Abstract
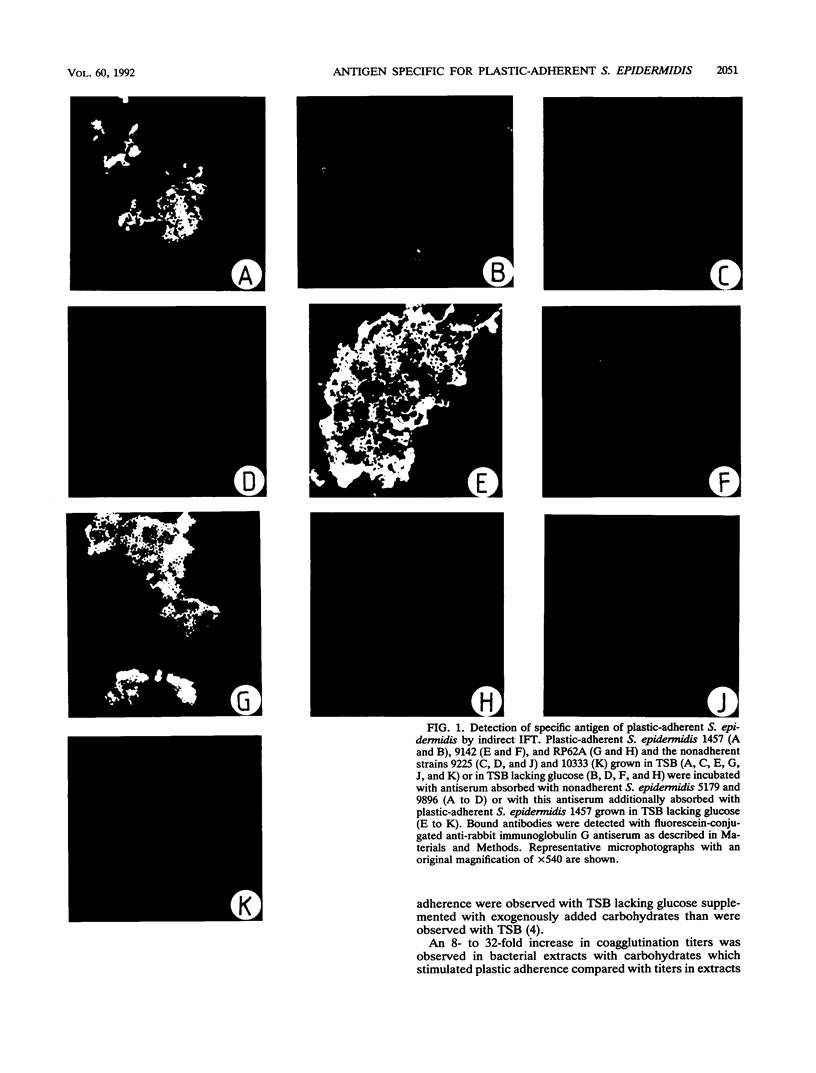
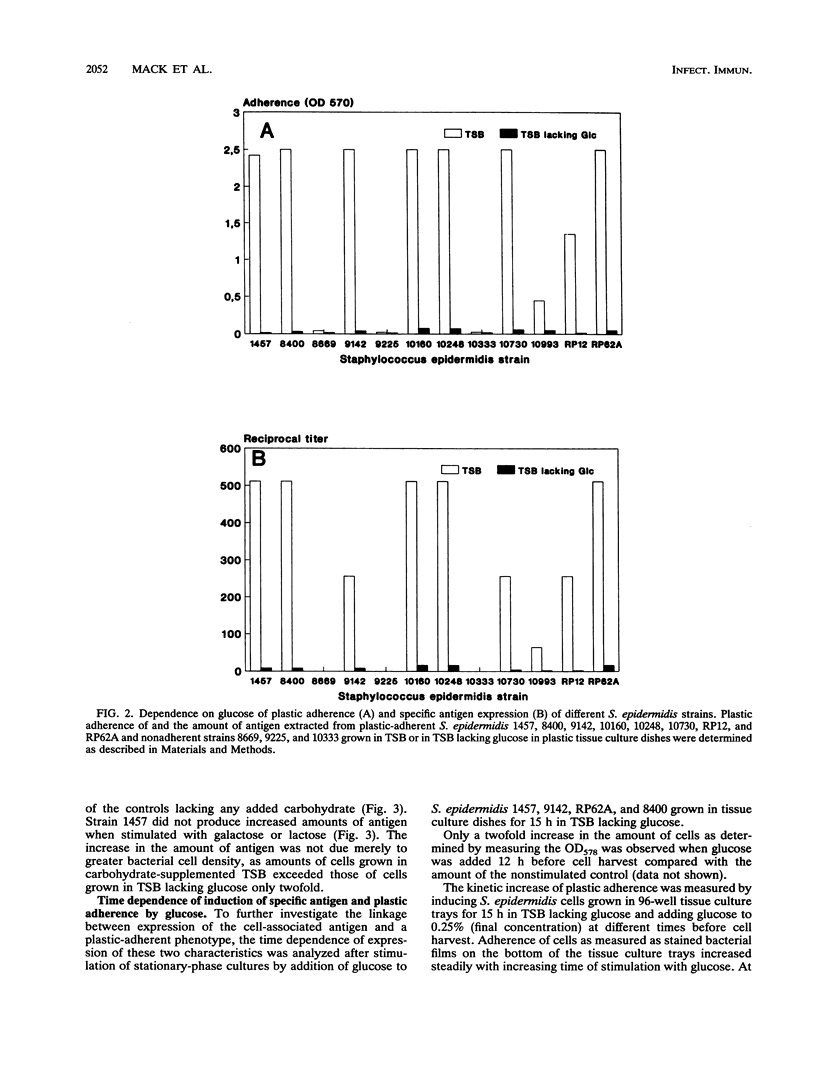
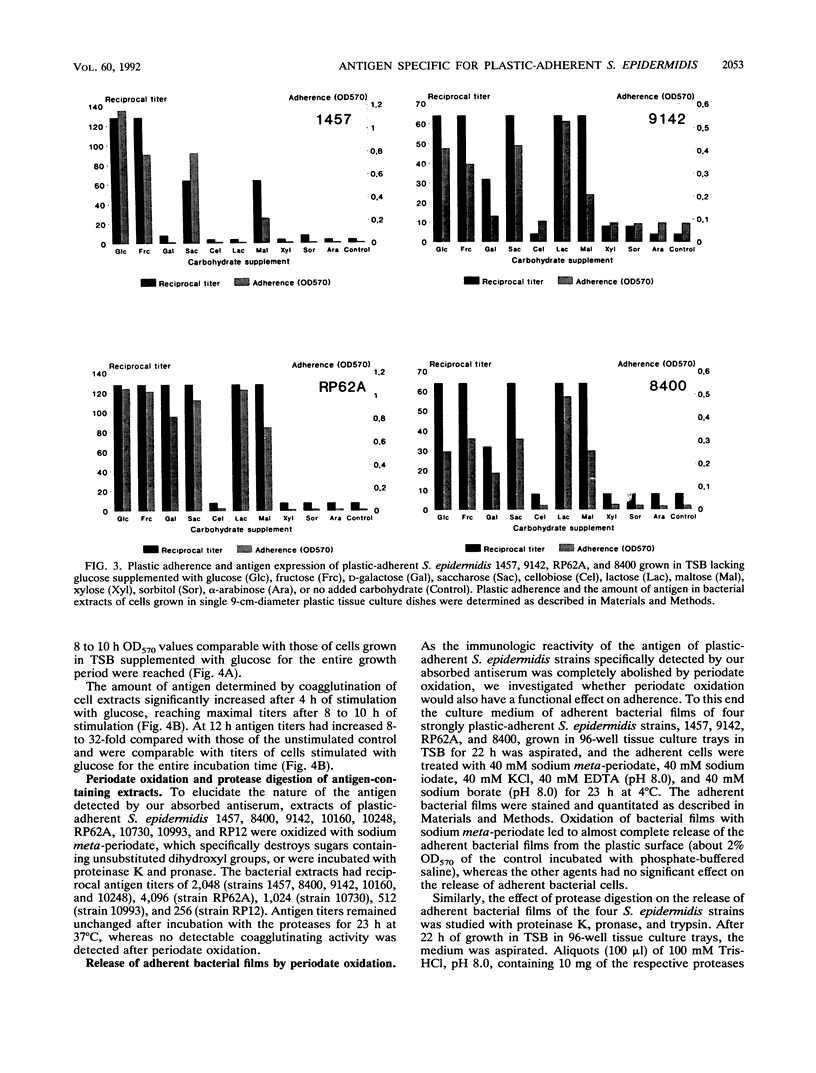
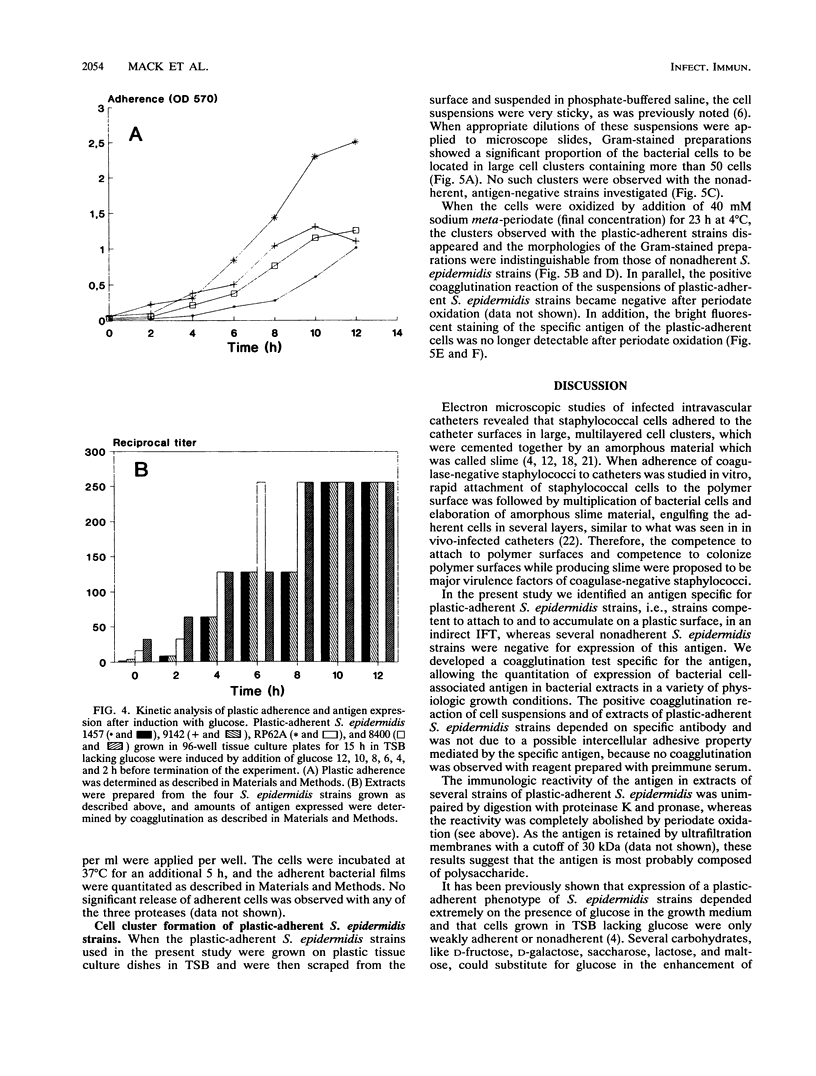
The initial attachment and the accumulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis on polymer surfaces in multilayered cell clusters embedded in amorphous slime, which together lead to the plastic-adherent phenotype detected by the adherence assay used in this study, have been proposed to be major virulence factors of these bacteria. An antigen specific for plastic-adherent S. epidermidis strains was detected by an indirect immunofluorescence test using absorbed antiserum raised against the strongly plastic-adherent S. epidermidis 1457. A coagglutination assay was established, which allowed the quantitation of the antigen in bacterial extracts under different physiologic growth conditions. Expression of the antigen and of plastic adherence depended significantly on the presence of glucose in the growth medium. Parallel to increased plastic adherence, a 32- to 64-fold increase in the amount of the antigen was detected in bacterial extracts of cells grown in tryptone soya broth (TSB) compared with that in extracts of cells grown in TSB lacking glucose. A parallel time-dependent increase of plastic adherence and expression of the antigen was observed after stimulation by glucose of stationary-phase cultures of plastic-adherent S. epidermidis strains grown in TSB lacking glucose. The antigen consisted most probably of polysaccharide, because its immunologic reactivity was completely abolished by periodate oxidation but was resistant to protease digestion. A significant proportion of cells of plastic-adherent as compared with nonadherent S. epidermidis strains grown in TSB were located in large cell clusters exceeding 50 cells, which completely disintegrated after periodate oxidation of the cell preparations. Periodate