Abstract
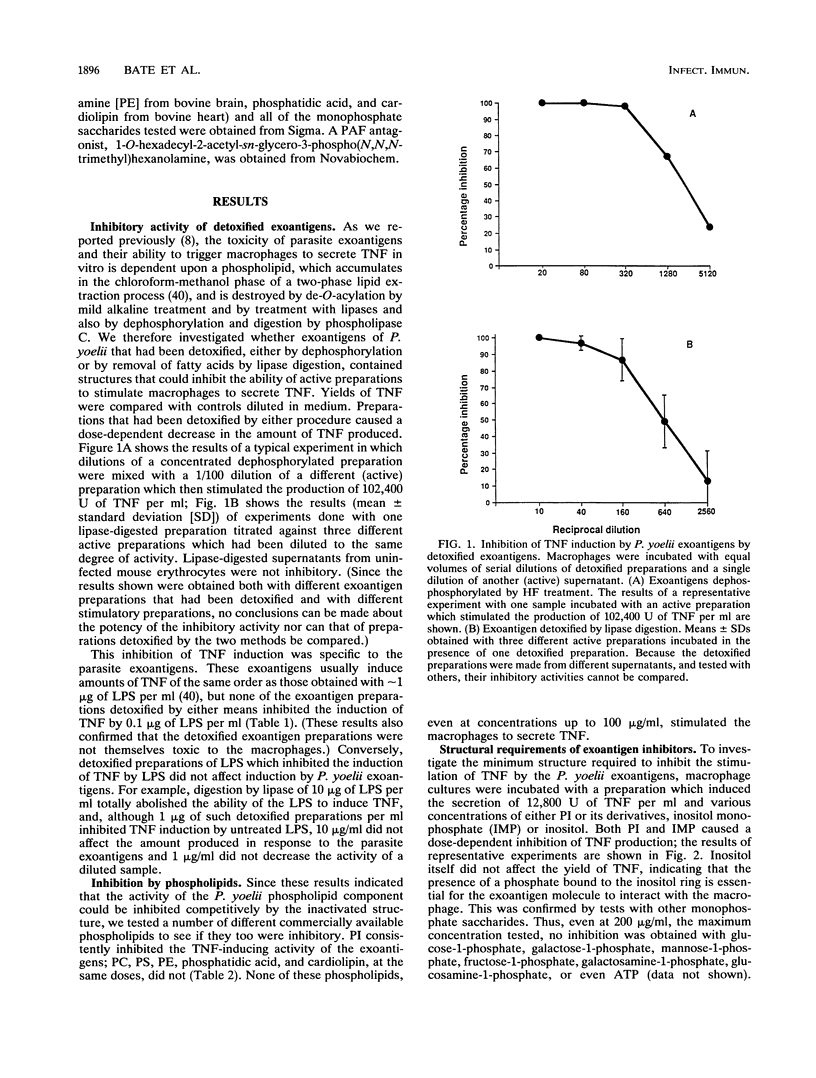
We have previously shown that malaria parasites liberate exoantigens which, through a phospholipid component, stimulate mouse macrophages to secrete tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which are toxic to D-galactosamine-sensitized mice, and which therefore might be involved in pathology. Plasmodium yoelii exoantigens detoxified by dephosphorylation or digestion with lipases do not induce TNF production. However, these partial structures inhibited its production in response to the exoantigens, although not to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). When pure phospholipids were tested in a macrophage assay, none stimulated the production of TNF, but phosphatidylinositol (PI) inhibited TNF induction by P. yoelii exoantigens. Moreover, inositol monophosphate (IMP) was the only one of a number of monophosphate saccharides tested which was inhibitory; inositol was not. Macrophages pretreated with PI, IMP, or detoxified exoantigens and then incubated with parasite exoantigens also yielded much less TNF. PI, IMP, and lipase-digested exoantigens of P. yoelii similarly inhibited the TNF-inducing activity of exoantigens of the human parasites Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. Neither PI nor IMP diminished TNF production in response to LPS, in contrast to a platelet-activating factor antagonist [1-O-hexadecyl-2-acetyl- sn-glycero-3-phospho(N,N,N-trimethyl hexanolamine)] which inhibited both exoantigen- and LPS-induced production of TNF. We conclude that at least two different parts of the molecule are involved in the induction of TNF secretion by parasite exoantigens: one requires the presence of a phosphate bound to inositol, and, since dephosphorylated exoantigens were also inhibitory, one does not. It would seem that both affect interactions between parasite-derived exoantigens and the macrophage receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving C. R. Antibodies to liposomes, phospholipids and phosphate esters. Chem Phys Lipids. 1986 Jun-Jul;40(2-4):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(86)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aschauer H., Grob A., Hildebrandt J., Schuetze E., Stuetz P. Highly purified lipid X is devoid of immunostimulatory activity. Isolation and characterization of immunostimulating contaminants in a batch of synthetic lipid X. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9159–9164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister L. H., Mitchell G. H. Lipidic vacuoles in Plasmodium knowlesi erythrocytic schizonts. J Protozool. 1986 May;33(2):271–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Davé A., Playfair J. H. Malaria exoantigens induce T-independent antibody that blocks their ability to induce TNF. Immunology. 1990 Jul;70(3):315–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Karunaweera N. D., Mendis K. N., Kwiatkowski D., Playfair J. H. Serological relationship of tumor necrosis factor-inducing exoantigens of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1241–1243. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1241-1243.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Playfair J. H. Malarial parasites induce TNF production by macrophages. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):227–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Playfair J. H. Soluble malarial antigens are toxic and induce the production of tumour necrosis factor in vivo. Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):600–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Román E., Moreno C., Playfair J. H. Tumour necrosis factor induction by malaria exoantigens depends upon phospholipid. Immunology. 1992 Jan;75(1):129–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein metabolism in the macrophage: implications for cholesterol deposition in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:223–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Beutler B. The role of cachectin/TNF in endotoxic shock and cachexia. Immunol Today. 1988 Jan;9(1):28–31. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. W., Feddersen C. O., Henson P. M., Voelkel N. F. Platelet-activating factor mediates hemodynamic changes and lung injury in endotoxin-treated rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1498–1509. doi: 10.1172/JCI112980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Chaudhri G., Cowden W. B. Roles of tumour necrosis factor in the illness and pathology of malaria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Jul-Aug;83(4):436–440. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(89)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A. Does endotoxin cause both the disease and parasite death in acute malaria and babesiosis? Lancet. 1978 Jul 8;2(8080):75–77. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emancipator K., Csako G., Elin R. J. In vitro inactivation of bacterial endotoxin by human lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):596–601. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.596-601.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erwin A. L., Mandrell R. E., Munford R. S. Enzymatically deacylated Neisseria lipopolysaccharide (LPS) inhibits murine splenocyte mitogenesis induced by LPS. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1881–1887. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1881-1887.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. R., Holder A. A. Characteristics of the protective response of BALB/c mice immunized with a purified Plasmodium yoelii schizont antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Dec;54(3):609–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Taylor T. E., Molyneux M. E., Wirima J. J., Vassalli P., Hommel M., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and disease severity in children with falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 15;320(24):1586–1591. