Abstract
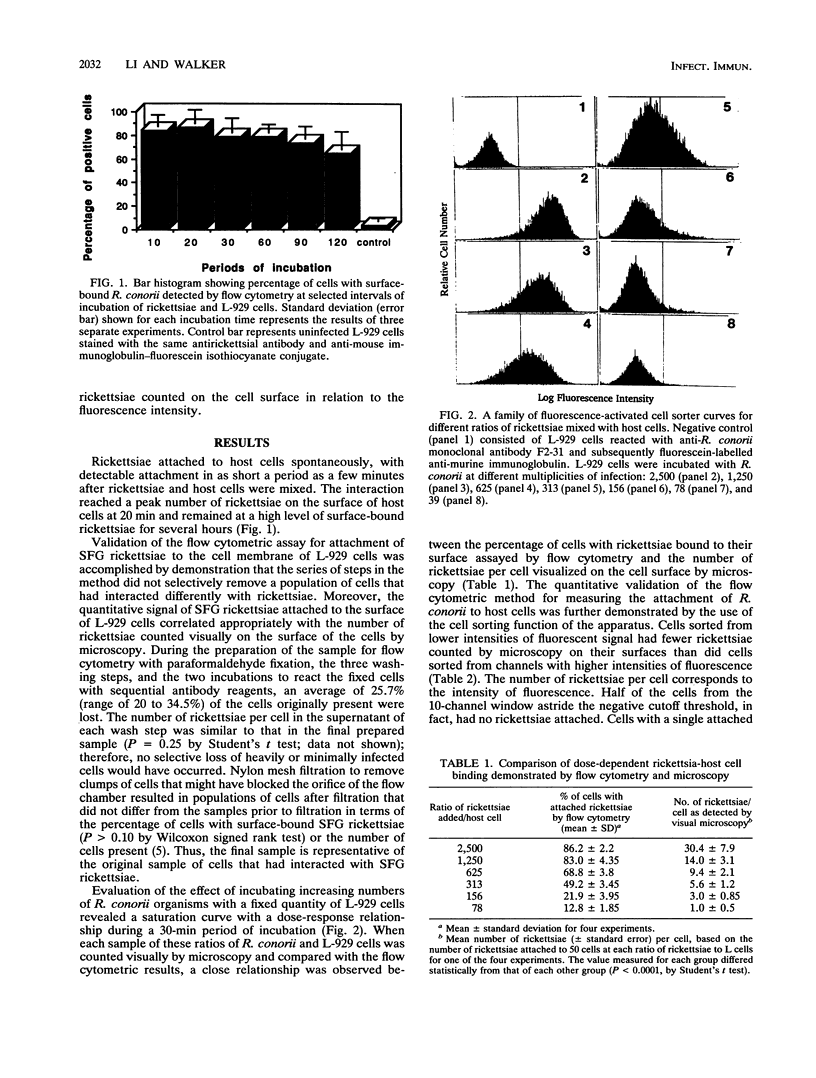
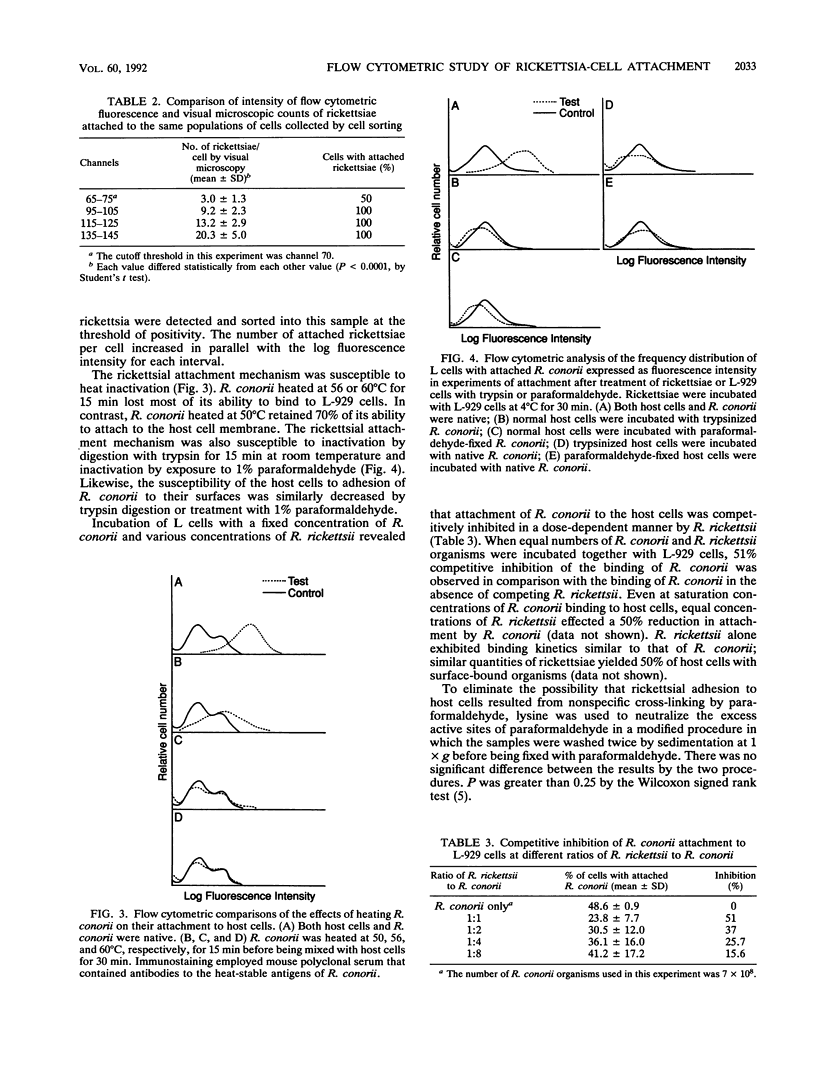
The mechanisms of rickettsial attachment have been studied by measuring quantitative changes in rickettsial binding to host cells by flow cytometry after different treatments of the rickettsiae and host cells. Time-dependent binding of Rickettsia conorii to host cells was demonstrated by the increasing intensity of host cell surface fluorescence of rickettsia-host cell combinations when examined with a rickettsia-specific monoclonal antibody. More than 70% of host cells had intensity of fluorescence above the threshold value after 10 min of incubation, owing to rickettsiae bound to the cell surface, and the greatest fluorescence intensity indicative of binding occurred at 20 min. The binding kinetics was rickettsial dose dependent. The binding of rickettsiae to host cells was greatly decreased when host cells or rickettsiae were treated with 1% paraformaldehyde for 30 min or 0.25% trypsin for 5 or 15 min, respectively. Rickettsiae that were heated at 56 degrees C for 15 min lost more than 80% of their ability to attach to host cells. R. rickettsii, an organism closely related to R. conorii, competitively inhibited the attachment of R. conorii (51% inhibition when mixed in equal numbers). These results indicate that the rickettsial binding structures are trypsin and heat sensitive and likely to be surface proteins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., List R. H., Mann R. E., Hayes S. F., Thomas L. A. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies protecting mice against Rickettsia rickettsii. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1052–1060. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anacker R. L., McDonald G. A., List R. H., Mann R. E. Neutralizing activity of monoclonal antibodies to heat-sensitive and heat-resistant epitopes of Rickettsia rickettsii surface proteins. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):825–827. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.825-827.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl M., Dasch G. A. The importance of the crystalline surface layer protein antigens of rickettsiae in T-cell immunity. J Autoimmun. 1989 Jun;2 (Suppl):81–91. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. A., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A., Silverman D. J. Some characteristics of heavy and light bands of Rickettsia prowazekii on Renografin gradients. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):596–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.596-604.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Eisemann C. S. Role of T-lymphocytes in production of antibody to antigens of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi and other Rickettsia species. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):666–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.666-674.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. V., Walker D. H. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Rickettsia rickettsii. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):289–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.289-294.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Zable B., Bard J. Binding, ingestion, and growth of Chlamydia trachomatis (L2 serovar) analyzed by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1986 Jul;7(4):378–383. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990070413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Jerrells T. R., Spitalny G. L., Walker D. H. Gamma interferon as a crucial host defense against Rickettsia conorii in vivo. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1252–1255. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1252-1255.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Lenz B., Walker D. H. Protective monoclonal antibodies recognize heat-labile epitopes on surface proteins of spotted fever group rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2587–2593. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2587-2593.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Walker D. H. Biological characterization of major polypeptides on the surface of spotted fever group rickettsiae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:389–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Identification of cholesterol in the receptor site for rickettsiae on sheep erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):120–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.120-126.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Fiset P., Wisseman C. L., Jr Simple, differential staining technique for enumerating rickettsiae in yolk sac, tissue culture extracts, or purified suspensions. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):437–440. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.437-440.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman F. M., Hadley W. K., Fulwyler M. J., Schachter J. Flow cytometric analysis of Chlamydia trachomatis interaction with L cells. Cytometry. 1987 Jan;8(1):55–59. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990080109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Crawford C. G., Cain B. G. Rickettsial infection of the pulmonary microcirculation: the basis for interstitial pneumonitis in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Hum Pathol. 1980 May;11(3):263–272. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Gear J. H. Correlation of the distribution of Rickettsia conorii, microscopic lesions, and clinical features in South African tick bite fever. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Mar;34(2):361–371. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S. Rickettsial interactions with human endothelial cells in vitro: adherence and entry. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):205–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.205-210.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Penetration of cultured mouse fibroblasts (L cells) by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Inhibitory and restorative effects of adenine nucleotides on rickettsial adsorption and hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):119–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.119-126.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D. In vitro studies on rickettsia-host cell interactions: intracellular growth cycle of virulent and attenuated Rickettsia prowazeki in chicken embryo cells in slide chamber cultures. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1391-1401.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Silverman D. J. In vitro studies on Rickettsia-host cell interactions: lag phase in intracellular growth cycle as a function of stage of growth of infecting Rickettsia prowazeki, with preliminary observations on inhibition of rickettsial uptake by host cell fragments. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1749–1760. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1749-1760.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



