Abstract
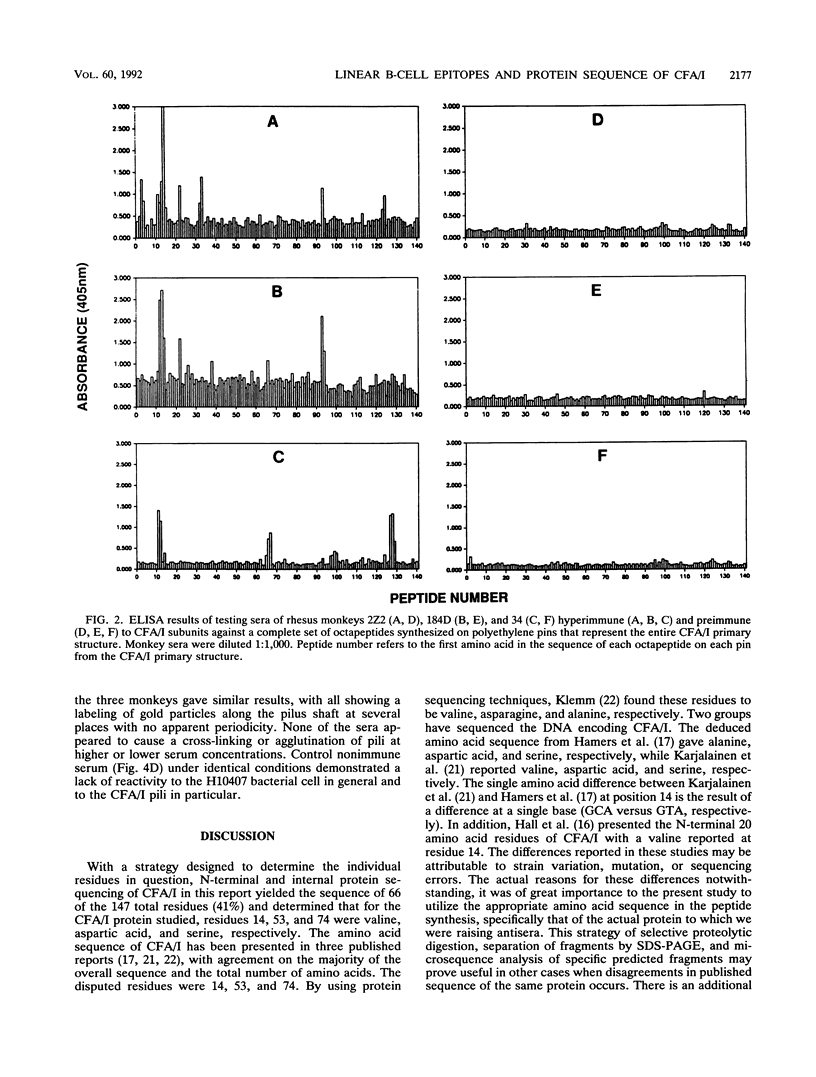
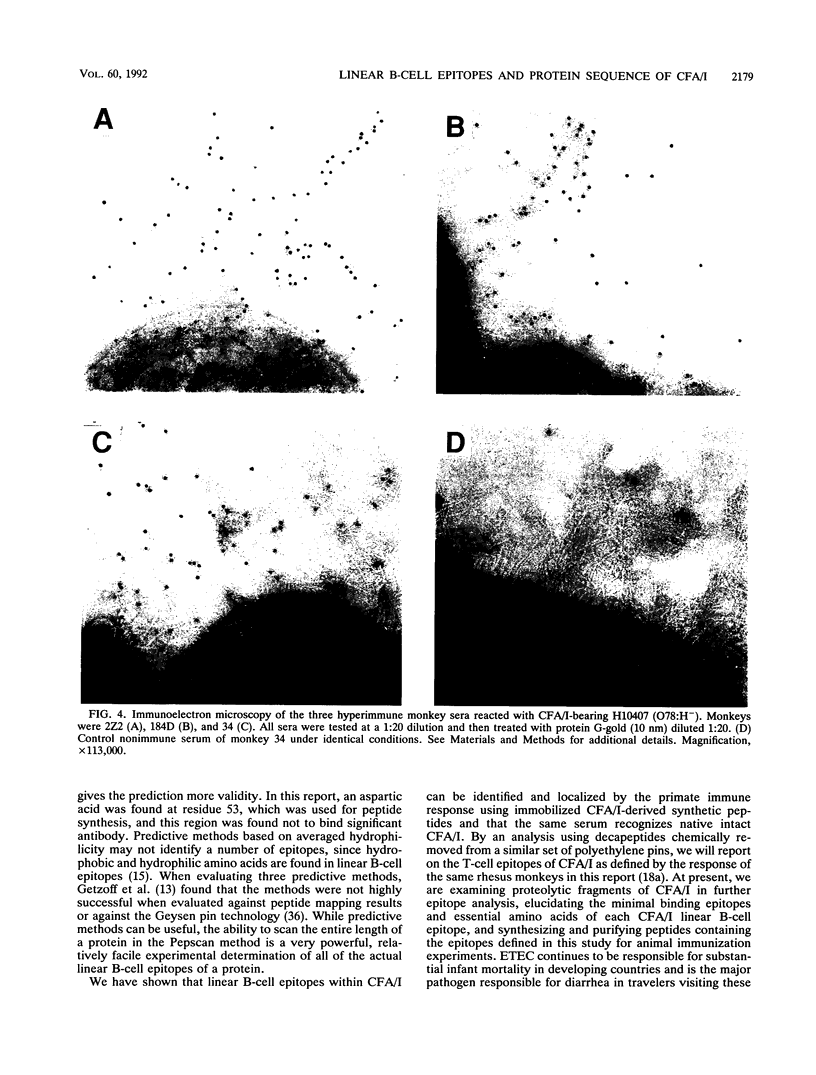
Colonization factor antigen I (CFA/I)-bearing strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) are responsible for a significant percentage of ETEC diarrheal disease worldwide whether the disease presents as infant diarrhea with high mortality or as traveler's diarrhea. CFA/I pili (fimbriae) are virulence determinants that consist of repeating protein subunits (pilin), are found in several ETEC serogroups, and promote attachment to human intestinal mucosa. While CFA/I pili are highly immunogenic, the antigenic determinants of CFA/I have not been defined. We wished to identify the linear B-cell epitopes within the CFA/I molecule as determined by primate response to the immunizing protein. To do this, we (i) resolved the discrepancies in the literature on the complete amino acid sequence of CFA/I by N-terminal and internal protein sequencing of purified and selected proteolytic fragments of CFA/I, (ii) utilized this sequence to synthesize 140 overlapping octapeptides covalently attached to polyethylene pins which represented the entire CFA/I protein, (iii) immunized three rhesus monkeys with multiple intramuscular injections of purified CFA/I subunit in Freund's adjuvant, and (iv) tested serum from each monkey for its ability to recognize the octapeptides in a capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Eight linear B-cell epitopes were identified; the region containing an epitope at amino acids 11 to 21 was strongly recognized by all three individual rhesus monkeys, while the amino acid stretches 22 to 29, 66 to 74, 93 to 101, and 124 to 136 each contained an epitope that was recognized by two of the three rhesus monkeys. The three other regions containing epitopes were recognized by one of the three individuals. The monkey antiserum to pilus subunits recognized native intact pili by immunogold labeling of CFA/I pili present on whole H10407 cells. Therefore, immunization with pilus subunits induces antibody that clearly recognizes both synthetic linear epitopes and intact pili. We are currently studying the importance of these defined epitope-containing regions as vaccine candidates.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atassi M. Z. Precise determination of the entire antigenic structure of lysozyme: molecular features of protein antigenic structures and potential of "surface-simulation" synthesis--a powerful new concept for protein binding sites. Immunochemistry. 1978 Dec;15(12):909–936. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M., Smyth C. J., Scott J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the major subunit of CS3 fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3297–3300. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3297-3300.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Boedeker E. C. Adherence of an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain, serotype O78:H11, to purified human intestinal brush borders. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1280–1284. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1280-1284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Taylor D. N., Changchawalit S., Smyth C. J., Twohig J., Rowe B. Plasmids coding for colonization factor antigens I and II, heat-labile enterotoxin, and heat-stable enterotoxin A2 in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):626–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.626-630.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. S., DuPont H. L. Detection and characterization of colonization factor of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):727–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.727-736.