Abstract
India's northward flight and collision with Asia was a major driver of global tectonics in the Cenozoic and, we argue, of atmospheric CO2 concentration (pCO2) and thus global climate. Subduction of Tethyan oceanic crust with a carpet of carbonate-rich pelagic sediments deposited during transit beneath the high-productivity equatorial belt resulted in a component flux of CO2 delivery to the atmosphere capable to maintain high pCO2 levels and warm climate conditions until the decarbonation factory shut down with the collision of Greater India with Asia at the Early Eocene climatic optimum at ≈50 Ma. At about this time, the India continent and the highly weatherable Deccan Traps drifted into the equatorial humid belt where uptake of CO2 by efficient silicate weathering further perturbed the delicate equilibrium between CO2 input to and removal from the atmosphere toward progressively lower pCO2 levels, thus marking the onset of a cooling trend over the Middle and Late Eocene that some suggest triggered the rapid expansion of Antarctic ice sheets at around the Eocene-Oligocene boundary.
Keywords: CO2, Deccan, Tethys, Himalaya, Eocene
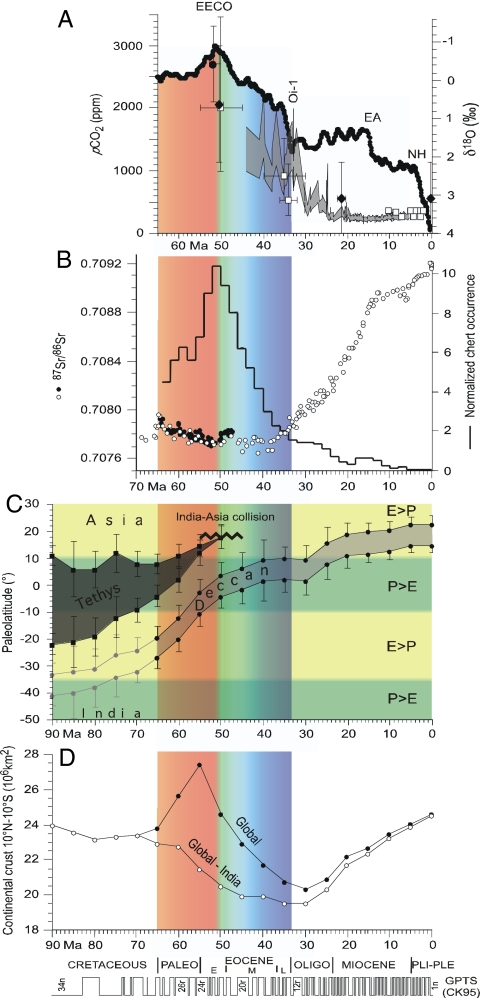
Modern-day glacial climate, characterized by polar ice at sea level, is the long-term cooling derivative of a Cretaceous-early Cenozoic world dominated by warm conditions and the general absence of ice sheets (1, 2). The zenith of global warmth in the Cenozoic (0–65 Ma) was reached at ≈50 Ma during the Early Eocene climatic optimum (EECO) as the culmination of a Late Paleocene-Early Eocene (≈60–50 Ma) warming trend in oceanic bottom waters (3) (Fig. 1A). The EECO was characterized by the widespread occurrence of cherts (4) (Fig. 1B) and reflected in warm climate conditions at even extreme high latitudes (5, 6). A persistent cooling trend ensued over the Middle and Late Eocene that eventually plummeted into a glacial climate mode with the inception of major Antarctic ice sheets at Oi-1 near the Eocene-Oligocene boundary at ≈34 Ma (7). Changes in ocean circulation and heat transport related to the opening of Southern Ocean gateways (8) occurred well after the start of the cooling trend at ≈50 Ma and do not seem to adequately account for inception of Antarctic glaciation according to recent climate models (e.g., refs. 9 and 10). Instead, reduction in greenhouse gas concentrations is the more likely fundamental cause of Antarctic freezing and global cooling (10). This is supported by the occurrence of high (albeit highly scattered) pCO2 estimated values of >1,000 ppm at around the EECO (e.g., 11, 12; see also ref. 13) and generally low (<500 ppm) pCO2 estimated values after Oi-1 that followed a decline that more or less parallels the long-term temperature record (14, 15) (Fig. 1A). However, what triggered the global cooling from the EECO to Oi-1 (and thus the cause of the long-term decrease in pCO2) is unclear (16).
Fig. 1.