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906153202404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Ferguson M. A., Cross G. A. Acylation of a Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface antigen via sn-1,2-diacyl glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4969–4974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen M., Palmer J. D., Lohman I. C., McManus L. M., Pinckard R. N. Respiratory and circulatory alterations induced by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine, a mediator of IgE anaphylaxis in the rabbit. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Dec;122(6):915–924. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.6.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Ma G. P., Chisolm G. M. Oxidized low density lipoprotein suppresses the expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA in stimulated murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2343–2350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P., Hemmer C. J., Van Damme J., Gruss H. J., Dietrich M. Elevated tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 serum levels as markers for complicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Am J Med. 1989 Aug;87(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80688-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Freeman M., Rohrer L., Zabrecky J., Matsudaira P., Krieger M. Type I macrophage scavenger receptor contains alpha-helical and collagen-like coiled coils. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):531–535. doi: 10.1038/343531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovach N. L., Yee E., Munford R. S., Raetz C. R., Harlan J. M. Lipid IVA inhibits synthesis and release of tumor necrosis factor induced by lipopolysaccharide in human whole blood ex vivo. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):77–84. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D., Cannon J. G., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Dinarello C. A., Greenwood B. M. Tumour necrosis factor production in Falciparum malaria and its association with schizont rupture. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Sep;77(3):361–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D., Hill A. V., Sambou I., Twumasi P., Castracane J., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Brewster D. R., Greenwood B. M. TNF concentration in fatal cerebral, non-fatal cerebral, and uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Lancet. 1990 Nov 17;336(8725):1201–1204. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92827-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam C., Hildebrandt J., Schütze E., Rosenwirth B., Proctor R. A., Liehl E., Stütz P. Immunostimulatory, but not antiendotoxin, activity of lipid X is due to small amounts of contaminating N,O-acylated disaccharide-1-phosphate: in vitro and in vivo reevaluation of the biological activity of synthetic lipid X. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2351–2358. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2351-2358.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasfargues A., Chaby R. Endotoxin-induced tumor necrosis factor (TNF): selective triggering of TNF and interleukin-1 production by distinct glucosamine-derived lipids. Cell Immunol. 1988 Aug;115(1):165–178. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machicao F., Mushack J., Seffer E., Ermel B., Häring H. U. Mannose, glucosamine and inositol monophosphate inhibit the effects of insulin on lipogenesis. Further evidence for a role for inositol phosphate-oligosaccharides in insulin action. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):909–916. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Arai H., Inoue K. Scavenger receptor-mediated uptake and metabolism of lipid vesicles containing acidic phospholipids by mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5226–5231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., Taverne J., Bate C. A., de Souza J. B. The malaria vaccine: anti-parasite or anti-disease? Immunol Today. 1990 Jan;11(1):25–27. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90007-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Raubitschek A. A., Larrick J. W. Human monoclonal antibodies that recognize conserved epitopes in the core-lipid A region of lipopolysaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1421–1430. doi: 10.1172/JCI112970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Will J. A., Burhop K. E., Raetz C. R. Protection of mice against lethal endotoxemia by a lipid A precursor. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):905–907. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.905-907.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. J., Schulman S., Vanderberg J. P. Rhoptry secretion of membranous whorls by Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jan;35(1):37–44. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Hsueh W. Bowel necrosis induced by tumor necrosis factor in rats is mediated by platelet-activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1328–1331. doi: 10.1172/JCI113459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Bate C. A., Kwiatkowski D., Jakobsen P. H., Playfair J. H. Two soluble antigens of Plasmodium falciparum induce tumor necrosis factor release from macrophages. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2923–2928. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2923-2928.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Bate C. A., Playfair J. H. Malaria exoantigens induce TNF, are toxic and are blocked by T-independent antibody. Immunol Lett. 1990 Aug;25(1-3):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Bate C. A., Sarkar D. A., Meager A., Rook G. A., Playfair J. H. Human and murine macrophages produce TNF in response to soluble antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. Parasite Immunol. 1990 Jan;12(1):33–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1990.tb00934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Structure, biosynthesis, and function of glycosylphosphatidylinositols. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5413–5422. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Thuet M. J., Philippot J. R. Phospholipid biosynthesis in synchronous Plasmodium falciparum cultures. J Protozool. 1982 May;29(2):258–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb04023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