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Graham D. Y., Evans D. J., Jr Administration of purified colonization factor antigens (CFA/I, CFA/II) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to volunteers. Response to challenge with virulent enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):934–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getzoff E. D., Tainer J. A., Lerner R. A., Geysen H. M. The chemistry and mechanism of antibody binding to protein antigens. Adv Immunol. 1988;43:1–98. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Tainer J. A., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Alexander H., Getzoff E. D., Lerner R. A. Chemistry of antibody binding to a protein. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.3823878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. H., Maneval D. R., Jr, Collins J. H., Theibert J. L., Levine M. M. Purification and analysis of colonization factor antigen I, coli surface antigen 1, and coli surface antigen 3 fimbriae from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6372–6374. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6372-6374.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamers A. M., Pel H. J., Willshaw G. A., Kusters J. G., van der Zeijst B. A., Gaastra W. The nucleotide sequence of the first two genes of the CFA/I fimbrial operon of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1989 Apr;6(4):297–309. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalajakumari M. B., Thomas C. J., Halter R., Manning P. A. Genes for biosynthesis and assembly of CS3 pili of CFA/II enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: novel regulation of pilus production by bypassing an amber codon. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1685–1695. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M., Schödel F. Epitope mapping of the d flagellar antigen of Salmonella muenchen. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3330–3332. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3330-3332.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Leying H., Goroncy-Bermes P., Kroll H. P., Opferkuch W. Three-dimensional structure of fimbriae determines specificity of immune response. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):517–522. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.517-522.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen T. K., Evans D. G., So M., Lee C. H. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the colonization factor antigen I gene of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1126–1130. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1126-1130.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Mikkelsen L. Prediction of antigenic determinants and secondary structures of the K88 and CFA1 fimbrial proteins from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):41–45. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.41-45.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Primary structure of the CFA1 fimbrial protein from human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May 17;124(2):339–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H. D., Wiltfang J., Karas M., Neuhoff V., Hilschmann N. Gas-phase sequencing after electroblotting on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes assigns correct molecular weights to myoglobin molecular weight markers. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L. New knowledge on pathogenesis of bacterial enteric infections as applied to vaccine development. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):510–550. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.510-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Vidal Y., Klemm P., Svennerholm A. M. Monoclonal antibodies against different epitopes on colonization factor antigen I of enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1967–1972. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1967-1972.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzi L., Rustici M., Corti M., Cusi M. G., Valensin P. E., Bracci L., Santucci A., Soldani P., Spreafico A., Neri P. Structure of rubella E1 glycoprotein epitopes established by multiple peptide synthesis. Arch Virol. 1990;110(3-4):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01311295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Vidal Y., Calva J. J., Trujillo A., Ponce de León A., Ramos A., Svennerholm A. M., Ruiz-Palacios G. M. Enterotoxins and adhesins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: are they risk factors for acute diarrhea in the community? J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):442–447. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald K. L., Cohen M. L. Epidemiology of travelers' diarrhea: current perspectives. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 May-Jun;8 (Suppl 2):S117–S121. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_2.s117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles M. A., Wallace G. R., Clarke J. L. Multiple peptide synthesis (Pepscan method) for the systematic analysis of B- and T-cell epitopes: Application to parasite proteins. Parasitol Today. 1989 Dec;5(12):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(89)90307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieroni P., Worobec E. A., Paranchych W., Armstrong G. D. Identification of a human erythrocyte receptor for colonization factor antigen I pili expressed by H10407 enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1334–1340. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1334-1340.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., O'Hanley P., Lark D., Schoolnik G. K. Synthetic peptides corresponding to protective epitopes of Escherichia coli digalactoside-binding pilin prevent infection in a murine pyelonephritis model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1247–1251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., Raupach B., Szulczynski M., Marzillier J. Identification of linear B-cell determinants of pertussis toxin associated with the receptor recognition site of the S3 subunit. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1402–1408. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1402-1408.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan X. H., Ratnam M., Huang S. M., Smith P. L., Freisheim J. H. Mapping the antigenic epitopes of human dihydrofolate reductase by systematic synthesis of peptides on solid supports. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8022–8026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troalen F., Razafindratsita A., Puisieux A., Voeltzel T., Bohuon C., Bellet D., Bidart J. M. Structural probing of human lutropin using antibodies raised against synthetic peptides constructed by classical and multiple antigen peptide system approaches. Mol Immunol. 1990 Apr;27(4):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. K., Andrews G. P., Tall B. D., McConnell M. M., Levine M. M., Boedeker E. C. Characterization of CS4 and CS6 antigenic components of PCF8775, a putative colonization factor complex from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli E8775. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):164–173. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.164-173.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zijderveld F. G., Anakotta J., Brouwers R. A., van Zijderveld A. M., Bakker D., de Graaf F. K. Epitope analysis of the F4 (K88) fimbrial antigen complex of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1870–1878. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1870-1878.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]