Abstract
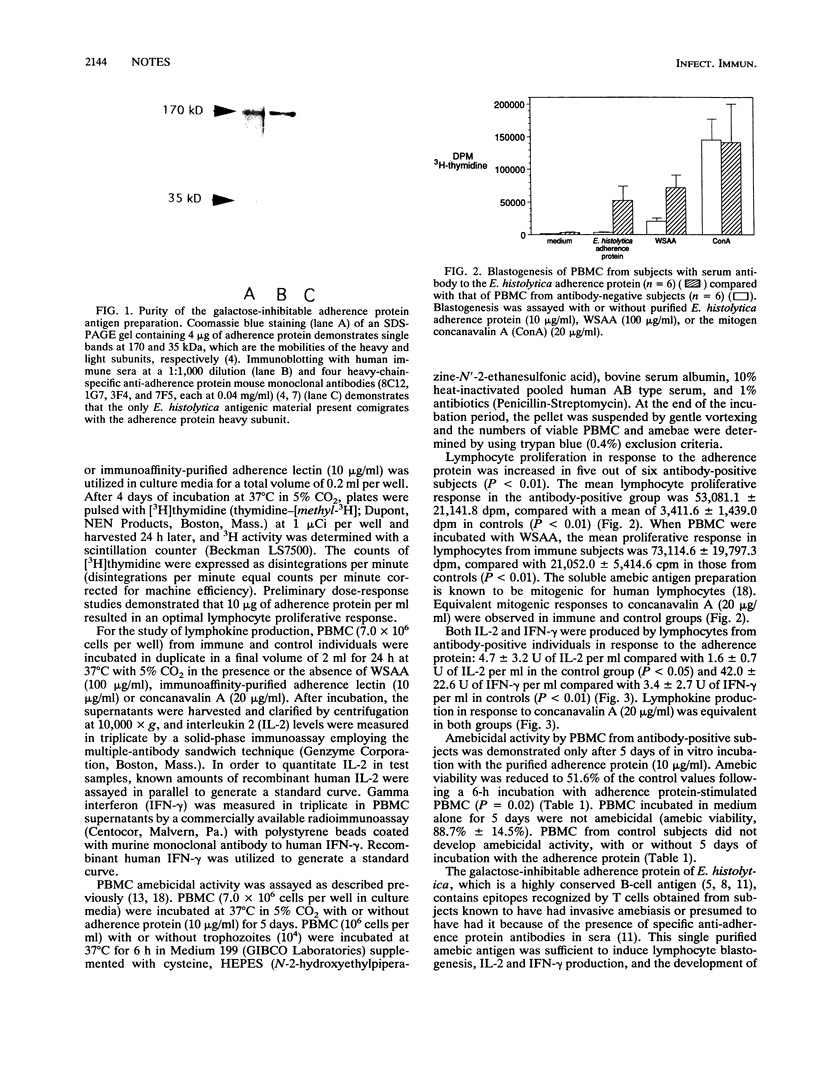
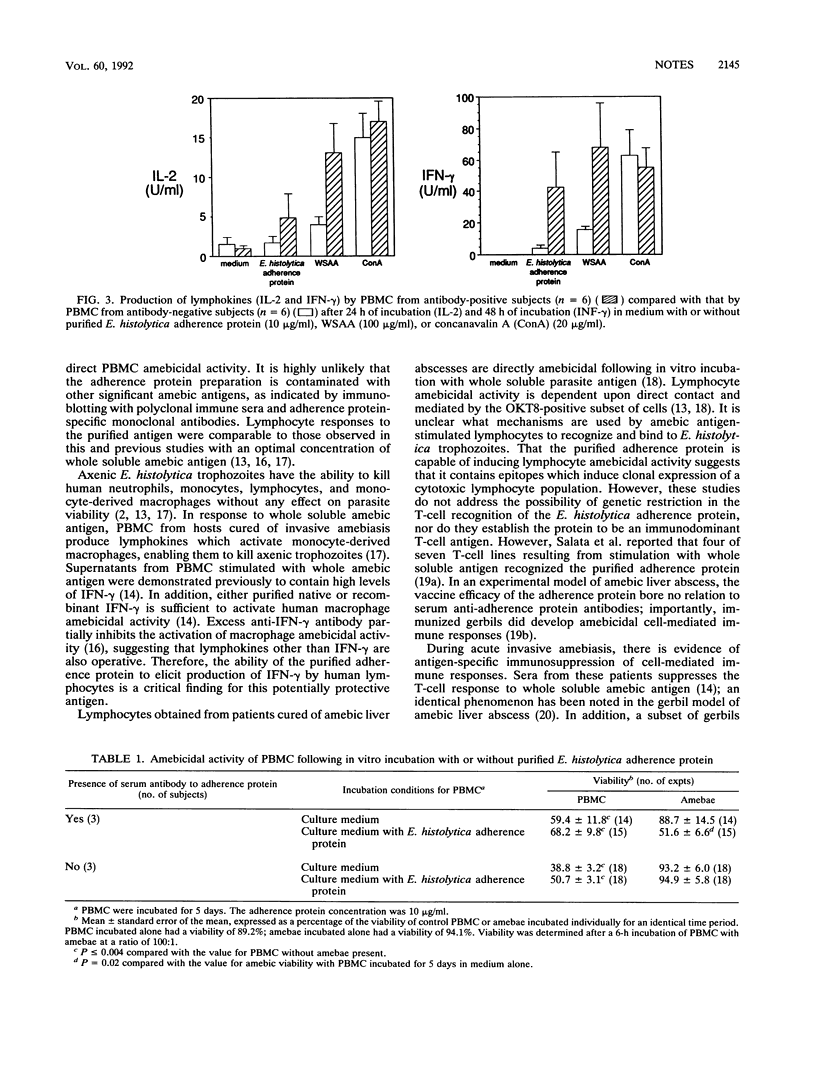
We studied human T-lymphocyte responses to the purified Entamoeba histolytica galactose-inhibitable adherence protein. Individuals having serum anti-adherence protein antibodies possess peripheral blood lymphocytes which demonstrate antigen-specific responses to the purified adherence protein (10 micrograms/ml) and whole soluble amebic antigen (100 micrograms/ml). This was determined by incorporation of [3H]thymidine (53,080 and 73,114 dpm, respectively) and by increased production of interleukin-2 and gamma interferon (42.0 and 67.5 U/ml, respectively) (P less than 0.05 for each in comparison with values for control lymphocyte responses). Lymphocytes from antiamebic antibody-positive subjects develop in vitro amebicidal activity only when incubated for 5 days with the purified adherence protein (P = 0.02). In conclusion, the E. histolytica galactose-inhibitable adherence protein elicits an in vitro amebicidal cell-mediated immune response, further supporting the potential for the use of this protein in a subunit amebiasis vaccine.
Full text
PDF

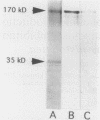
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chadee K., Petri W. A., Jr, Innes D. J., Ravdin J. I. Rat and human colonic mucins bind to and inhibit adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1245–1254. doi: 10.1172/JCI113199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brush J., Ravdin J. I., Sullivan J. A., Mandell G. L. Interaction between Entamoeba histolytica and human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):83–93. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann B. J., Torian B. E., Vedvick T. S., Petri W. A., Jr Sequence of a cysteine-rich galactose-specific lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3248–3252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Broman J., Healy G., Quinn T., Ravdin J. I. Antigenic stability and immunodominance of the Gal/GalNAc adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. Am J Med Sci. 1989 Mar;297(3):163–165. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198903000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Chapman M. D., Snodgrass T., Mann B. J., Broman J., Ravdin J. I. Subunit structure of the galactose and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3007–3012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Joyce M. P., Broman J., Smith R. D., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Recognition of the galactose- or N-acetylgalactosamine-binding lectin of Entamoeba histolytica by human immune sera. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2327–2331. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2327-2331.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Ravdin J. I. Protection of gerbils from amebic liver abscess by immunization with the galactose-specific adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.97-101.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Smith R. D., Schlesinger P. H., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Isolation of the galactose-binding lectin that mediates the in vitro adherence of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1238–1244. doi: 10.1172/JCI113198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman F. E., el-Hashimi W. K., Pittman J. C. Studies of human amebiasis. II. Light and electron-microscopic observations of colonic mucosa and exudate in acute amebic colitis. Gastroenterology. 