Abstract
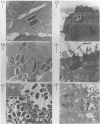
Although penetration of the epithelial mucosa has not been identified as a virulence mechanism in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC), we have found that this pathogen is capable of invading human intestinal cell lines. Classical ETEC strain H10407 was most invasive for epithelial cell lines derived from ileocecal and colonic tissues. An ETEC cosmid library was screened for clones that could direct E. coli HB101 to invade cultured human ileocecal epithelial cells (HCT 8 cells). Three invasive recombinant cosmid clones were isolated. These cosmids could direct HB101 invasion at an efficiency that was equal to or greater than that of the parent ETEC strain. The invasion cosmids also allowed for enhanced HCT 8 cell adherence by HB101. Electron micrographs of ETEC and recombinant HB101 strains revealed intracellular bacteria contained within endocytic vacuoles. Restriction endonuclease mapping and hybridization analyses showed that the three ETEC clones represent two separate invasion systems present in the parent ETEC strain and that both systems are chromosomally encoded. The parent ETEC strain and one cloned invasion system did not invade HeLa cells. Interestingly, one cloned invasion system was capable of directing HB101 to invade HeLa cells. Invasion of HCT 8 cells by recombinant HB101 strains and the parent ETEC strain was inhibited by cytochalasin D, indicating that the wild-type and both cloned invasion systems trigger an actin polymerization-dependent uptake process. It is not known whether the invasive phenotype of ETEC is relevant for enterotoxigenic disease. However, the parent ETEC strain, as well as recombinant HB101 strains, was capable of transcytosis through polarized HCT 8 monolayers. This transcytosis suggests that ETEC may cross the gut epithelium in vivo and that this invasion may have a previously unrecognized role in the disease process.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M., Candy D. C., Moon H. W. Plasmid-mediated adhesion in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):534–538. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302030-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banwell J. G., Gorbach S. L., Pierce N. F., Mitra R., Mondal A. Acute undifferentiated human diarrhea in the tropics. II. Alterations in intestinal fluid and electrolyte movements. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):890–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI106561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buysse J. M., Stover C. K., Oaks E. V., Venkatesan M., Kopecko D. J. Molecular cloning of invasion plasmid antigen (ipa) genes from Shigella flexneri: analysis of ipa gene products and genetic mapping. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2561–2569. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2561-2569.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darfeuille-Michaud A., Aubel D., Chauviere G., Rich C., Bourges M., Servin A., Joly B. Adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 in culture. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):893–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.893-902.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darfeuille-Michaud A., Aubel D., Forestier C., Rich C., Joly B. Facteurs intervenant dans les variations du pouvoir d'adhésion des colibacilles entérotoxinogènes (ETEC) aux entérocytes humains in vitro. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1991 Mar;39(3):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Epithelial cell invasion: an overlooked property of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) associated with the EPEC adherence factor. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):452–459. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Construction of an eae deletion mutant of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by using a positive-selection suicide vector. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4310–4317. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4310-4317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Fogh J. M., Orfeo T. One hundred and twenty-seven cultured human tumor cell lines producing tumors in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):221–226. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Hornick R. B. Invasive Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):641–644. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. L., Jerse A. E., Kaper J. B., Falkow S. Characterization of interactions of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O127:H6 with mammalian cells in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;164(4):693–703. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Distribution of the invA, -B, -C, and -D genes of Salmonella typhimurium among other Salmonella serovars: invA mutants of Salmonella typhi are deficient for entry into mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2901–2908. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2901-2908.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Chatterjee B. D., Jacobs B., Sack R. B. Acute undifferentiated human diarrhea in the tropics. I. Alterations in intestinal micrflora. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):881–889. doi: 10.1172/JCI106560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Plaut A. G., Nahas L., Weinstein L., Spanknebel G., Levitan R. Studies of intestinal microflora. II. Microorganisms of the small intestine and their relations to oral and fecal flora. Gastroenterology. 1967 Dec;53(6):856–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L. Microbial toxins and diarrhoeal diseases: introduction and overview. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;112:1–13. doi: 10.1002/9780470720936.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Kaper J. B. The eae gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli encodes a 94-kilodalton membrane protein, the expression of which is influenced by the EAF plasmid. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4302–4309. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4302-4309.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Baudry B., d'Hauteville H., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Cloning of plasmid DNA sequences involved in invasion of HeLa cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.164-171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Bliska J. B., Falkow S. Nucleotide sequence of the Yersinia enterocolitica ail gene and characterization of the Ail protein product. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1062–1069. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1062-1069.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hill W. E., Falkow S. The ail locus is found uniquely in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes commonly associated with disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.121-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. A., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens B and C: epitope location and characterization with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2933–2941. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2933-2941.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Wachsmuth I. K., Buxton A. E., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Mason E., Barrett F. F. Infantile diarrhea produced by heat-stable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):849–853. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlager T. A., Wanke C. A., Guerrant R. L. Net fluid secretion and impaired villous function induced by colonization of the small intestine by nontoxigenic colonizing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1337–1343. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1337-1343.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. L., Falkow S. Identification of regions on a 230-kilobase plasmid from enteroinvasive Escherichia coli that are required for entry into HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):225–229. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.225-229.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins W. A., Watrach A. M., Schmale J. D., Schultz R. M., Harris J. A. Cultural and antigenic properties of newly established cell strains derived from adenocarcinomas of the human colon and rectum. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1101–1110. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M., Buysse J. M., Vandendries E., Kopecko D. J. Development and testing of invasion-associated DNA probes for detection of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):261–266. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.261-266.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]