Abstract
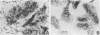
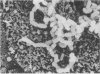
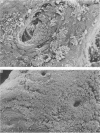
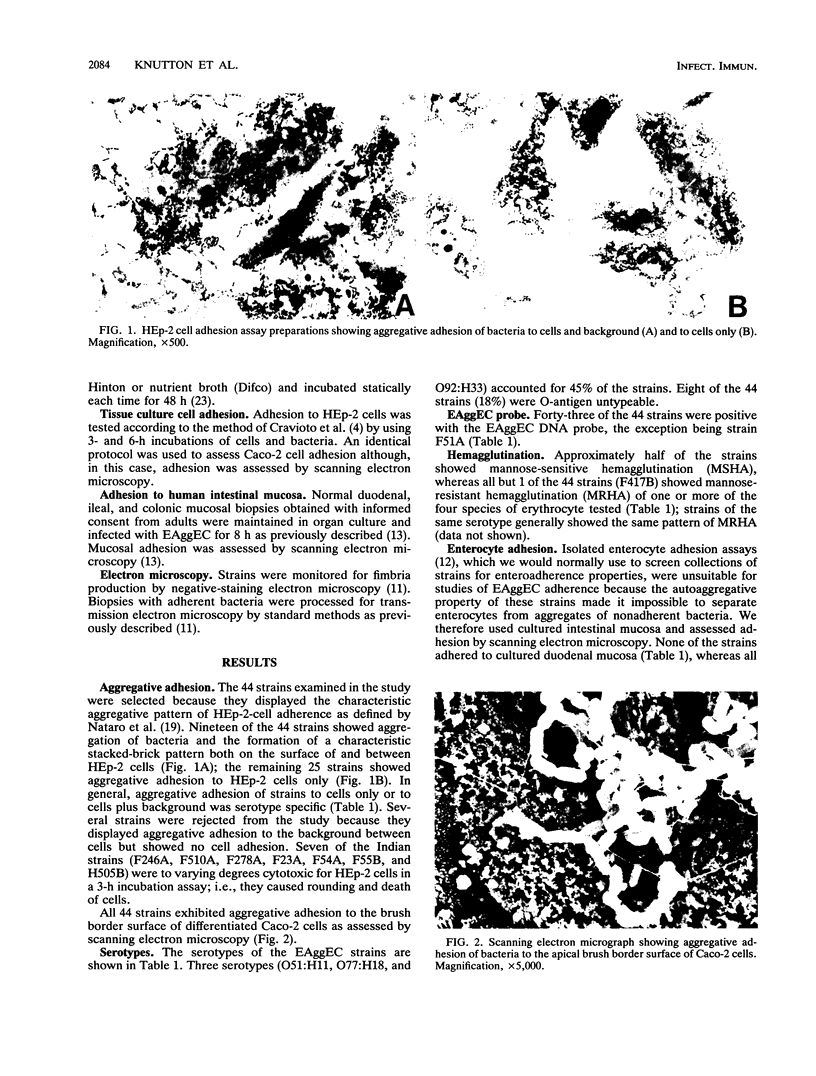
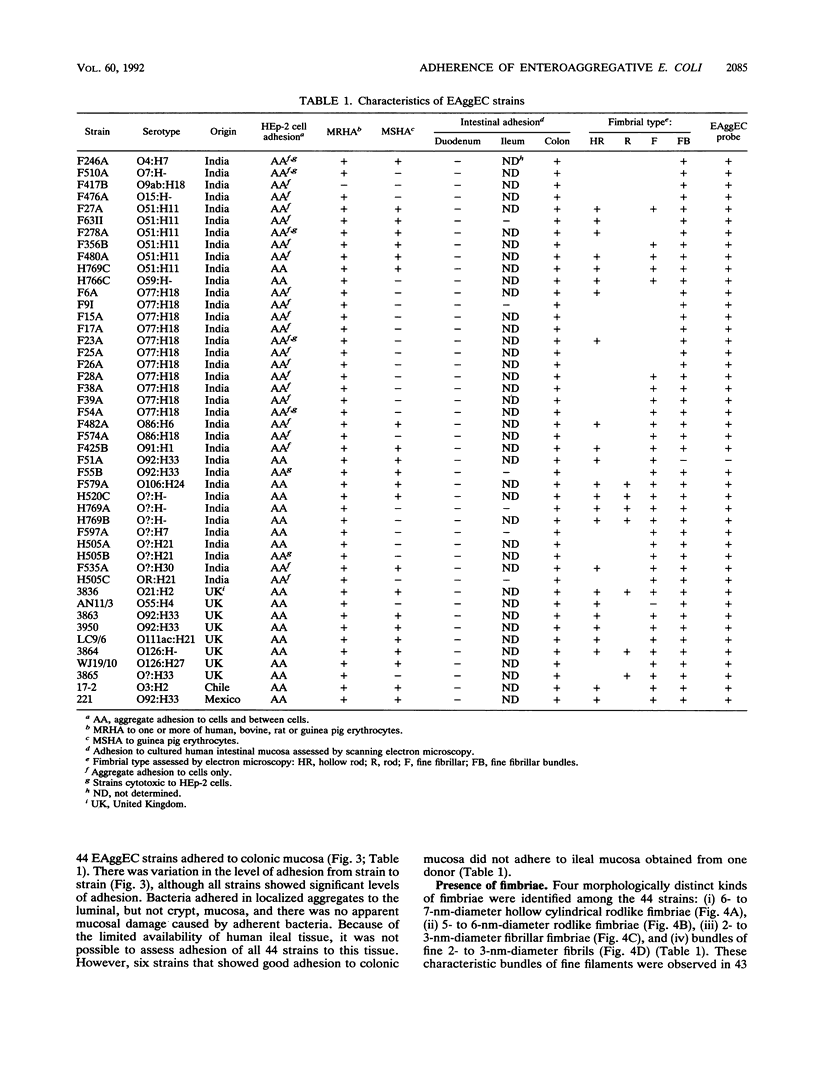
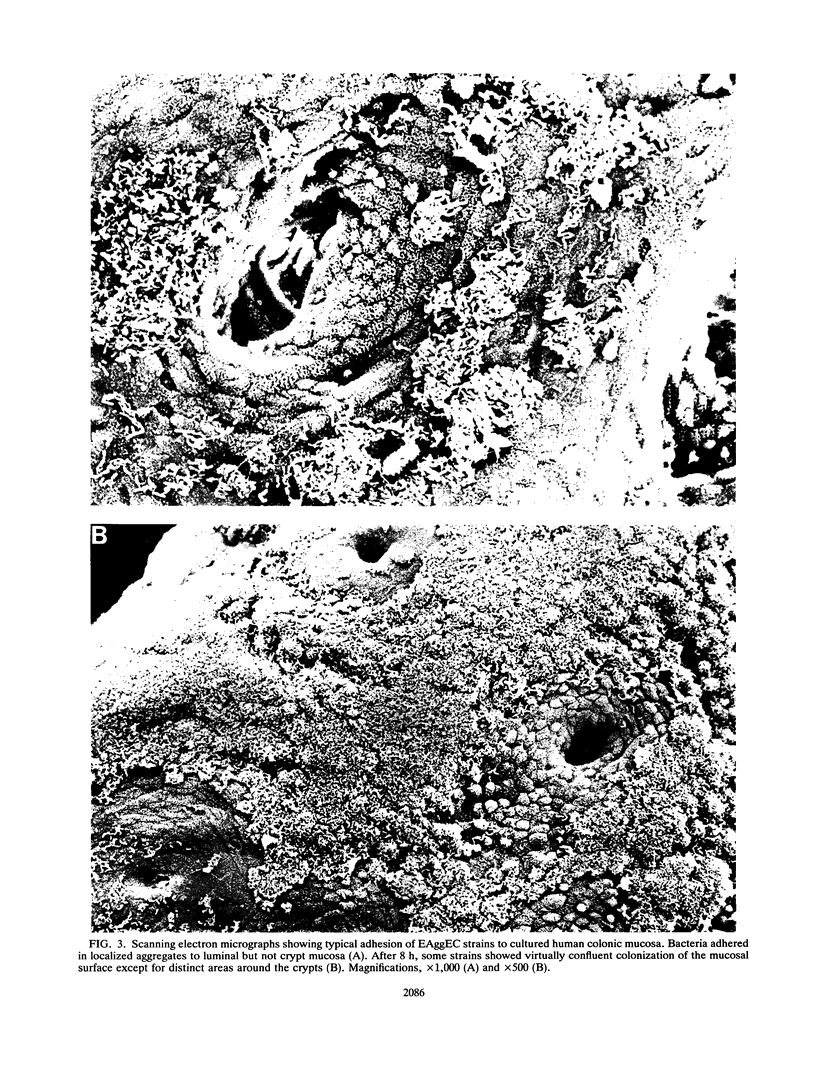
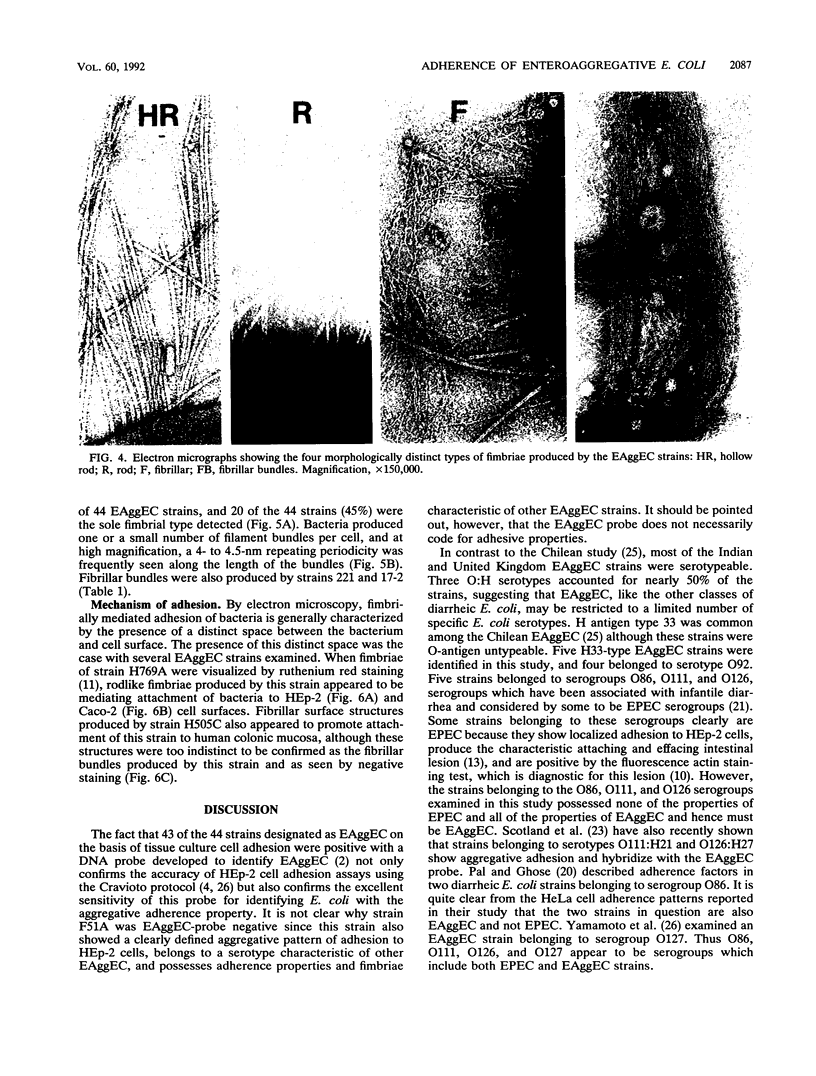
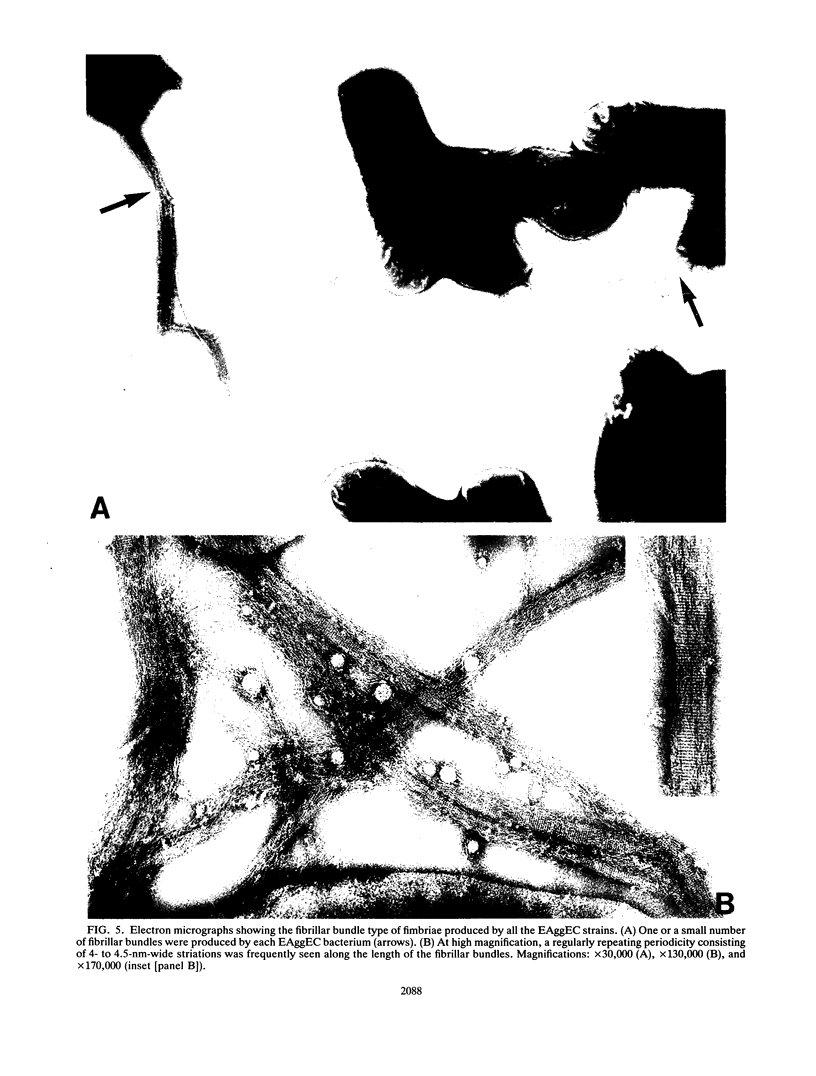
A collection of 44 enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAggEC) strains isolated from infants with diarrhea in India and the United Kingdom were examined for their ability to adhere in vitro to human intestinal mucosa and by electron microscopy for production of putative adherence factors. None of the strains adhered to human duodenal mucosa, and six strains tested did not adhere to ileal mucosa; all 44 strains, however, adhered to human colonic mucosa in localized aggregates. Electron microscopy of infected colonic mucosa indicated fimbrially mediated adhesion of the EAggEC strains. Four morphologically distinct kinds of fimbriae, including a new morphological type of E. coli fimbriae consisting of bundles of fine filaments, were identified among the EAggEC strains; this new type of fimbria was observed in 43 of the 44 EAggEC strains. Forty-three of the 44 EAggEC strains were positive with a DNA probe developed to identify EAggEC, and most of the strains belonged to serotypes unrelated to the other major classes of diarrheic E. coli. These results suggest that EAggEC may be a large-bowel pathogen and colonize the colon by a fimbrially mediated adhesion mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. J., Knutton S., Sellers L., Hernandez H. A., Aitken A., Williams P. H. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli strains secrete a heat-labile toxin antigenically related to E. coli hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2092–2095. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2092-2095.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry B., Savarino S. J., Vial P., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M. A sensitive and specific DNA probe to identify enteroaggregative Escherichia coli, a recently discovered diarrheal pathogen. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1249–1251. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan M. K., Raj P., Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Bhandari N., Srivastava R., Kumar R., Sazawal S. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli associated with persistent diarrhea in a cohort of rural children in India. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jun;159(6):1061–1064. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cravioto A., Tello A., Navarro A., Ruiz J., Villafán H., Uribe F., Eslava C. Association of Escherichia coli HEp-2 adherence patterns with type and duration of diarrhoea. Lancet. 1991 Feb 2;337(8736):262–264. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90868-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girón J. A., Ho A. S., Schoolnik G. K. An inducible bundle-forming pilus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):710–713. doi: 10.1126/science.1683004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girón J. A., Jones T., Millán-Velasco F., Castro-Muñoz E., Zárate L., Fry J., Frankel G., Moseley S. L., Baudry B., Kaper J. B. Diffuse-adhering Escherichia coli (DAEC) as a putative cause of diarrhea in Mayan children in Mexico. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):507–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. H., Vial P. A., Kaper J. B., Mekalanos J. J., Levine M. M. Morphological studies on fimbriae expressed by Vibrio cholerae 01. Microb Pathog. 1988 Apr;4(4):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., Candy D. C., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to human small intestinal enterocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):824–831. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.824-831.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., Candy D. C., McNeish A. S. Ultrastructural study of adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to erythrocytes and human intestinal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.519-527.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal enterocytes and cultured human intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.69-77.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Phillips A. D., Smith H. R., Gross R. J., Shaw R., Watson P., Price E. Screening for enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in infants with diarrhea by the fluorescent-actin staining test. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):365–371. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.365-371.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson J. J., Johnson P. C., DuPont H. L., Satterwhite T. K., Winsor D. K. Pathogenicity of enteroadherent Escherichia coli in adult volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):524–527. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Kaper J. B., Robins-Browne R., Prado V., Vial P., Levine M. M. Patterns of adherence of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Sep;6(9):829–831. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198709000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Ghose A. C. Identification of plasmid-encoded mannose-resistant hemagglutinin and HEp-2 and HeLa cell adherence factors of two diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains belonging to an enteropathogenic serogroup. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1106–1113. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1106-1113.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M. Traditional enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of infantile diarrhea. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):28–53. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savarino S. J., Fasano A., Robertson D. C., Levine M. M. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli elaborate a heat-stable enterotoxin demonstrable in an in vitro rabbit intestinal model. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1450–1455. doi: 10.1172/JCI115151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Said B., Willshaw G. A., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Identification of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated in Britain as enteroaggregative or as members of a subclass of attaching-and-effacing E. coli not hybridising with the EPEC adherence-factor probe. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Nov;35(5):278–283. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-5-278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial P. A., Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L., Guers L., Levine M. M. Comparison of two assay methods for patterns of adherence to HEp-2 cells of Escherichia coli from patients with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):882–885. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.882-885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial P. A., Robins-Browne R., Lior H., Prado V., Kaper J. B., Nataro J. P., Maneval D., Elsayed A., Levine M. M. Characterization of enteroadherent-aggregative Escherichia coli, a putative agent of diarrheal disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):70–79. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Endo S., Yokota T., Echeverria P. Characteristics of adherence of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli to human and animal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3722–3739. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3722-3739.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]