Abstract
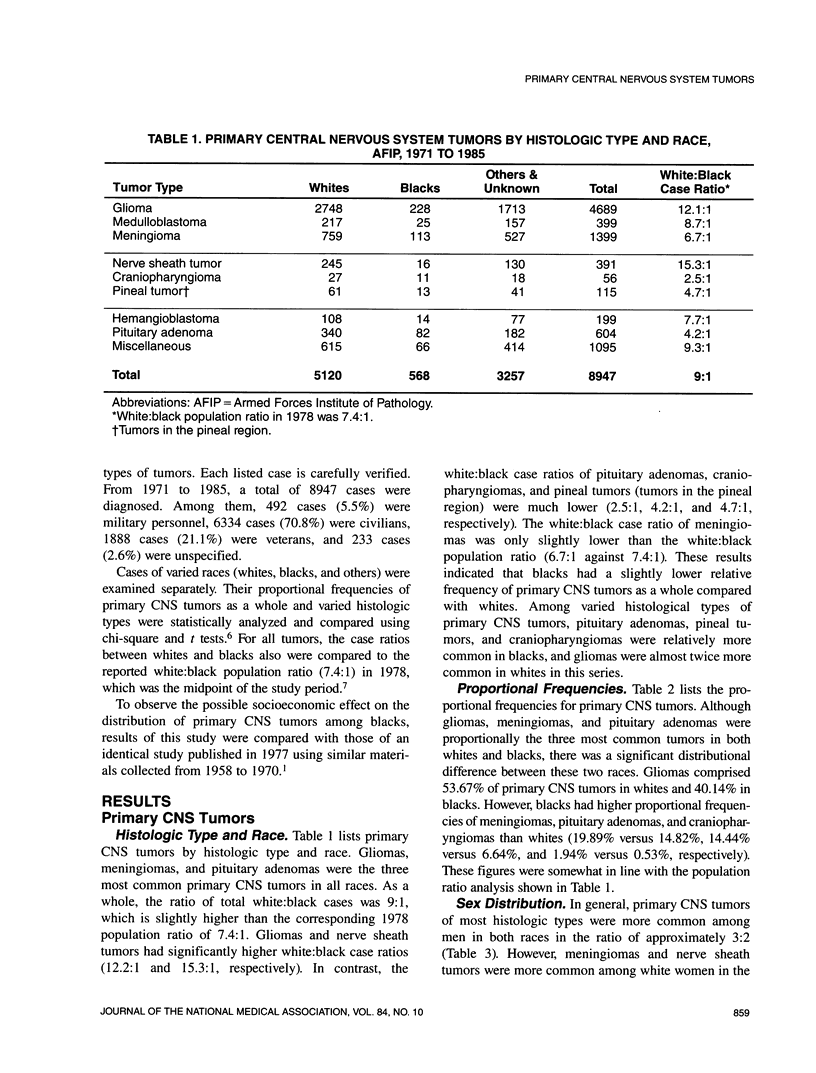
An ethnic analysis was made of 8947 cases of primary central nervous system (CNS) tumors seen at the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP), Washington, DC, from 1971 to 1985. Results showed a slightly higher frequency of primary CNS tumors in whites than in blacks with a white:black case ratio of 9:1 against the white:black population ratio in the United States of 7.4:1. Gliomas appeared to be twofold more frequent in whites than in blacks with a white:black case ratio of 12.1:1. However, meningiomas and pituitary adenomas were more common in blacks with a white:black case ratio of 6.7:1 and 4.2:1, respectively. When these results were compared with the results of a previous identical study using similar materials collected at AFIP from 1958 to 1970, the relative paucity of gliomas and higher frequency of meningiomas and pituitary adenomas in American blacks is again confirmed, thus re-emphasizing the importance of genetic factors in the genesis of primary CNS tumors. The remarkable decreasing white:black case ratio of primary CNS tumors as a whole (9:1 compared with 13.7:1) since 1970 probably reflects the socioeconomic improvement of American blacks during the same period.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng M. K. Brain tumors in the People's Republic of China: a statistical review. Neurosurgery. 1982 Jan;10(1):16–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi N. W., Schuman L. M., Gullen W. H. Epidemiology of primary central nervous system neoplasms. II. Case-control study. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 May;91(5):467–485. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan K. J., Kovi J., Earle K. M. The ethnic distribution of primary central nervous system tumors: AFIP, 1958 to 1970. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1977 Jan;36(1):41–49. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197701000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATSURA S., SUZUKI J., WADA T. A statistical study of brain tumors in the neurosurgical clinics in Japan. J Neurosurg. 1959 Sep;16:570–580. doi: 10.3171/jns.1959.16.5.0570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasili E. G., Cameron H. M., Ruberti R. F., Chopra S. A. Histopathology of brain tumours in the African in Kenya. Afr J Med Sci. 1973 Apr;4(2):99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepes J. J., Chen W. Y., Pang L. C., Kepes M. Tumors of the central nervous system in Taiwan, Republic of China. Surg Neurol. 1984 Aug;22(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(84)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy L. F. Brain tumours in Malawi, Rhodesia and Zambia. Afr J Med Sci. 1973 Oct;4(4):393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfredonia M. Tumours of the nervous system in the African in Eritrea (Ethiopia). Afr J Med Sci. 1973 Oct;4(4):383–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeku E. L., Osuntokun B. O., Adeloye A., Williams A. O. Tumors of the brain and its coverings. An African series. Int Surg. 1972 Oct;57(10):798–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogl S., Ohnums T., Perloff M., Holland J. F. Combination chemotherapy with adriamycin and cis-diamminedichloroplatinum in patients with neoplastic diseases. Cancer. 1976 Jul;38(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197607)38:1<21::aid-cncr2820380105>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen-qing H., Shi-ju Z., Qing-sheng T., Jian-qing H., Yu-xia L., Qing-zhong X., Zi-jun L., Wen-cui Z. Statistical analysis of central nervous system tumors in China. J Neurosurg. 1982 Apr;56(4):555–564. doi: 10.3171/jns.1982.56.4.0555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


