Abstract
Former studies have shown that Helicobacter pylori can induce vacuolation of vacuolation of epithelial cells in vitro and possibly in vivo, either by direct action of a cytotoxin or by the action of its strong urease, which breaks down the urea physiologically present in the stomach into cytotoxic ammonia. We have developed a test using HEp2 cells with adherent H. pylori bacteria in order to compare the effects of an H. pylori urease-negative variant with those of its urease-positive parent strain in the presence of 10 mM urea. The level of ammonia production as well as cell vacuolation and viability were monitored for 72 h. The ammonia produced (20 mM) was found to be the essential determinant of the degree of cell vacuolation and viability of HEp2 cells. However, the addition of acetohydroxamic acid (200 mg/liter), a potent urease inhibitor which inhibits ammonia production, did not completely restore cell growth, suggesting the difficulty of neutralizing the ammonia in the vicinity of the cells. Antibodies directed against H. pylori did not neutralize the urease activity. When H. mustelae was tested in the same manner, the detrimental effects were not observed because a lower quantity of ammonia (5 mM) was generated. This was due to a lower urease activity, although the adherence properties of H. mustelae were different from those of H. pylori both quantitatively (greater adherence) and qualitatively (localized instead of diffuse adherence). We conclude that H. pylori-induced ammonia is an essential determinant of its cell toxicity as well as its adherence properties, which allow a high concentration of ammonia at the cellular level.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barer M. R., Elliott T. S., Berkeley D., Thomas J. E., Eastham E. J. Cytopathic effects of Campylobacter pylori urease. J Clin Pathol. 1988 May;41(5):597–597. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.5.597-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
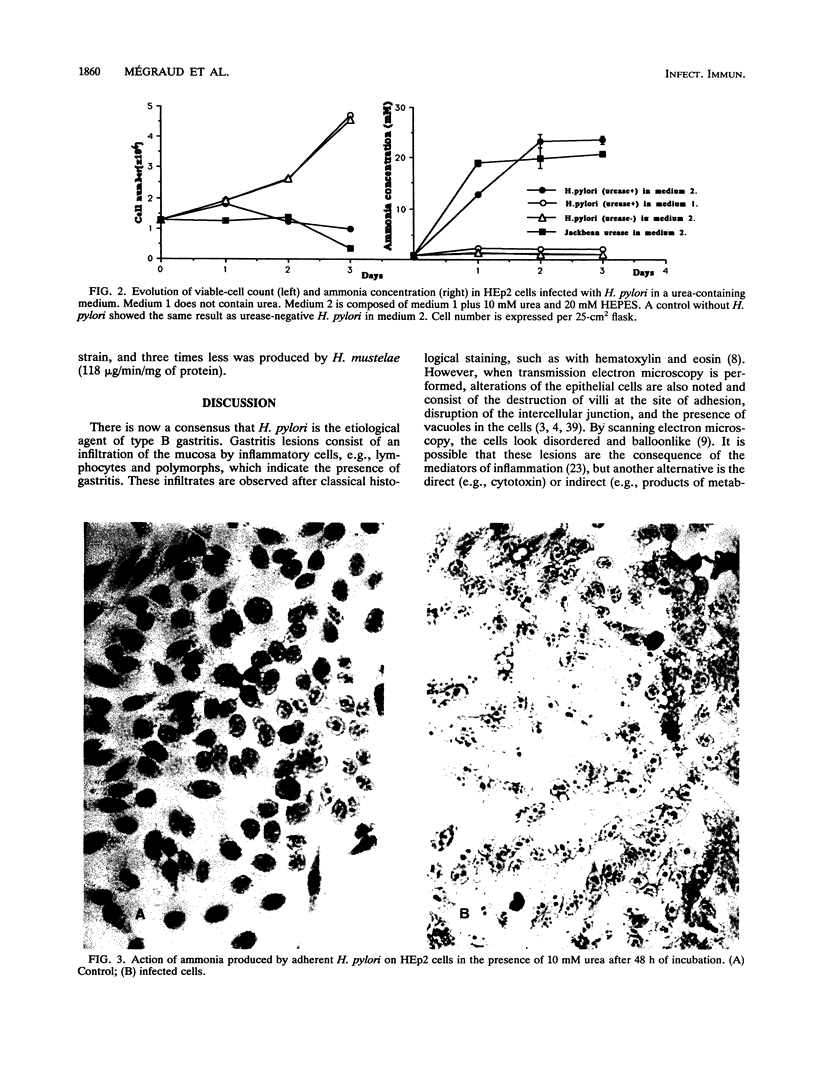
- Bode G., Malfertheiner P., Ditschuneit H. Pathogenetic implications of ultrastructural findings in Campylobacter pylori related gastroduodenal disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1988;142:25–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. G., Correa P., Offerhaus J., Rodriguez E., Janney F., Hoffmann E., Fox J., Hunter F., Diavolitsis S. Ultrastructure of the gastric mucosa harboring Campylobacter-like organisms. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;86(5):575–582. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittajallu R. S., Neithercut W. D., Macdonald A. M., McColl K. E. Effect of increasing Helicobacter pylori ammonia production by urea infusion on plasma gastrin concentrations. Gut. 1991 Jan;32(1):21–24. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Dooley C. P., Blaser M. J. Characterization of and human serologic response to proteins in Helicobacter pylori broth culture supernatants with vacuolizing cytotoxin activity. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):603–610. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.603-610.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Puryear W., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Effect of urease on HeLa cell vacuolation induced by Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1264–1270. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1264-1270.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Campbell G. P., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Purification and characterization of urease from Helicobacter pylori. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9464–9469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Brooks C. L., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Essential role of urease in pathogenesis of gastritis induced by Helicobacter pylori in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2470-2475.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero R. L., Hazell S. L., Lee A. The urease enzymes of Campylobacter pylori and a related bacterium. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Sep;27(1):33–40. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figura N., Guglielmetti P., Rossolini A., Barberi A., Cusi G., Musmanno R. A., Russi M., Quaranta S. Cytotoxin production by Campylobacter pylori strains isolated from patients with peptic ulcers and from patients with chronic gastritis only. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):225–226. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.225-226.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Edrise B. M., Cabot E. B., Beaucage C., Murphy J. C., Prostak K. S. Campylobacter-like organisms isolated from gastric mucosa of ferrets. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Feb;47(2):236–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Otto G., Taylor N. S., Rosenblad W., Murphy J. C. Helicobacter mustelae-induced gastritis and elevated gastric pH in the ferret (Mustela putorius furo). Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1875–1880. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1875-1880.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Lee A. Campylobacter pyloridis, urease, hydrogen ion back diffusion, and gastric ulcers. Lancet. 1986 Jul 5;2(8497):15–17. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92561-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessey S. J., Spencer J., Wyatt J. I., Sobala G., Rathbone B. J., Axon A. T., Dixon M. F. Bacterial adhesion and disease activity in Helicobacter associated chronic gastritis. Gut. 1990 Feb;31(2):134–138. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.2.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc H., Beji A., Vincent P. Marqueurs moléculaires et identification des souches de Campylobacter pylori. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1989;13(1 Pt 1):44B–48B. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunk R. D., Johnson P. T., David B. C., Kraft W. G., Morgan D. R. Cytotoxic activity in broth-culture filtrates of Campylobacter pylori. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(2):93–99. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-2-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Law H., Pellizzari A., Sherman P., Drumm B. Gastric glycerolipid as a receptor for Campylobacter pylori. Lancet. 1989 Jul 29;2(8657):238–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Barrett L. J., Prakash C., McCallum R. W., Guerrant R. L. Urea protects Helicobacter (Campylobacter) pylori from the bactericidal effect of acid. Gastroenterology. 1990 Sep;99(3):697–702. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90957-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Langton S. R. Urea hydrolysis in patients with Campylobacter pyloridis infection. Lancet. 1986 Apr 26;1(8487):965–966. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megraud F., Bonnet F., Garnier M., Lamouliatte H. Characterization of "Campylobacter pyloridis" by culture, enzymatic profile, and protein content. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1007–1010. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1007-1010.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Cortesia M. J., Rosenthal L. E., Jones B. D. Characterization of urease from Campylobacter pylori. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):831–836. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.831-836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Yoo J. K., Inada M., Miyake T. Effect of ammonia on the gastric mucosa in rats: pathophysiological importance of urease in gastric ulcer disease. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;47(3):330–332. doi: 10.1254/jjp.47.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mégraud F., Brassens-Rabbé M. P., Denis F., Belbouri A., Hoa D. Q. Seroepidemiology of Campylobacter pylori infection in various populations. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1870–1873. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1870-1873.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neman-Simha V., Mégraud F. In vitro model for Campylobacter pylori adherence properties. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3329–3333. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3329-3333.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Zafriri D., Goldhar J., Eisenstein B. I. Inability of toxin inhibitors to neutralize enhanced toxicity caused by bacteria adherent to tissue culture cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3737–3742. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3737-3742.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarosiek J., Slomiany A., Slomiany B. L. Evidence for weakening of gastric mucus integrity by Campylobacter pylori. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Jun;23(5):585–590. doi: 10.3109/00365528809093916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Reith A. Ammonia inhibition of protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Quantitative ultrastructural alterations in the lysosomal system. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jul;100(2):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siurala M., Isokoski M., Varis K., Kekki M. Prevalence of gastritis in a rural population. Bioptic study of subjects selected at random. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1968;3(2):211–223. doi: 10.3109/00365526809180125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany B. L., Kasinathan C., Slomiany A. Lipolytic activity of Campylobacter pylori: effect of colloidal bismuth subcitrate (De-Nol) Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Oct;84(10):1273–1277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoot D. T., Mobley H. L., Chippendale G. R., Lewison J. F., Resau J. H. Helicobacter pylori urease activity is toxic to human gastric epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1992–1994. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1992-1994.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen L., Tasman-Jones C., Morris A., Wiggins P., Lee S., Forlong C. Ammonia produced by Campylobacter pylori neutralizes H+ moving through gastric mucus. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1989 Aug;24(6):761–768. doi: 10.3109/00365528909093119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins D. S., Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J., West A. P. The characterization and pathological significance of gastric Campylobacter-like organisms in the ferret: a model for chronic gastritis? Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Oct;101(2):269–278. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800054182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricottet V., Bruneval P., Vire O., Camilleri J. P., Bloch F., Bonte N., Roge J. Campylobacter-like organisms and surface epithelium abnormalities in active, chronic gastritis in humans: an ultrastructural study. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1986;10(2):113–122. doi: 10.3109/01913128609014587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J., Dixon M. F., Heatley R. V. Campylobacter pyloridis and acid induced gastric metaplasia in the pathogenesis of duodenitis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Aug;40(8):841–848. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.8.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J. K., Goodwin C. S., Cooper M., Robinson J. Intracellular vacuolization caused by the urease of Helicobacter pylori. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1302–1304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafriri D., Oron Y., Eisenstein B. I., Ofek I. Growth advantage and enhanced toxicity of Escherichia coli adherent to tissue culture cells due to restricted diffusion of products secreted by the cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1210–1216. doi: 10.1172/JCI112939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]