Abstract
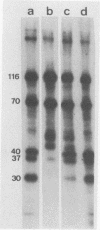
Activation and deposition of C3 on Aspergillus fumigatus conidia have been previously demonstrated. This study investigated in further detail the interactions between complement component C3 and the conidia of A. fumigatus. Immunoblotting and 125I-C3 binding studies showed that C3 deposition was rapid (less than 15 min) and parallel to the formation of iC3b. Immunoblotting experiments identified a 54- to 58-kDa conidial protein which binds human complement component C3 and/or a C3 fragment(s). 125I labeling of the outer layer of the conidia demonstrated that this protein doublet was present on the surface of the spore. The further degradation of C3 to low-molecular-mass fragments (40, 37, and 30 kDa), in the absence of plasma, by intact living conidia and a preparation of the outer conidial wall layer indicated the ability of fungal components to cleave C3. These data suggest that interactions between conidia and C3 are not limited only to deposition via activation of the alternative complement pathway; they also include degradation of bound C3.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calderone R. A., Linehan L. The role of complement in host resistance to systemic fungal infection. Immunol Ser. 1989;47:225–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Sandberg A. L. Identification of C3d receptors on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):252–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.252-258.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Gaither T. A., O'Shea J. J., Rotrosen D., Lawley T. J., Wright S. A., Frank M. M., Green I. Expression of specific binding sites on Candida with functional and antigenic characteristics of human complement receptors. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3577–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigentler A., Schulz T. F., Larcher C., Breitwieser E. M., Myones B. L., Petzer A. L., Dierich M. P. C3bi-binding protein on Candida albicans: temperature-dependent expression and relationship to human complement receptor type 3. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):616–622. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.616-622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratamico P. M., Buckley H. R. Identification and characterization of an immunodominant 58-kilodalton antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus recognized by sera of patients with invasive aspergillosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):309–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.309-315.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratamico P. M., Long W. K., Buckley H. R. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to a 58-kilodalton antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):316–322. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.316-322.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore B. J., Retsinas E. M., Lorenz J. S., Hostetter M. K. An iC3b receptor on Candida albicans: structure, function, and correlates for pathogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich F., Dierich M. P. Candida albicans and Candida stellatoidea, in contrast to other Candida species, bind iC3b and C3d but not C3b. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):598–600. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.598-600.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter M. K., Lorenz J. S., Preus L., Kendrick K. E. The iC3b receptor on Candida albicans: subcellular localization and modulation of receptor expression by glucose. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):761–768. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter M. K. Serotypic variations among virulent pneumococci in deposition and degradation of covalently bound C3b: implications for phagocytosis and antibody production. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):682–693. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Brown E. J., Frank M. M. Complement and bacteria: chemistry and biology in host defense. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:461–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan V. L., Bennett J. E. Beta 1,4-oligoglucosides inhibit the binding of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia to human monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1154–1156. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Wilson M. A., Farrell T. P., Levitz S. M. Activation of C3 and binding to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia and hyphae. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3412–3417. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3412-3417.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Fearon D. T., Levine R. P. Action of the C3b-inactivator on the cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Jan R. G. Interaction of Aspergillus fumigatus Spores with Human Leukocytes and Serum. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):345–350. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.345-350.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. Candida albicans C3d receptor, isolated by using a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1981–1986. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1981-1986.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W. Immunity to fungi. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989;2(3):360–367. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Activation and control of the complement system. Essays Biochem. 1986;22:27–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. D., Kerr K. M., Seaton A. Killing of Aspergillus fumigatus spores by human lung macrophages: a paradoxical effect of heat-labile serum components. J Med Vet Mycol. 1989;27(5):295–302. doi: 10.1080/02681218980000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Calderone R. Purification and characterization of the extracellular C3d-binding protein of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):309–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.309-314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smail E. H., Jones J. M. Demonstration and solubilization of antigens expressed primarily on the surfaces of Candida albicans germ tubes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.74-81.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldorf A. R., Diamond R. D. Neutrophil chemotactic responses induced by fresh and swollen Rhizopus oryzae spores and Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):458–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.458-463.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn R. G., DeHart D. J., Agwu D. E., Bryant-Varela B. J., Julian N. C. Aspergillus fumigatus complement inhibitor: production, characterization, and purification by hydrophobic interaction and thin-layer chromatography. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3508–3515. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3508-3515.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn R. G., Hammer C. H., Bennett J. E. Inhibition of complement by culture supernatants of Aspergillus fumigatus. J Infect Dis. 1986 Dec;154(6):944–951. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.6.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]