Abstract
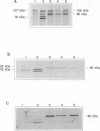
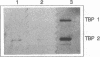
There is now considerable evidence to show that in the Neisseria and Haemophilus species, membrane receptors specific for either transferrin or lactoferrin are involved in the acquisition of iron from these glycoproteins. In Neisseria meningitidis, the transferrin receptor appears to consist of two proteins, one of which (TBP 1) has an M(r) of 95,000 and the other of which (TBP 2) has an M(r) ranging from 68,000 to 85,000, depending on the strain; TBP 2 binds transferrin after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and electroblotting, but TBP 1 does not do so. The relative contributions of these two proteins to the binding reaction observed with intact cells and to iron uptake are presently unknown. However, they are being considered as potential components of a group B meningococcal vaccine. Analogous higher- and lower-molecular-weight proteins associated with transferrin binding have been found in N. gonorrhoeae and Haemophilus influenzae. Previous work with polyclonal antibodies raised in mice with whole cells of iron-restricted N. meningitidis showed that the meningococcal TBP 2 exhibits considerable antigenic heterogeneity. Here, we report that antiserum against purified TBP 2 from one strain of N. meningitidis cross-reacts on immunoblotting with the TBP 2 of all meningococcal isolates examined, as well as with the TBP 2 of N. gonorrhoeae. This antiserum also cross-reacted with the TBP 2 of several strains of H. influenzae type b, thus showing the presence of common antigenic domains among these functionally equivalent proteins in different pathogens; no cross-reaction was detected with a purified sample of the human transferrin receptor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ala'Aldeen D. A., Davies H. A., Wall R. A., Borriello S. P. The 70 kilodalton iron regulated protein of Neisseria meningitidis is not the human transferrin receptor. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90409-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee-Bhatnagar N., Frasch C. E. Expression of Neisseria meningitidis iron-regulated outer membrane proteins, including a 70-kilodalton transferrin receptor, and their potential for use as vaccines. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2875–2881. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2875-2881.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton K. J., Biswas G. D., Tsai J., Adams J., Dyer D. W., Davis S. M., Koch G. G., Sen P. K., Sparling P. F. Genetic evidence that Neisseria gonorrhoeae produces specific receptors for transferrin and lactoferrin. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5225–5235. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5225-5235.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Griffiths E. Antigenic and molecular homology of the ferric enterobactin receptor protein of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1503–1509. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. Genetics and molecular biology of siderophore-mediated iron transport in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):517–530. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.517-530.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Stevenson P., Ray A. Antigenic and molecular heterogeneity of the transferrin-binding protein of Neisseria meningitidis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90408-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Stevenson P., Thorpe R., Chart H. Naturally occurring antibodies in human sera that react with the iron-regulated outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):808–813. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.808-813.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Towner K. J., Williams P. Isolation and characterisation of Haemophilus influenzae type b mutants defective in transferrin-binding and iron assimilation. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 15;61(2-3):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90566-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. S., Moxon E. R. Genetic and phenotypic variation in the capsulation and virulence of culture collection strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Microb Pathog. 1989 Dec;7(6):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez J. L., Delgado-Iribarren A., Baquero F. Mechanisms of iron acquisition and bacterial virulence. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;6(1):45–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna W. R., Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F., Dyer D. W. Iron uptake from lactoferrin and transferrin by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.785-791.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. J., Williams P. Siderophore-independent acquisition of transferrin-bound iron by Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 May;136(5):927–933. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-5-927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. J., Williams P. Utilization of transferrin-bound iron by Haemophilus species of human and porcine origins. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90378-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Kroll J. S., Granoff D. M., Moxon E. R., Brodeur B. R., Campos J., Dabernat H., Frederiksen W., Hamel J., Hammond G. Global genetic structure and molecular epidemiology of encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12(1):75–111. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven D. F., Donga J., Archibald F. S. Responses of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae to iron restriction: changes in the outer membrane protein profile and the removal of iron from porcine transferrin. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1083–1089. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padda J. S., Schryvers A. B. N-linked oligosaccharides of human transferrin are not required for binding to bacterial transferrin receptors. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2972–2976. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2972-2976.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Gonzalez G. C. Comparison of the abilities of different protein sources of iron to enhance Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2425–2429. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2425-2429.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B. Identification of the transferrin- and lactoferrin-binding proteins in Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):121–130. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Lee B. C. Comparative analysis of the transferrin and lactoferrin binding proteins in the family Neisseriaceae. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Mar;35(3):409–415. doi: 10.1139/m89-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the human lactoferrin-binding protein from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1144-1149.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the transferrin receptor from Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taetle R., Rhyner K., Castagnola J., To D., Mendelsohn J. Role of transferrin, Fe, and transferrin receptors in myeloid leukemia cell growth. Studies with an antitransferrin receptor monoclonal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):1061–1067. doi: 10.1172/JCI111768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Lopez F. Monoclonal antibody to transferrin receptor blocks transferrin binding and inhibits human tumor cell growth in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1175–1179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J., Dyer D. W., Sparling P. F. Loss of transferrin receptor activity in Neisseria meningitidis correlates with inability to use transferrin as an iron source. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3132–3138. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3132-3138.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. A., Davies H. A., Borriello S. P. Epitopes of serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis analysed in vitro and directly from cerebrospinal fluid. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Cellular regulation of iron assimilation. Q Rev Biol. 1989 Sep;64(3):261–290. doi: 10.1086/416359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser J. N., Maskell D. J., Butler P. D., Lindberg A. A., Moxon E. R. Characterization of repetitive sequences controlling phase variation of Haemophilus influenzae lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3304–3309. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3304-3309.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Geelen-van den Broek L., van Ham M. In vivo and in vitro expression of outer membrane components of Haemophilus influenzae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Apr;8(4):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90053-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]