1973 Oct;65(4):588–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Jackson T. F., Petri W. A., Jr, Murphy C. F., Ungar B. L., Gathiram V., Skilogiannis J., Simjee A. E. Association of serum antibodies to adherence lectin with invasive amebiasis and asymptomatic infection with pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):768–772. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Stanley P., Murphy C. F., Petri W. A., Jr Characterization of cell surface carbohydrate receptors for Entamoeba histolytica adherence lectin. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2179–2186. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2179-2186.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Cox J. G., Ravdin J. I. The interaction of human T-lymphocytes and Entamoeba histolytica: killing of virulent amoebae by lectin-dependent lymphocytes. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Mar;9(2):249–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Martinez-Palomo A., Canales L., Murray H. W., Trevino N., Ravdin J. I. Suppression of T-lymphocyte responses to Entamoeba histolytica antigen by immune sera. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3941–3946. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3941-3946.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Martinez-Palomo A., Murray H. W., Conales L., Trevino N., Segovia E., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Patients treated for amebic liver abscess develop cell-mediated immune responses effective in vitro against Entamoeba histolytica. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2633–2639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Ravdin J. I. The role of gamma interferon in the generation of human macrophages cytotoxic for Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jul;37(1):72–78. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Pearson R. D., Ravdin J. I. Interaction of human leukocytes and Entamoeba histolytica. Killing of virulent amebae by the activated macrophage. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):491–499. doi: 10.1172/JCI111998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Ravdin J. I. N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. II. Mitogenic activity for human lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):816–822. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Ravdin J. I. Review of the human immune mechanisms directed against Entamoeba histolytica. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):261–272. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Phillips B. P. Electron microscope studies of experimental Entamoeba histolytica infection in the guinea pig. I. Penetration of the intestinal epithelium by trophozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Jan;24(1):34–48. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1975.24.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Ebert F., Horstmann R. D. Primary structure of the 170-kDa surface lectin of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]