oxidation of adherent bacterial films in situ led to release of the adherent cells from the plastic surface. These results strongly indicate a functional relation of the antigen to adherence of S. epidermidis to polymer surfaces, most probably by mediating intercellular adhesion of cells leading to accumulation in multilayered cell clusters.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensen G. D., Baddour L. M., Simpson W. A. Phenotypic variation of Staphylococcus epidermidis slime production in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2870–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2870-2877.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Barker L. P., Mawhinney T. P., Baddour L. M., Simpson W. A. Identification of an antigenic marker of slime production for Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2906–2911. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2906-2911.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Experimental foreign body infections in mice challenged with slime-producing Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):407–410. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.407-410.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Younger J. J., Baddour L. M., Barrett F. F., Melton D. M., Beachey E. H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.996-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd Genetic analysis of Streptococcus mutans virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:253–277. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport D. S., Massanari R. M., Pfaller M. A., Bale M. J., Streed S. A., Hierholzer W. J., Jr Usefulness of a test for slime production as a marker for clinically significant infections with coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):332–339. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deighton M. A., Balkau B. Adherence measured by microtiter assay as a virulence marker for Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2442–2447. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2442-2447.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Mitoma F., Harding G. K., Hoban D. J., Roberts R. S., Low D. E. Clinical significance of a test for slime production in ventriculoperitoneal shunt infections caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):555–560. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne W. M., Jr, Nelson D. B., Chusid M. J. Epidemiologic markers of pediatric infections caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Nov;6(11):1031–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson T. R., Sheth N. K., Rose H. D., Sohnle P. G. Scanning electron microscopy of bacteria adherent to intravascular catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.500-505.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak M. A., Gröschel D. H., Mandell G. L., Wenzel R. P. Association of slime with pathogenicity of coagulase-negative staphylococci causing nosocomial septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1025-1029.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Davidson R. S., McNamee K. C., Russell G., Goodwin D., Holborow E. J. Fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy: a study of the phenomenon and its remedy. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 17;55(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Tojo M., Goldmann D. A., Tosteson T. D., Pier G. B. Antibody to the capsular polysaccharide/adhesin protects rabbits against catheter-related bacteremia due to coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):435–441. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Costerton J. W. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of in situ bacterial colonization of intravenous and intraarterial catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):687–693. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.687-693.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchison H., Larrimore S., Curtiss R., 3rd Isolation and characterization of Streptococcus mutans mutants defective in adherence and aggregation. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1044–1055. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1044-1055.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):479–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Microbial colonization of prosthetic devices. II. Scanning electron microscopy of naturally infected intravenous catheters. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1981;173(5):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Herwaldt L. A. Laboratory, clinical, and epidemiological aspects of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jul;1(3):281–299. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staat R. H., Langley S. D., Doyle R. J. Streptococcus mutans adherence: presumptive evidence for protein-mediated attachment followed by glucan-dependent cellular accumulation. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):675–681. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.675-681.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo M., Yamashita N., Goldmann D. A., Pier G. B. Isolation and characterization of a capsular polysaccharide adhesin from Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):713–722. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younger J. J., Christensen G. D., Bartley D. L., Simmons J. C., Barrett F. F. Coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from cerebrospinal fluid shunts: importance of slime production, species identification, and shunt removal to clinical outcome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):548–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]