Cenozoic time series on a common timescale (36, 39) shown at bottom of figure. (A) Benthic foraminiferal oxygen isotope synthesis (1) indicating early Cenozoic warming culminating at the Early Eocene climate optimum (EECO) and subsequent Middle and Late Eocene cooling culminating with plummeting global cooling (Oi-1) and the inception of major Antarctic glaciations at around the Eocene-Oligocene boundary. A 1.5‰ decrease/increase in benthic foraminifera δ18O values corresponds to a ≈6°C warming/cooling of bottom waters before formation of major continental ice sheets at Oi-1. Expansion of East Antarctic (EA) and Northern Hemisphere (NH) ice sheets are also indicated for reference. Selected estimates of atmospheric concentrations of CO2 (pCO2, plotted with 95% confidence intervals) generally registering the highest levels based on alkenones (shaded curve) (14), pedogenic goethite (filled circle) (11), trona and nahcolite (filled diamonds) (12), and leaf stomata (open circles) (81, 82; see review in ref. 83) of the general trend of high pCO2 values in the early Cenozoic that decrease to more-or-less present-day levels by the end of the Oligocene. (B) Strontium isotopic ratios (87Sr/86Sr) of seawater as measured in foraminifera [open circles (25); filled circles (3)], where rise in values starting at ≈38 Ma may reflect uplift and erosion of the Himalayas (69, 71, 72). Histogram shows chert occurrences in deep-sea sediments (4), where peak at ≈50 Ma is thought to reflect enhanced chemical weathering during EECO. (C) Changes in paleolatitude of the N–S extent of eventual (light shading) and erupted Deccan Traps (darker shading) as India drifted northward. Also shown is the N–S extent of the subducting Tethys Ocean calculated between southern Tibet and the northern margin of Greater India; error bars from paleomagnetic data of ref. 84 for India and ref. 27 for the Asian blocks. A zonally averaged model profile of evaporation (E) relative to precipitation (P) for 8 pCO2 with an idealized geography (59) was used to approximate the position of the humid (P>E) and arid (E>P) belts. (D) Changes with age in the continental land area within 10° of the equator as the continents drifted, showing a gradual decrease from at least 90 Ma to 30 Ma followed by a steady increase from 30 Ma to the present for most of the world's continents when India is excluded (curve labeled Global-India) but when India is included (curve labeled Global), its northward drift resulted in a peak in equatorial land mass centered at ≈55 Ma.
The BLAG model (17, 18) postulates that long-term changes in pCO2 and resulting climate were driven primarily by variations in mantle outgassing tied to global seafloor production rates. However, a constant rate of ocean floor production since 180 Ma cannot be excluded based on the observed age distribution of preserved oceanic crust (19, 20). For example, almost 50% of oceanic crust that formed since about the beginning of the Eocene (≈55 Ma) has already been removed by subduction (D. Rowley, personal communication) so that estimated changes in production rates (e.g., 21, 22) are perforce based on increasingly severe and usually ill-constrained extrapolations for missing oceanic crust. Alternatively, Raymo and Ruddiman (23) proposed that uplift of the Tibetan Plateau induced increases in chemical weathering that resulted in a general drawdown of pCO2 that cooled global climate. However, the seawater 87Sr/86Sr isotope record preserved in marine carbonates (24, 25), which was assumed to be a proxy for chemical erosion rates, does not show a pronounced increase until ≈38 Ma and 87Sr/86Sr values were comparatively stable or even decreasing before that time (3) (Fig. 1B), making this mechanism unlikely as an explanation for the long-term cooling that started at ≈50 Ma.
We suggest that high pCO2 levels and the associated major turnaround in early Cenozoic climate at ≈50 Ma were closely related to the convergence of Greater India (hereafter simply referred to as India) with Eurasia in the equatorial climate belt. According to this hypothesis, the warming trend that culminated at the EECO was sustained by release of CO2 from subduction of carbonate-rich pelagic sediments deposited in the high-productivity equatorial belt on Tethyan seafloor between Eurasia and rapidly converging India (Fig. 1C). The subsequent cooling trend resulted from the closure of the Tethyan CO2 factory and the broadly concomitant onset of efficient drawdown of pCO2 from chemical weathering as the India subcontinent, and especially the highly weatherable Deccan Traps, drifted into the equatorial humid belt (Fig. 1 C and D). The EECO thus seems to broadly coincide with a turning point in the long-term delicate balance between the rate of volcanic input of CO2 and the rate of chemical weathering of silicates and deposition of carbonate that ultimately removes CO2 from the ocean–atmosphere (17, 26).
