Abstract
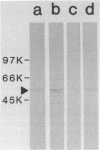
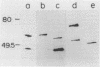
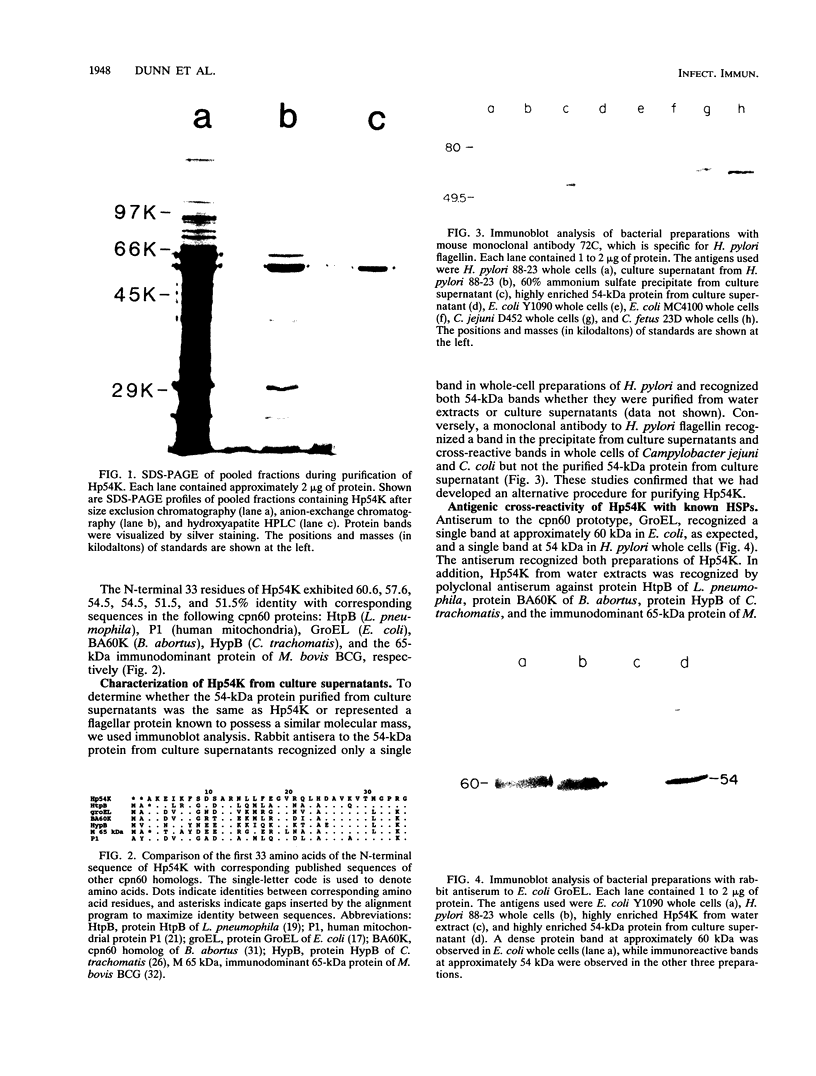
Helicobacter pylori is associated with gastritis and peptic ulcer disease in humans. We have identified a homolog of the chaperonin cpn60 family of heat shock proteins in H. pylori, referred to as Hp54K. Hp54K, purified from water-extractable H. pylori proteins, migrated as a single band at 54 kDa by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Its native molecular mass was 740 kDa; thus, Hp54K apparently comprises a 14-mer. The N-terminal 33 residues of Hp54K exhibited 60.6, 57.6, 54.5, 54.5, 51.5, and 51.5% identity with corresponding sequences in the following cpn60 homologs: HtpB (Legionella pneumophila), P1 (human mitochondria), GroEL (Escherichia coli), BA60K (Brucella abortus), HypB (Chlamydia trachomatis), and the 65-kDa immunodominant protein of Mycobacterium bovis BCG, respectively. Hp54K was the only protein recognized in whole-cell preparations of H. pylori by immunoblotting using monospecific antisera against cpn60 homologs from L. pneumophila, E. coli, C. trachomatis, and M. bovis BCG. Antiserum against Hp54K recognized proteins with molecular masses of 50 to 60 kDa in a large number of gram-negative bacteria, consistent with the known highly conserved nature of cpn60 proteins. Hp54K is a major protein and is immunogenic in humans infected with H. pylori. Thus, Hp54K shares many similarities with known cpn60 homologs. On the basis of the proposed role of other cpn60 proteins in induction of chronic inflammation, immune cross-reactivity between Hp54K and gastric tissue may provide an important link between H. pylori infection and gastritis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin J. W., Doig P., Stewart M., Trust T. J. Macromolecular structure and aggregation states of Helicobacter pylori urease. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5663–5667. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5663-5667.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):626–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Reardon C., Kubo R., Shinnick T., Brennan P., O'Brien R. Recognition of heat shock proteins and gamma delta cell function. Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):40–43. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Dooley C. P., Blaser M. J. Characterization of and human serologic response to proteins in Helicobacter pylori broth culture supernatants with vacuolizing cytotoxin activity. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):603–610. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.603-610.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Molecular chaperones. Unfolding protein folding. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):17–18. doi: 10.1038/352017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czinn S., Carr H., Sheffler L., Aronoff S. Serum IgG antibody to the outer membrane proteins of Campylobacter pylori in children with gastroduodenal disease. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):586–589. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Campbell G. P., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Purification and characterization of urease from Helicobacter pylori. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9464–9469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting of Campylobacter pylori proteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1825–1833. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1825-1833.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Sung C. C., Taylor N. S., Fox J. G. Purification and characterization of Helicobacter mustelae urease. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3343–3345. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3343-3345.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J. The molecular chaperone concept. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engstrand L., Scheynius A., Påhlson C. An increased number of gamma/delta T-cells and gastric epithelial cell expression of the groEL stress-protein homologue in Helicobacter pylori-associated chronic gastritis of the antrum. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991 Aug;86(8):976–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goloubinoff P., Christeller J. T., Gatenby A. A., Lorimer G. H. Reconstitution of active dimeric ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from an unfoleded state depends on two chaperonin proteins and Mg-ATP. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):884–889. doi: 10.1038/342884a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Evans D. J., Jr, Graham D. Y. Helicobacter pylori catalase. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Jan;137(1):57–61. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Purification and properties of groE, a host protein involved in bacteriophage assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Houston L., Butler C. A. Legionella pneumophila htpAB heat shock operon: nucleotide sequence and expression of the 60-kilodalton antigen in L. pneumophila-infected HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3380–3387. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3380-3387.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Hohn B., Engel A., Wurtz M., Smith P. R. Isolation and characterization of the host protein groE involved in bacteriophage lambda assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):359–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90501-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jindal S., Dudani A. K., Singh B., Harley C. B., Gupta R. S. Primary structure of a human mitochondrial protein homologous to the bacterial and plant chaperonins and to the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Schoel B., Wand-Württenberger A., Steinhoff U., Munk M. E., Koga T. T-cells, stress proteins, and pathogenesis of mycobacterial infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;155:125–141. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74983-4_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostrzynska M., Betts J. D., Austin J. W., Trust T. J. Identification, characterization, and spatial localization of two flagellin species in Helicobacter pylori flagella. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):937–946. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.937-946.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunk R. D., Johnson P. T., David B. C., Kraft W. G., Morgan D. R. Cytotoxic activity in broth-culture filtrates of Campylobacter pylori. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(2):93–99. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-2-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J. Campylobacter pylori: its link to gastritis and peptic ulcer disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12 (Suppl 1):S87–S93. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_1.s87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Su H., Lyng K., Yuan Y. The Chlamydia trachomatis hyp operon is homologous to the groE stress response operon of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2701–2705. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2701-2705.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrini R., Lisato L., Zanella I., Cavazzini L., Gullini S., Villanacci V., Poiesi C., Albertini A., Ghielmi S. Helicobacter pylori infection induces antibodies cross-reacting with human gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1991 Aug;101(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90023-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G. Identification of the outer membrane proteins of Campylobacter pyloridis and antigenic cross-reactivity between C. pyloridis and C. jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jan;133(1):163–170. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Conservation and diversity of Campylobacter pyloridis major antigens. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1256–1263. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1256-1263.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson W. L. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 11;324(15):1043–1048. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104113241507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Sweetser D., Thole J., van Embden J., Young R. A. The etiologic agents of leprosy and tuberculosis share an immunoreactive protein antigen with the vaccine strain Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1932–1935. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1932-1935.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton antigen is a heat shock protein which corresponds to common antigen and to the Escherichia coli GroEL protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.446-451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B. Chaperonins and the immune response. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):27–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]