3):286–289. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.3.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Maslan S. Effect of cyclophosphamide on experimental Nocardia asteroides infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):995–1004. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.995-1004.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Maslan S., Scates S., Rosen J. Effect of route on inoculation on host resistance to Nocardia. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):185–189. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.185-189.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Moring S. E. Relationship among cell wall composition, stage of growth, and virulence of Nocardia asteroides GUH-2. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):557–563. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.557-563.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradsher R. W., Monson T. P., Steele R. W. Brain abscess due to Nocardia caviae. Report of a fatal outcome associated with abnormal phagocyte function. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jul;78(1):124–127. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne E., Brophy B. P., Perrett L. V. Nocardia cerebral abscess: New concepts in diagnosis, management, and prognosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Nov;42(11):1038–1045. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.11.1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry W. A. Human nocardiosis. A clinical review with selected case reports. Arch Intern Med. 1980 Jun;140(6):818–826. doi: 10.1001/archinte.140.6.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delić V., Hopwood D. A., Friend E. J. Mutangenesis by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (NTG) in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mutat Res. 1970 Feb;9(2):167–182. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(70)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. A., Martinez A. J., Dummer J. S., Griffith B. P., Hardesty R. L., Bahnson H. T., Lunsford L. D. Central nervous system infections in heart and heart-lung transplant recipients. Arch Neurol. 1989 Feb;46(2):173–177. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520380077017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkes G. K., Fryer J., Rushworth R., Pritchard R., Wilson R. M., Joffe R. Cerebral nocardiosis--clinical and pathological findings in three patients. Aust N Z J Med. 1989 Oct;19(5):475–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1989.tb00311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUEGER E. G., NORSA L., KENNEY M., PRICE P. A. Nocardiosis of the central nervous system. J Neurosurg. 1954 May;11(3):226–233. doi: 10.3171/jns.1954.11.3.0226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohbata S., Beaman B. L. L-dopa-responsive movement disorder caused by Nocardia asteroides localized in the brains of mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):181–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.181-191.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Väisänen-Rhen V., Rhen M., Pere A., Parkkinen J., Finne J. Escherichia coli fimbriae recognizing sialyl galactosides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):762–766. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.762-766.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer E. P. Pulmonary and cerebral nocardial abscess. Med J Aust. 1972 Sep 2;2(10):538–540. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1972.tb47462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. L., Harvey R. L., Wheeler J. K. Diagnostic and therapeutic considerations in Nocardia asteroides infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Sep;53(5):391–401. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197409000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Korhonen T. K., Pere A., Hacker J., Soinila S. Binding sites in the rat brain for Escherichia coli S fimbriae associated with neonatal meningitis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):860–865. doi: 10.1172/JCI113395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter R. W., Silva M., Neu H. C., Silverstein P. M. The neurological aspects of Nocardia asteroides infection. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1968;44:424–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. D., Sherwood J. A., Spitalnik S. L., Panton L. J., Howard R. J., Dixit V. M., Frazier W. A., Miller L. H., Ginsburg V. Thrombospondin binds falciparum malaria parasitized erythrocytes and may mediate cytoadherence. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):64–66. doi: 10.1038/318064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. J., Drake M. E., Jr Unilateral pruritus and Nocardia brain abscess. Neurology. 1984 Jun;34(6):828–829. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.6.828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanski A., Furie M. B., Benach J. L., Lane B. P., Fleit H. B. Interaction between Borrelia burgdorferi and endothelium in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1637–1647. doi: 10.1172/JCI114615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Navab M., Haake D. A., Fogelman A. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Treponema pallidum invades intercellular junctions of endothelial cell monolayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson G. W., Welsh J. E., Butler A. B., Jane J. A., Winn H. R. Primary cerebellar nocardiosis. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1979 Sep;51(3):408–414. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.3.0408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S. Rickettsial interactions with human endothelial cells in vitro: adherence and entry. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):205–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.205-210.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub M. I., Glaser G. H. Nocardial brain abscess and pure motor hemiplegia. N Y State J Med. 1970 Nov 1;70(21):2717–2721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