Drift of India and Collision with Eurasia
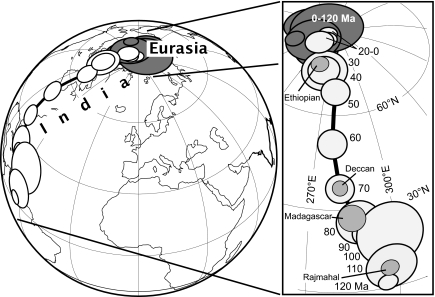
We applied an apparent polar wander synthesis (25) and paleomagnetic data for the Asian blocks (mainly Tibet) (27), in conjunction with a plate kinematic model (28, 29), to reconstruct the paleogeographic evolution of India and surrounding continents over the Mesozoic-Cenozoic. India resided in the southern hemisphere for much of the Mesozoic era as part of the Gondwana supercontinent (30), which began to disperse with the opening of the Somali basin during the middle Jurassic (31) and the separation of East Gondwana (which included India, Madagascar, Antarctica, and Australia) from West Gondwana (Africa and South America). India with Madagascar separated from Antarctica at ≈120 Ma and commenced its long northward journey toward Eurasia. The synthetic apparent polar wander path of Besse and Courtillot (25), compared with paleomagnetic poles from the Rajmahal (≈117 Ma), Madagascar (≈90 Ma), Deccan (≈65 Ma), and Ethiopian (≈30 Ma) traps as reliability checks, charts the drift history of India with respect to the geographic axis since the Early Cretaceous (Fig. 2). Rapid polar motion of India ensued at ≈90 Ma after separation from Madagascar and lasted up to ≈50 Ma on collision with Eurasia. Major outpourings of the Deccan lavas with an estimated eruptive volume of up to 4 × 106 km3 (32) occurred over a ≈1-Myr interval at ≈65 Ma, although the contribution of CO2 to the atmosphere was apparently relatively minor (33, 34). Detailed plate kinematic reconstructions (29) show that India was converging with the southern margin of Eurasia in Tibet, a terrane accreted to Eurasia before the late Jurassic (35), at high rates of 15–25 cm/yr before Anomaly 22 [49.5 Ma according to the CK95 (36) timescale used throughout]. Convergence rates decreased sharply by Anomaly 21 (48.5 Ma) as India was colliding with the southern margin of Tibet (Eurasia) (29), located at a paleolatitude of 13° ± 6.5°N in the early Cenozoic (37) .
Fig. 2.
Mean paleomagnetic poles at 10-Myr intervals from 120 Ma to the present from the global synthetic apparent polar wander path (84) shown as circles of 95% confidence for Eurasia (dark shading) and for India (lighter shading), compared with individual paleomagnetic poles from the ≈117 Ma Rajmahal (85), ≈90 Ma Madagascar (86), ≈65 Ma Deccan (87), and ≈30 Ma Ethiopian (88) traps as reliability checks on paleopole path for India. Madagascar and Ethiopian paleopoles were rotated into India coordinates by using rotation parameters from ref. 84.
These findings from paleomagnetic and plate kinematic data on the onset of India-Eurasia collision find confirmation and refinement from geologic constraints. The end of marine sedimentation and the first onlap of fluvio-deltaic sediments and redbeds on the Indian northern passive margin in the western Himalaya is dated as foraminiferal Zone P8 (38), correlative with Chron C22r of latest Early Eocene age [≈50.5 Ma (39, 40)]. This first direct timing constraint on the initiation of collision between India and Asia has stood up well (41–43) and is supported, for example, by field studies in northwest Pakistan, where the suture and Indian craton were overlapped by shallow-marine strata of latest Early Eocene age (Zone P9), showing that suturing was largely completed by ≈49 Ma (44). Evidence of subduction and final collision derives also from the occurrence of island arc volcanics and related intrusives, and massive calc-alkaline plutonism associated with the last major pulse dated at ≈50 Ma in the Ladakh Himalayas, for example (45–47).
Tethyan Subduction Factory
The subduction of several thousand kilometers of Tethyan oceanic crust associated with the northward drift of India from the time it separated from Antarctica at ≈120 Ma and Madagascar at ≈90 Ma until incipient collision with Eurasia at ≈50 Ma occurred within the time frame of the shift at ≈145 Ma from predominantly shallow water to pelagic carbonate accumulation in the world ocean (48). Significantly, the southern margin of Tibet (Eurasia) maintained relatively stable northern hemisphere paleolatitudes all this time, from ≈10°N in the Cretaceous (27, 37) to ≈13°N in the early Cenozoic (37), implying that much of the Tethyan oceanic crust advancing with India from the southern hemisphere must have transited through the equatorial upwelling belt (Fig. 1C) where high productivity and enhanced deposition of biogenic sediments is likely to occur (49). When subducted, this carpet of equatorial bulge pelagic carbonates would be prone to metamorphic decarbonation, augmenting the global flux of CO2 to the atmosphere (50, 51). Calc-alkaline magmatism of Cretaceous-Eocene age related to Andean-type and island arc subduction of Tethyan oceanic lithosphere occur over >2,000 km from the west (e.g., Karakoram, Ladakh) to the east where they constitute the backbone of the Transhimalayan belt (e.g., 38, 45). The net yield of metamorphic CO2 from the Himalayan orogen itself is debatable (52, 53), although sampling of hot springs in Nepal indicate that there may be a net positive flux of CO2 to today's atmosphere (54). More generally, 3He data suggest that ≈80% of the CO2 flux at global convergent margins is derived from slab metamorphism (55). The persistent subduction of carbonate-rich Tethyan sea floor should thus have constituted an unusually productive factory of metamorphic CO2 that most probably acted as a principal agent of long-term warming in the Cretaceous and early Cenozoic (56).
