Abstract
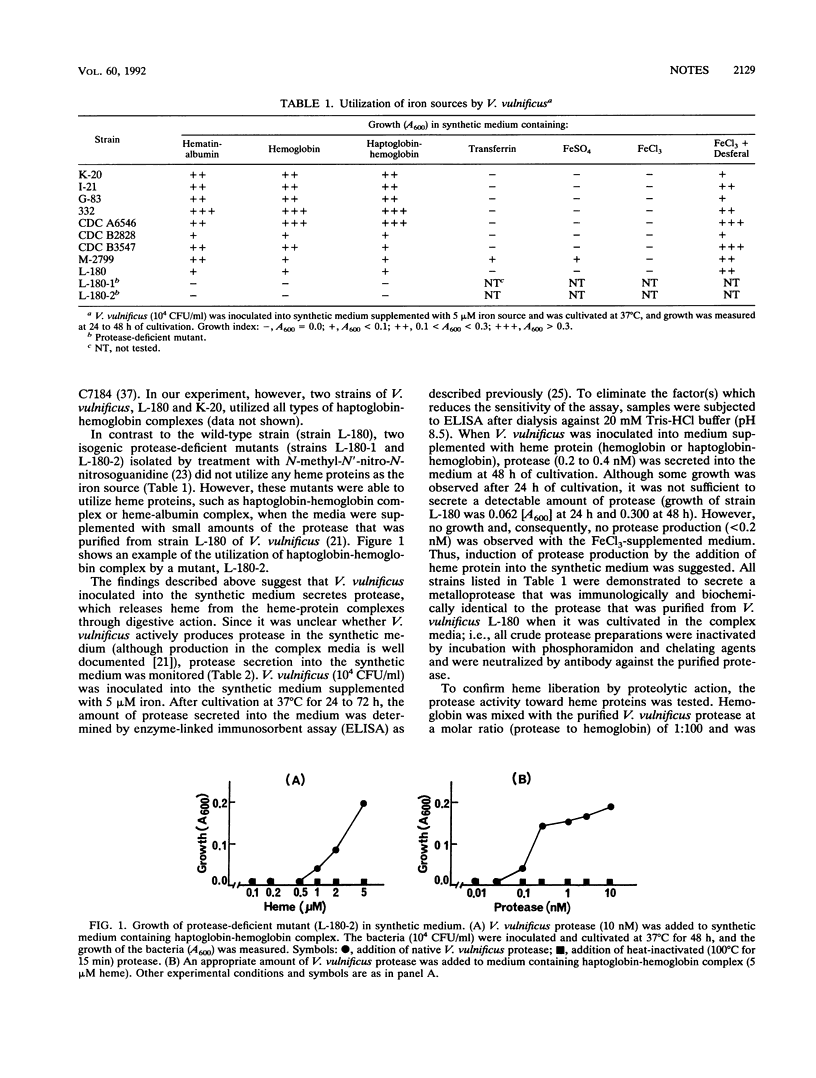
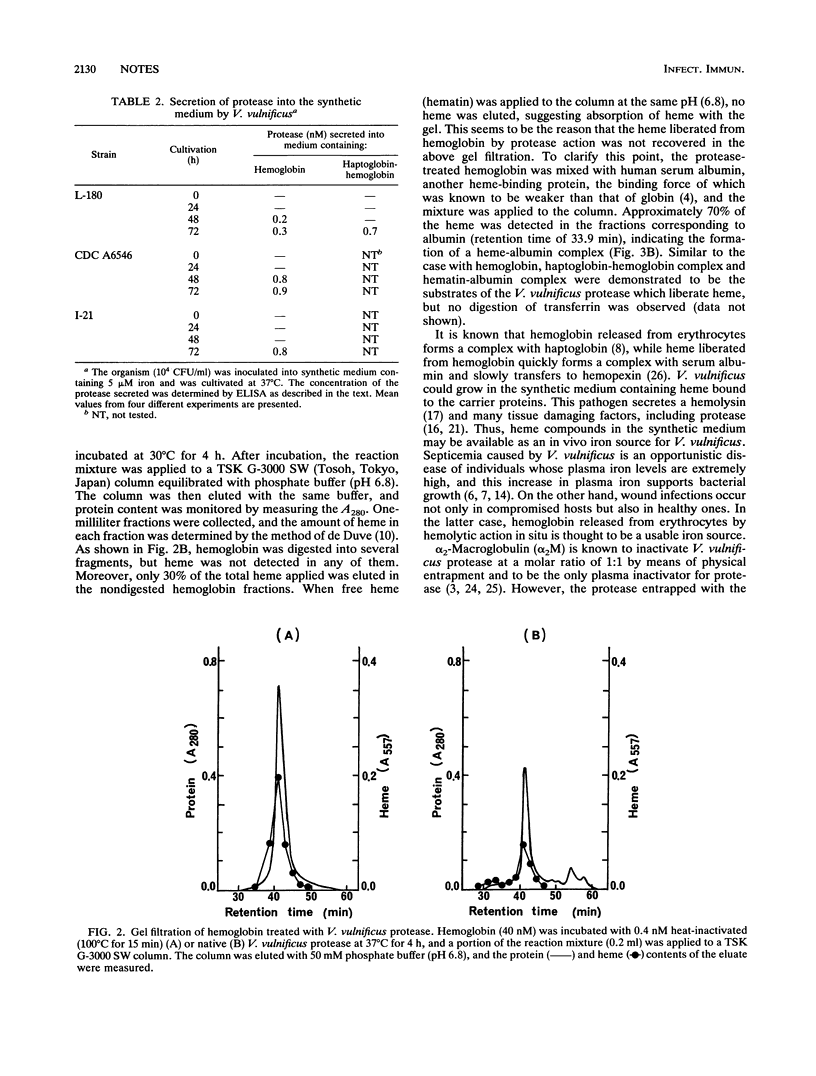
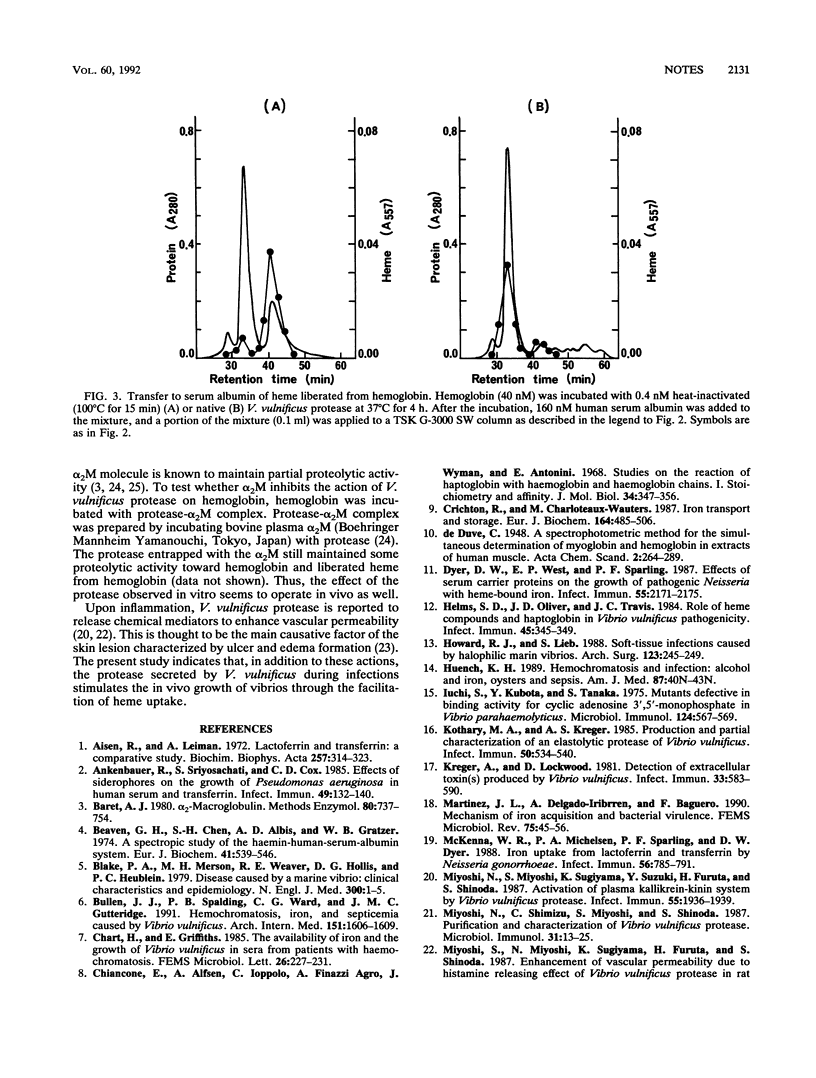
Clinical and environmental isolates of Vibrio vulnificus could grow in a synthetic medium supplemented with heme protein as the iron source. Protease-deficient mutants of the bacterium could not utilize any of the heme proteins in the synthetic medium, but the addition of purified V. vulnificus protease restored their growth. The protease digested all heme proteins tested and elicited heme liberation from the proteins. Furthermore, the induction of protease production by the heme proteins was demonstrated. These observations suggest that protease contributes to the efficient utilization of heme by V. vulnificus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Leibman A. Lactoferrin and transferrin: a comparative study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):314–323. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ankenbauer R., Sriyosachati S., Cox C. D. Effects of siderophores on the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in human serum and transferrin. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):132–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.132-140.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven G. H., Chen S. H., d' Albis A., Gratzer W. B. A spectroscopic study of the haemin--human-serum-albumin system. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 1;41(3):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Merson M. H., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G., Heublein P. C. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 4;300(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901043000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Spalding P. B., Ward C. G., Gutteridge J. M. Hemochromatosis, iron and septicemia caused by Vibrio vulnificus. Arch Intern Med. 1991 Aug;151(8):1606–1609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiancone E., Alfsen A., Ioppolo C., Vecchini P., Agrò A. F., Wyman J., Antonini E. Studies on the reaction of haptoglobin with haemoglobin and haemoglobin chains. I. Stoichiometry and affinity. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crichton R. R., Charloteaux-Wauters M. Iron transport and storage. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):485–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., West E. P., Sparling P. F. Effects of serum carrier proteins on the growth of pathogenic neisseriae with heme-bound iron. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2171–2175. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2171-2175.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms S. D., Oliver J. D., Travis J. C. Role of heme compounds and haptoglobin in Vibrio vulnificus pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):345–349. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.345-349.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Lieb S. Soft-tissue infections caused by halophilic marine vibrios. Arch Surg. 1988 Feb;123(2):245–249. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400260133018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Kubota Y., Tanaka S. Mutants defective in binding activity for cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):567–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.567-569.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothary M. H., Kreger A. S. Production and partial characterization of an elastolytic protease of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):534–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.534-540.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A., Lockwood D. Detection of extracellular toxin(s) produced by Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.583-590.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez J. L., Delgado-Iribarren A., Baquero F. Mechanisms of iron acquisition and bacterial virulence. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;6(1):45–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna W. R., Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F., Dyer D. W. Iron uptake from lactoferrin and transferrin by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.785-791.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi N., Miyoshi S., Sugiyama K., Suzuki Y., Furuta H., Shinoda S. Activation of the plasma kallikrein-kinin system by Vibrio vulnificus protease. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1936–1939. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1936-1939.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi N., Shimizu C., Miyoshi S., Shinoda S. Purification and characterization of Vibrio vulnificus protease. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(1):13–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi S., Shinoda S. Alpha-macroglobulin-like plasma inactivator for Vibrio vulnificus metalloprotease. J Biochem. 1991 Oct;110(4):548–552. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi S., Shinoda S. Inhibitory effect of alpha 2-macroglobulin on Vibrio vulnificus protease. J Biochem. 1989 Aug;106(2):299–303. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi S., Shinoda S. Role of the protease in the permeability enhancement by Vibrio vulnificus. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(10):1025–1032. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T., Liem H. H., Sutor R. P., Muller-Ebergard U. Transfer of heme from heme-albumin to hemopexin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 24;444(2):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90387-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidcock K. A., Wooten J. A., Daley B. A., Stull T. L. Iron acquisition by Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):721–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.721-725.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Gonzalez G. C. Receptors for transferrin in pathogenic bacteria are specific for the host's protein. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Feb;36(2):145–147. doi: 10.1139/m90-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the human lactoferrin-binding protein from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1144-1149.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. M., Oliver J. D. Siderophore production by Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):644–649. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.644-649.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriyosachati S., Cox C. D. Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition from transferrin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):885–891. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.885-891.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L. Protein sources of heme for Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):148–153. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.148-153.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Brenner F., Blake P. A. Clinical features and an epidemiological study of Vibrio vulnificus infections. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):558–561. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria-Meehan Z., Massad G., Simpson L. M., Travis J. C., Oliver J. D. Ability of Vibrio vulnificus to obtain iron from hemoglobin-haptoglobin complexes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):275–277. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.275-277.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


