Abstract
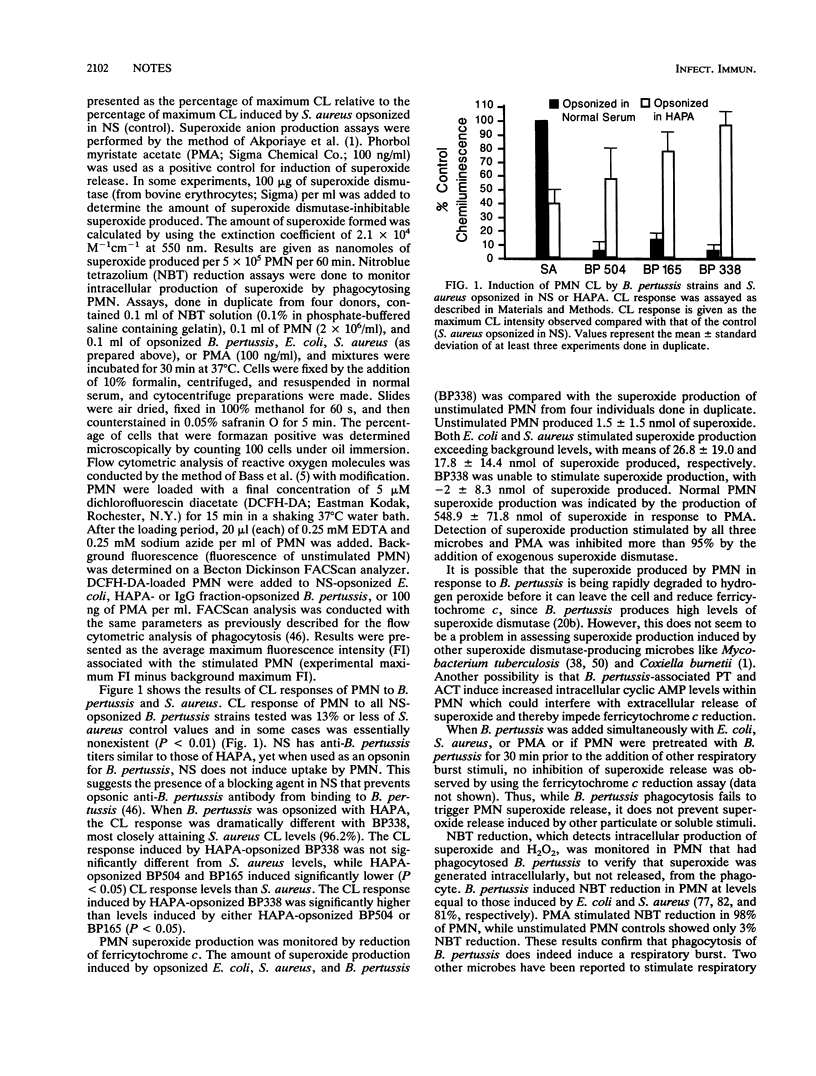
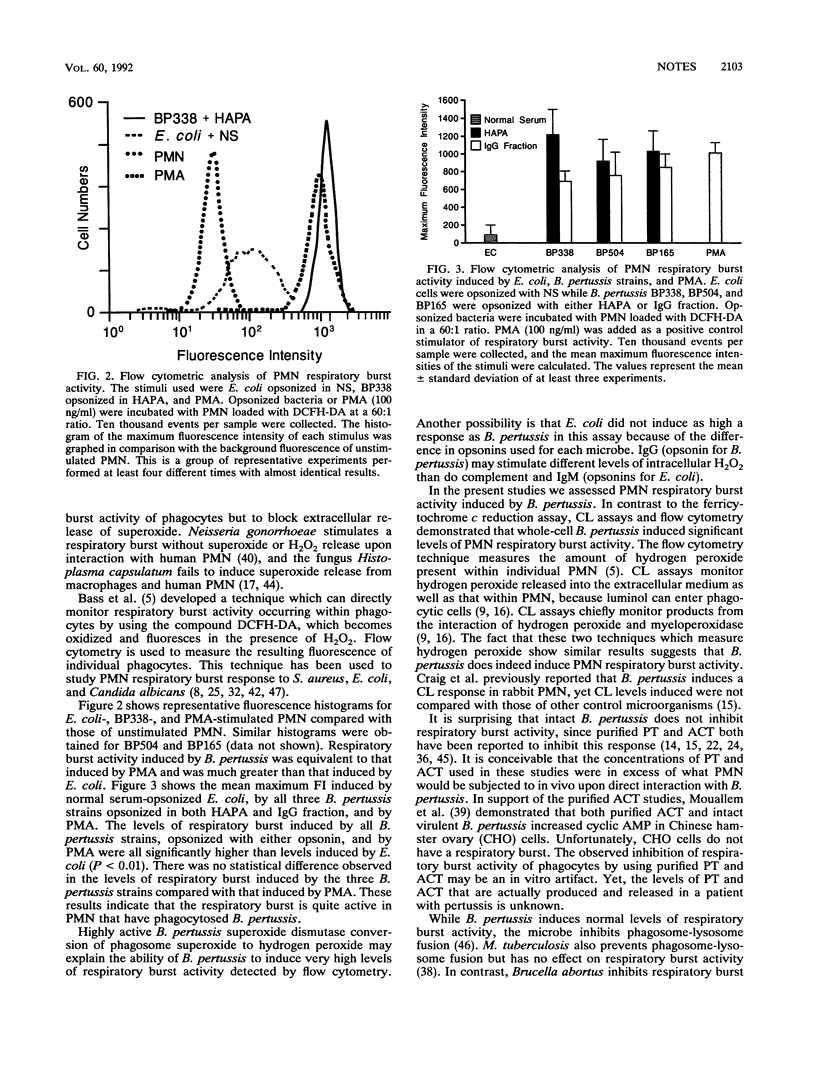
Virulent Bordetella pertussis strains survive intracellularly within human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN), at least in part because of inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion (L. L. Steed, M. Setareh, and R. L. Friedman, J. Leukocyte Biol. 50:321-330, 1991). Further investigations were done to determine if B. pertussis also inhibited respiratory burst activity of PMN as an additional mechanism of intracellular survival. Chemiluminescence and flow cytometry assays showed that B. pertussis induced significant levels of hydrogen peroxide production. In contrast, ferricytochrome c reduction showed that B. pertussis suppressed extracellular release of superoxide. PMN intracellular reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium verified that superoxide was indeed produced intracellularly during B. pertussis phagocytosis. Therefore, B. pertussis does not inhibit production of superoxide but inhibits only its release. Thus, while phagosome-lysosome fusion is inhibited by B. pertussis, respiratory burst activity of PMN occurs at normal levels.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akporiaye E. T., Stefanovich D., Tsosie V., Baca G. Coxiella burnetii fails to stimulate human neutrophil superoxide anion production. Acta Virol. 1990 Feb;34(1):64–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of normal and activated human macrophages on Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1154–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M. J., Kowalski-Saunders P., Gurney S., Tolcher R., Bull F. G., Wright R. Reduction of ferricytochrome C may underestimate superoxide production by monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. The respiratory burst of phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):599–601. doi: 10.1172/JCI111249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. A., Parce J. W., Dechatelet L. R., Szejda P., Seeds M. C., Thomas M. Flow cytometric studies of oxidative product formation by neutrophils: a graded response to membrane stimulation. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1910–1917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Black C. M., Doughty F., Beaman L. Role of superoxide dismutase and catalase as determinants of pathogenicity of Nocardia asteroides: importance in resistance to microbicidal activities of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):135–141. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.135-141.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Kermode J. C., Naccache P. H., Yassin R., Munoz J. J., Marsh M. L., Huang C. K., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin as a probe of neutrophil activation. Fed Proc. 1986 Jun;45(7):2151–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerknes R., Vindenes H., Pitkänen J., Ninnemann J., Laerum O. D., Abyholm F. Altered polymorphonuclear neutrophilic granulocyte functions in patients with large burns. J Trauma. 1989 Jun;29(6):847–855. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198906000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briheim G., Stendahl O., Dahlgren C. Intra- and extracellular events in luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.1-5.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg K., Tannis G., Steiner P. Detection of Bordetella pertussis associated with the alveolar macrophages of children with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4715–4719. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4715-4719.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnetzky W. T., Shuford W. W. Survival and growth of Yersinia pestis within macrophages and an effect of the loss of the 47-megadalton plasmid on growth in macrophages. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):234–241. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.234-241.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Gray D. F. Macrophage behaviour during the complaisant phase of murine pertussis. Immunology. 1969 Dec;17(6):875–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A. The human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1140–1147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer D. L., Eaton J. W. Phagocyte impotence caused by an invasive bacterial adenylate cyclase. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.6287574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig F. F., Lackie J. M., Parton R., Freer J. H. Interaction of Bordetella pertussis virulence components with neutrophils: effect on chemiluminescence induced by a chemotactic peptide and by intact bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Aug;134(8):2201–2211. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-8-2201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren C., Aniansson H., Magnusson K. E. Pattern of formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced luminol- and lucigenin-dependent chemiluminescence in human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):326–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.326-328.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg L. G., Goldman W. E. Histoplasma capsulatum fails to trigger release of superoxide from macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.29-34.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewanowich C. A., Melton A. R., Weiss A. A., Sherburne R. K., Peppler M. S. Invasion of HeLa 229 cells by virulent Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2698–2704. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2698-2704.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewanowich C. A., Sherburne R. K., Man S. F., Peppler M. S. Bordetella parapertussis invasion of HeLa 229 cells and human respiratory epithelial cells in primary culture. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1240–1247. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1240-1247.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzon V. L., Arondel J., Sansonetti P. J. Contribution of superoxide dismutase and catalase activities to Shigella flexneri pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):529–535. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.529-535.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Fiederlein R. L., Glasser L., Galgiani J. N. Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase: effects of affinity-purified adenylate cyclase on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.135-140.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Lochner J. E., Bigley R. H., Iglewski B. H. The effects of Legionella pneumophila toxin on oxidative processes and bacterial killing of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):328–334. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Hewlett E. L., Friedman R. L. Effects of adenylate cyclase toxin from Bordetella pertussis on human neutrophil interactions with Coccidioides immitis and Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):751–755. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.751-755.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. L., Rice J. L., McDonald P. J. Regulation of human neutrophil type 3 complement receptor (iC3b receptor) expression during phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Immunology. 1989 Aug;67(4):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. F., Cheers C. The steady state in cellular immunity. II. Immunological complaisance in murine pertussis. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Aug;45(4):417–426. doi: 10.1038/icb.1967.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschlag M. R., Suntharalingam K., Fikrig S. The effect of Chlamydia trachomatis on luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: requirements for opsonization. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1045–1051. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer T. J., Nelson K. E., Crispen R. G., Andersen B. R. Mycobacterium leprae fails to stimulate phagocytic cell superoxide anion generation. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):514–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.514-520.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopewell J. W., Holt L. B., Desombre T. R. An electron-microscope study of intracerebral infection of mice with low-virulence Bordetella pertussis. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Feb;5(1):154–157. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-1-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Influence of the Escherichia coli capsule on complement fixation and on phagocytosis and killing by human phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):82–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI109663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. The Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2108–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A. A., Jr, Ward R. A., Wellhausen S. R., McLeish K. R. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte function during hemodialysis: relationship to complement activation. Nephron. 1989;52(2):119–124. doi: 10.1159/000185613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossack R. E., Guerrant R. L., Densen P., Schadelin J., Mandell G. L. Diminished neutrophil oxidative metabolism after phagocytosis of virulent Salmonella typhi. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):674–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.674-678.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer D. L., Dreyfus L. A., Robertson D. C. Interaction of polymorphonuclear leukocytes with smooth and rough strains of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):737–742. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.737-742.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Roberts A. L., Finn T. M., Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. A new assay for invasion of HeLa 229 cells by Bordetella pertussis: effects of inhibitors, phenotypic modulation, and genetic alterations. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2516–2522. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2516-2522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leusch M. S., Paulaitis S., Friedman R. L. Adenylate cyclase toxin of Bordetella pertussis: production, purification, and partial characterization. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3621–3626. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3621-3626.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Catalase, superoxide dismutase, and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. In vitro and in vivo studies with emphasis on staphylococcal--leukocyte interaction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):561–566. doi: 10.1172/JCI107963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May M. E., Spagnuolo P. J. Evidence for activation of a respiratory burst in the interaction of human neutrophils with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2304–2307. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2304-2307.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouallem M., Farfel Z., Hanski E. Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin: intoxication of host cells by bacterial invasion. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3759–3764. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3759-3764.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naids F. L., Rest R. F. Stimulation of human neutrophil oxidative metabolism by nonopsonized Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4383–4390. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4383-4390.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. K., Robertson D. C. Ingestion and intracellular survival of Brucella abortus in human and bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):224–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.224-230.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe G., Valet G. Flow cytometric analysis of respiratory burst activity in phagocytes with hydroethidine and 2',7'-dichlorofluorescin. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 May;47(5):440–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Cabellos C., Burroughs M., Prasad S., Tuomanen E. Integrin-mediated localization of Bordetella pertussis within macrophages: role in pulmonary colonization. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1143–1149. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnur R. A., Newman S. L. The respiratory burst response to Histoplasma capsulatum by human neutrophils. Evidence for intracellular trapping of superoxide anion. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4765–4772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangrude G. J., Sacchi F., Hill H. R., Van Epps D. E., Daynes R. A. Inhibition of lymphocyte and neutrophil chemotaxis by pertussis toxin. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4135–4143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steed L. L., Setareh M., Friedman R. L. Intracellular survival of virulent Bordetella pertussis in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Oct;50(4):321–330. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szejda P., Parce J. W., Seeds M. S., Bass D. A. Flow cytometric quantitation of oxidative product formation by polymorphonuclear leukocytes during phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3303–3307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P., Kim Y., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Opsonic requirements for staphylococcal phagocytosis. Heterogeneity among strains. Immunology. 1977 Aug;33(2):191–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Lathigra R., Garbe T., Catty D., Young D. Genetic analysis of superoxide dismutase, the 23 kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):381–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