Weathering of Deccan Traps in Equatorial Humid Belt
The Tethyan subduction factory of CO2 must have radically reduced its production with the collision and marked decrease in convergence rate between India and Eurasia, which broadly coincided with the acme of Cenozoic warmth (and presumably peak pCO2) at the EECO at ≈50 Ma. At about the same time that the India-Eurasia collision was occurring, the silicate weathering machine went into higher gear as India entered the equatorial humid belt (Fig. 1 C and D). Today, the equatorial humid belt, where mean annual precipitation exceeds evaporation (P > E), is on average 15–20° wide in latitude and shifted several degrees northward because of interhemispheric temperature asymmetry (57, 58). Although the precise latitudinal registry may have varied in the geologic past because of different continental distributions, the overall latitudinal width of the equatorial humid belt may be a stable feature of global climate. This is suggested by climate model calculations showing relatively similar latitudinal patterns of P–E for pCO2 values ranging up to 10 times the preindustrial level (59) and is supported by the paleolatitudinal distribution over geologic time of evaporites, which is approximately the same as occurs today (60). We use a zonally averaged P–E latitudinal profile calculated for 8 × pCO2 with an idealized geography (59) for the approximate position of the equatorial humid belt in the early Cenozoic (Fig. 3).
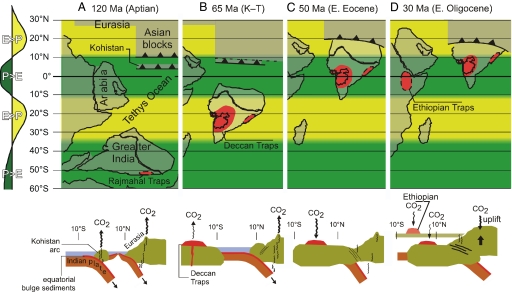
Fig. 3.
Palaeogeographic reconstructions of the Indian Ocean region at key times obtained by using finite rotation poles and paleomagnetic poles from the synthetic apparent polar wander path of ref. 84, and the latitudinal positions of the Asian blocks (mainly Tibet) from ref. 27. A zonally averaged model profile of evaporation (E) relative to precipitation (P) for 8 × pCO2 with an idealized geography (59) was used to approximate the position of the equatorial humid belt and the adjacent tropical arid belts in the early Cenozoic. (A) Reconstruction for the Aptian (early Cretaceous, ≈120 Ma, Anomaly M0) at the time of separation of Greater India from Antarctica. (B) Reconstruction for just after the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary (≈65 Ma, Anomaly 29) and the emplacement of the Deccan Traps, the present-day outline of which is superposed to the inferred original extension at the time of emplacement. (C) Reconstruction for the Early Eocene (≈50 Ma, Anomaly 22) shortly after initial collision of India with Asia that resulted in the shutdown of the Tethyan carbonate subduction factory and entry of the Deccan Traps in equatorial humid belt. (D) Reconstruction for the early Oligocene (≈30 Ma, Anomaly 13) and the emplacement of the Ethiopian Traps. In A and B, andean-type and/or island arc (e.g., Kohistan) subduction of Tethyan oceanic lithosphere under the Asian margin (Tibet) are diagrammatically sketched after refs. 89 and 90. The Kohistan arc was initiated offshore of Asia during the mid-Cretaceous above northward subducting Tethyan oceanic crust. The arc sutured to Asia at ≈90 Ma but subduction of oceanic crust beneath the arc continued until Indian Plate continental rocks began to underthrust the arc at ≈50 Ma ago (89). Reconstructions made with PaleoMac 6.1 (91).
At the onset of the Cenozoic (65 Ma), the amount of Indian continental crust transiting through the equatorial belt (10°S to 10°N) was only ≈3% of the global continental crust, but at about the time of incipient collision it boosted to values on the order of ≈20% (50–55 Ma) and then eventually decreased to ≈5% toward the close of the Eocene (≈34 Ma) (Fig. 1D). This should have represented a perturbation of the global weathering regime considering only the granitic continental crust, but piggybacked on the Indian continent was the Deccan Traps, with an estimated original surface area of ≈106 km2 or double what remains today (32), that entered the equatorial humid belt at ≈55 Ma and dwelled thereabout for ≈20 Myr (Fig. 3). Basaltic rocks like the Deccan become potent carbon sinks when exposed to terrestrial weathering and consume 5–10 times more atmospheric CO2 than granitic rocks under similar conditions (61). The highly weatherable Deccan Traps (62) must have suffered intense weathering when they entered the equatorial humid belt, because CO2 consumption rates for basalts from today's equatorial humid regions (e.g., Java) can be an order of magnitude greater than tropical arid regions of comparable mean surface temperature (e.g., Parana) (63). Moreover, the equatorial region was likely to have been especially hot and humid in the Early Eocene with the high pCO2 levels. Evidence of intense ancient weathering of the Deccan Traps is indicated by the formation of thick, mature laterites preserved at high elevations with Eocene magnetization directions (64, 65).
Osmium isotopes are sensitive to inputs from unradiogenic extraterrestrial and mantle sources (low 187Os/186Os or 187Os/188Os ratios) compared with the dominant background radiogenic contribution from riverine sources (high 187Os/188Os ratios). In an Os isotope record for the entire Cenozoic in a slowly deposited deep-sea sediment core (66), a spike of low Os isotope values was associated with an extraterrestrial impact event at the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary (KTB). In a higher-resolution Ocean Drilling Project sediment core (67), the spike of low Os isotope values at the KTB could be differentiated from a decrease due to Deccan volcanism that apparently started ≈0.5 Myr before the KTB, whereas sustained delivery of unradiogenic Os from weathering of Deccan was thought to contribute to relatively low Os isotope values for several million years after Deccan emplacement. A distinct decrease in Os isotope ratios was also found at ≈50–55 Ma in the slowly deposited deep-sea sediment core and attributed to weathering of Tethyan ophiolites that became exposed during the India-Eurasia collision (66). Alternatively, we suggest that this decrease in Os isotopes could be due to enhanced weathering of the Deccan Traps when this large province of continental basalts drifted into the equatorial humid belt at ≈55 Ma. The marine Sr isotope record hardly shows any change associated with this proposed weathering event (Fig. 1B) and even the emplacement of the Deccan Traps is marked by only a small inflection in the Sr isotope record (68). Instead, marine Sr isotope values seem to be more strongly influenced by the exhumation of radiogenic rocks, such as leucogranites, in a massive orogen like the Himalaya (69). The sharp increase in marine 87Sr/86Sr values at ≈38 Ma (Fig. 1B) suggests that vigorous erosion and weathering of rapidly exhumed Himalayan silicates (70–72) may have taken over as an important CO2 sink as the Deccan Traps footprint began to creep out of the equatorial humid belt (Fig. 3D).
Caveats and Conclusions
The apparent trend of decreasing pCO2 over the Middle and Late Eocene may have reached sufficiently low levels to have triggered the rapid expansion of Antarctic ice sheets at around the Eocene-Oligocene boundary (10, 14). However, the strong variability (and associated uncertainties) superimposed on the decreasing trend in pCO2 (Fig. 1A) suggest that other processes, such as changes in heat transport from the opening or closing of oceanic gateways (e.g., 8, 73), also helped steer global climate. This may have been the case especially once pCO2 decreased to around modern levels in the Oligocene and long-term changes in pCO2 and global climate became less obviously coupled (14, 74; but see ref. 75).
In conclusion, the equatorial convergence of India hypothesis suggests that high pCO2 levels and warm global climate that culminated in the EECO at ≈50 Ma can be attributed to enhanced CO2 recycling from prolonged subduction of pelagic carbonate-rich Tethyan crust rather than to increased mantle outgassing tied to global oceanic crust production rates (e.g., 17, 76), which some analyses suggest may not even have varied significantly over the past 180 Ma (20). The subsequent decrease of pCO2 levels and parallel cooling trend in the Middle and Late Eocene can thus be attributed to the shutdown of the Tethyan decarbonation subduction factory when India collided with Eurasia. However, although CO2-driven weathering feedback (26) provides the most plausible thermostatic control on maximum temperatures (77) and, for example, has prevented a runaway greenhouse atmosphere, the weathering thermostat may not work so well in limiting minimum temperatures in the apparent absence of coupling between CO2 consumption and tectonic forcing of weathering, for example, due to mountain building (70), paleogeography, and climate zonality (78). A case in point is the drift of India into the equatorial humid belt where we suggest that runoff-enhanced continental weathering, especially of the highly weatherable Deccan large igneous province (61), introduced a CO2 sink that may have tipped the delicate long-term carbon cycle balance toward a glacial mode. Atmospheric CO2 levels from late Pleistocene ice cores show a long-term trend of up to 22 ppm over the past 610 kyr, providing evidence for a close long-term balance between the supply and uptake of CO2 that supports the role of CO2-driven silicate weathering feedback (79). However, a simple projection of this trend over timescales of tens of million years would suggest that atmospheric CO2 levels could vary by a factor of 2 or more because of an underlying slight imbalance between CO2 input to and removal from the atmosphere. In other words, small residual imbalances over ≈106 Myr timescale that might be due to factors like variable decarbonation in subduction and changing weatherability due to the latitudinal distribution of continents and large igneous provinces can result in large drift in climate when integrated over longer (≈107 Myr) timescales, allowing global climate to range from nonglacial conditions like the EECO to extreme pan-glacial conditions like the late Proterozoic Marinoan glaciation (80).
Acknowledgments.
We thank Ben Cramer, Jim Wright, Mimi Katz, Ken Miller, and Geoffery Abers for stimulating discussions and comments, and Ted Irving and Karl Turekian for critical reviews of the manuscript. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation. Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory contribution no. 7192.
Footnotes
This contribution is part of the special series of Inaugural Articles by members of the National Academy of Sciences elected in 2004.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
See Commentary on page 16061.
References
- 1.Miller KG, Wright JD, Browning JV. Visions of ice sheets in a greenhouse world. Marine Geol. 2005;217:215–231. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zachos J, Pagani MN, Sloan L, Thomas E, Billups K. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to Present. Science. 2001;292:686–693. doi: 10.1126/science.1059412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hodell DA, et al. Variations in the strontium isotope composition of seawater during the Paleocene and early Eocene from ODP Leg 208 (Walvis Ridge) Geochem Geophys Geosyst. 2007;8:Q09001. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Muttoni G, Kent DV. Widespread formation of cherts during the early Eocene climate optimum. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. 2007;253:348–362. [Google Scholar]
- 5.McKenna MC. Eocene paleolatitude, climate, and mammals of Ellesmere island. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. 1980;30:349–362. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moran K, et al. The Cenozoic palaeoenvironment of the Arctic Ocean. Nature. 2006;441:601–605. doi: 10.1038/nature04800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Miller KG, Wright JD, Fairbanks RG. Unlocking the ice house: Oligocene-Miocene oxygen isotopes, eustasy, and margin erosion. J Geophys Res. 1991;96:6829–6848. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kennett JP. Cenozoic evolution of Antarctic glaciation, the circum-antarctic ocean and their impact on global paleoceanography. J Geophys Res. 1977;82:3843–3860. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huber M, Nof D. The ocean circulation in the southern hemisphere and its climatic impacts in the Eocene. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. 2006;231:9–28. [Google Scholar]
- 10.DeConto RM, Pollard D. Rapic Cenozoic glaciation of Antarctica induced by declining atmospheric CO2. Nature. 2003;421:245–249. doi: 10.1038/nature01290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yapp CJ. Fe(CO3)OH in goethite from a mid-latitude North American oxisol: estimate of atmospheric CO2 concentration in the Early Eocene “climatic optimum.”. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2004;68:935–947. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lowenstein TK, Demicco RV. Elevated Eocene atmospheric CO2 and its subsequent decline. Science. 2006;313:1928–1929. doi: 10.1126/science.1129555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Royer DL, Berner RA, Montanez IP, Tabor NJ, Beerling DJ. CO2 as a primary driver of Phanerozoic climate. GSA Today. 2004;14:4–10. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pagani M, Zachos JC, Freeman KH, Tipple B, Bohaty S. Marked decline in atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations during the Paleogene. Science. 2005;309:600–603. doi: 10.1126/science.1110063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Thomas E. Descent into the Icehouse. Geology. 2008;36:191–192. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Thomas E, Brinkhuis H, Huber M, Röhl U. An ocean view of the early Cenozoic greenhouse world. Oceanography. 2006;19:63–72. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Berner RA, Lasaga AC, Garrels RM. The carbonate-silicate geochemical cycle and its effect on atmospheric carbon dioxide over the past 100 million years. Am J Sci. 1983;283:641–683. doi: 10.2475/ajs.284.10.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Berner RA. Atmospheric carbon dioxide levels over Phanerozoic time. Science. 1990;249:1382–1386. doi: 10.1126/science.249.4975.1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Parsons B. Causes and consequences of the relation between area and age of the ocean floor. J Geophys Res. 1982;87:289–302. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rowley DB. Rate of plate creation and destruction: 180 Ma to present. Geol Soc Am Bull. 2002;114:927–933. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kominz MA. Oceanic ridge volumes and sea-level change: An error analysis. Am Assoc Petroleum Geol Memoir. 1984;36:109–127. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Muller RD, Sdrolias M, Gaina C, Steinberger B, Heine C. Long-term sea-level fluctuations driven by ocean basin dynamics. Science. 2008;319:1357–1362. doi: 10.1126/science.1151540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Raymo ME, Ruddiman WF. Tectonic forcing of late Cenozoic climate. Nature. 1992;359:117–122. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Richter FM, Rowley DB, DePaolo DJ. Sr isotope evolution of seawater: The role of tectonics. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 1992;109:11–23. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hess J, Bender ML, Schilling J-G. Evolution of the ratio of strontium-87 to strontium-86 in seawater from Cretaceous to Present. Science. 1986;231:979–984. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4741.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Walker JCG, Hays PB, Kasting JF. A negative feedback mechanism for the long-term stabilization of Earth's surface-temperature. J Geophys Res Atmos. 1981;86:9776–9782. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen Y, et al. The configuration of Asia prior to the collision of India: Cretaceous paleomagnetic constraints. J Geophys Res. 1993;98:21927–21941. [Google Scholar]
- 28.McKenzie DP, Sclater JG. The evolution of the Indian Ocean since the Late Cretaceous. Geophys J R Astron Soc. 1971;24:437–528. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Patriat P, Achache J. India-Eurasia collision chronology has implications for crustal shortening and driving mechanism of plates. Nature. 1984;311:615–621. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Smith AG, Briden JC, Drewry GE. Organisms and Continents Through Time. London: Paleontological Society; 1973. Phanerozoic world maps; pp. 1–42. Special Papers in Palaeontology 12. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rabinowitz PD, Coffin MF, Falvey D. The separation of Madagascar and Africa. Science. 1983;220:67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.220.4592.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Courtillot VE, Renne PR. On the ages of flood basalt events. C R Geosci. 2003;335:113–140. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Self S, Widdowson M, Thordarson T, Jay AE. Volatile fluxes during flood basalt eruptions and potential effects on the global environment: A Deccan perspective. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 2006;248:518–532. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Caldeira K, Rampino MR. Carbon dioxide emissions from Deccan volcanism and a K/T boundary greenhouse effect. Geophys Res Lett. 1990;17:1299–1302. doi: 10.1029/gl017i009p01299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Allegre CJ, et al. Structure and evolution of the Himalaya-Tibet orogenic belt. Nature. 1984;307:17–22. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cande SC, Kent DV. Revised calibration of the geomagnetic polarity time scale for the Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic. J Geophys Res. 1995;100:6093–6095. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Achache J, Courtillot V, Zhou YX. Paleogeographic and tectonic evolution of southern Tibet since middle Cretaceous time: New paleomagnetic data and synthesis. J Geophys Res. 1984;89:10311–10339. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Garzanti E, Baud A, Mascle G. Sedimentary record of the northward flight of India and its collision with Eurasia (Ladakh Himalaya, India) Geodinamica Acta (Paris) 1987;1:297–312. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Berggren WA, Kent DV, Swisher CC, Aubry MP. A revised Cenozoic geochronology and chronostratigraphy. In: Berggren WA, Kent DV, Aubry M-P, Hardenbol J, editors. Geochronology, Time Scales and Global Stratigraphic Correlations. Tulsa, OK: SEPM (Society for Sedimentary Geology); 1995. pp. 129–212. SEPM Special Volume 54. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Berggren WA, Pearson PN. A revised tropical to subtropical Paleogene planktonic foraminiferal zonation. J Foraminiferal Res. 2005;35:279–298. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rowley DB. Age of initiation of collision between india and Asia: A review of stratigraphic data. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 1996;145:1–13. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Garzanti E. Comment on “When and where did India and Asia collide?” by Jonathan C. Aitchison, Jason R. Ali, and Aileen M. Davis. J Geophys Res. 2008;113:B004411. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hodges KV. Tectonics of the Himalaya and southern Tibet from two perspectives. Geol Soc Am Bull. 2000;112:324–350. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Beck RA, et al. Stratigraphic evidence for an early collision between northwest India and Asia. Nature. 1995;373:55–58. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Honegger K, et al. Magmatism and metamorphism in the Ladakh Himalayas (the Indus-Tsangpo suture zone) Earth Planet Sci Lett. 1982;60:253–292. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Weinberg RF, Dunlap WJ. Growth and deformation of the Ladakh Batholith, Northwest Himalayas: Implications for timing of continental collision and origin of calc-alkaline batholiths. J Geol. 2000;108:303–320. doi: 10.1086/314405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Maheo G, et al. Relicts of an intra-oceanic arc in the Sapi-Shergol melange zone (Ladakh, NW Himalaya, India): Implications for the closure of the Neo-Tethys Ocean. J Asian Earth Sci. 2006;26:695–707. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wilkinson BH, Walker JCG. Phanerozoic cycling of sedimentary carbonate. Am J Sci. 1989;289:525–548. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Berger WH, Winterer EL. Plate stratigraphy and the fluctuating carbonate line. In: Hsu KJ, Jenkins HC, editors. Pelagic Sediments: On Land and Under the Sea. No. 1. Vol 1. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1974. pp. 11–48. Special Publications of the International Association of Sedimentologists. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Volk T. Sensitivity of climate and atmospheric CO2 to deep-ocean and shallow-ocean carbonate burial. Nature. 1989;337:637–640. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Caldeira K. Enhanced Cenozoic chemical weathering and the subduction of pelagic carbonate. Nature. 1992;357:578–581. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kerrick DM, Caldeira K. Was the Himalayan orogen a climatically significant coupled source and sink for atmospheric CO2 during the Cenozoic? Earth Planet Sci Lett. 1999;173:195–203. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kerrick DM, Caldeira K. Metamorphic CO2 degassing from orogenic belts. Chem Geol. 1998;145:213–232. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Evans MJ, Derry LA, France-Lanord C. Degassing of metamorphic carbon dioxide from the Nepal Himalya. Geochem Geophys Geosyst. 2008;9:Q04021. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Marty B, Tolstikhin IN. CO2 fluxes from mid-ocean ridges, arcs and plumes. Chem Geol. 1998;145:233–248. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Edmond JM, Huh Y. Non-steady state carbonate recycling and implications for the evolution of atmospheric PCO2. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 2003;216:125–139. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Broccoli AJ, Dahl KA, Stouffer RJ. Response of the ITCZ to Northern Hemisphere cooling. Geophys Res Lett. 2006;33:L01702. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Crowley TJ, North GR. Paleoclimatology. Oxford: Oxford Univ Press; 1991. p. 349. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Manabe S, Bryan K. CO2-induced change in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model and its paleoclimatic implications. J Geophys Res. 1985;90:11689–11708. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Evans DAD. Proterozoic low orbital obliquity and axial-dipolar geomagnetic field from evaporite palaeolatitudes. Nature. 2006;444:51–55. doi: 10.1038/nature05203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Dessert C, Dupre B, Gaillardet J, Francois L, Allegre C. Basalt weathering laws and the impact of basalt weathering on the global carbon cycle. Chem Geol. 2003;202:257–273. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Das A, Krishnaswamli S, Sarin MM, Pande K. Chemical weathering in the Krishna Basin and Western Ghats of the Deccan Traps, India: Rates of basalt weathering and their controls. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2005;69:2067–2084. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Dessert C, et al. Erosion of Deccan Traps determined by river geochemistry: Impact on the global climate and the 87Sr/86Sr ratio of seawater. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 2001;188:459–474. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Schmidt PW, Prasad V, Ramam PK. Magnetic ages of some Indian laterites. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. 1983;44:185–202. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kumar A. Palaeolatitudes and the age of Indian laterites. Palaegeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. 1986;53:231–237. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Turekian KK, Pegram WJ. Os isotope record in a Cenozoic deep-sea core: Its relation to global tectonics and climate. In: Ruddiman W, editor. Tectonic Uplift and Climate Change. New York: Plenum Press; 1997. pp. 383–397. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ravizza G, Peucker-Ehrenbrink B. Chemostratigraphic evidence of Deccan volcanism from the marine osmium isotope record. Science. 2003;302:1392–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.1089209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Vonhof HB, Smit J. High-resolution late Maastrichtian-early Danian oceanic 87Sr/86Sr record: Implications for Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary events. Geology. 1997;25:347–350. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Edmond JM. Himalayan tectonics, weathering processes, and the strontium isotope record in marine limestones. Science. 1992;258:1594–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.258.5088.1594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Raymo ME, Ruddiman WF, Froelich PN. Influence of late Cenozoic mountain building on ocean geochemical cycles. Geology. 1988;16:649–653. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Najman Y, Bickle M, Chapman H. Early Himalayan exhumation: Isotopic constraints from the Indian foreland basin. Terra Nova. 2000;12(1):28–34. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Najman Y, et al. The Paleogene record of Himalayan erosion: Bengal Basin, Bangladesh. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 2008;273:1–14. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Molnar P. Closing of the Central American Seaway and the Ice Age: A critical review. Paleoceanography. 2008;23:PA2201. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Pagani M, Arthur MA, Freeman KH. Miocene evolution of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Paleoceanography. 1999;14:273–292. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kuerschner WM, Kvacek Z, Dilcher DL. The impact of Miocene atmospheric carbon dioxide fluctuations on climate and the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:449–453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708588105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Caldeira K, Rampino MR. The mid-Cretaceous super plume, carbon dioxide, and global warming. Geophys Res Lett. 1991;18:987–990. doi: 10.1029/91gl01237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Broecker WS, Sanyal A. Does atmospheric CO2 police the rate of chemical weathering? Global Biogeochem Cycles. 1998;12:403–408. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Francois LM, Walker JCG. Modelling the Phanerozoic carbon cycle and climate: Constraints from the 87Sr/86Sr isotopic ratio of seawater. Am J Sci. 1992;292:81–135. doi: 10.2475/ajs.292.2.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Zeebe RE, Caldeira K. Close mass balance of long-term carbon fluxes from ice-core CO2 and ocean chemistry records. Nat Geosci. 2008;1:312–315. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Hoffman PF, Kaufman AJ, Halverson GP, Schrag DP. A Neoproterozoic snowball Earth. Science. 1998;281:1342–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5381.1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Retallack GJ. A 300-million-year record of atmospheric carbon dioxide from fossil plant cuticles. Nature. 2001;411:287–290. doi: 10.1038/35077041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Van Der Burgh J, Visscher H, Dilcher DL, Kurschner WM. Paleoatmospheric signatures in Neogene fossil leaves. Science. 1993;260:1788–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.260.5115.1788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Royer DL. CO2-forced climate thresholds during the Phanerozoic. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2006;70:5665–5675. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Besse J, Courtillot V. Apparent and true polar wander and the geometry of the geomagnetic field over the last 200 Myr. J Geophys Res. 2002;107:2300. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Klootwijk CT. Palaeomagnetism of the Upper Gondwana Rajmahal Traps, Northeast India. Tectonophysics. 1971;12:449–467. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Meert JG, Tamrat E. Paleomagnetic evidence for a stationary Marion hotspot: Additional paleomagnetic from Madagascar. Gondwana Res. 2006;10:340–348. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Vandamme D, Courtillot V, Besse J, Montigny R. Paleomagnetism and age determinations of the Deccan Traps (India): Results of a Nagpur-Bombay traverse and review of earlier work. Rev Geophys. 1991;29:159–190. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Kidane T, Abebe B, Courtillot V, Herrero E. New paleomagnetic result from the Ethiopian flood basalts in the Abbay (Blue Nile) and Kessem gorges. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 2002;203:353–367. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Petterson MG, Treloar PJ. Volcanostratigraphy of arc volcanic sequences in the Kohistan arc, North Pakistan: Volcanism within island arc, back-arc-basin, and intra-continental tectonic settings. J Volcanol Geotherm Res. 2004;130:147–178. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Rolland Y, et al. The Cretaceous Ladakh arc of NW Himalaya—Slab melting and melt–mantle interaction during fast northward drift of Indian Plate. Chem Geol. 2002;182:139–178. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Cogné JP. PaleoMac: A Macintosh™ application for treating paleomagnetic data and making plate reconstructions. Geochem Geophys Geosyst. 2003;4 doi: 10.1029/2001GC000227. [DOI] [Google Scholar]