Abstract
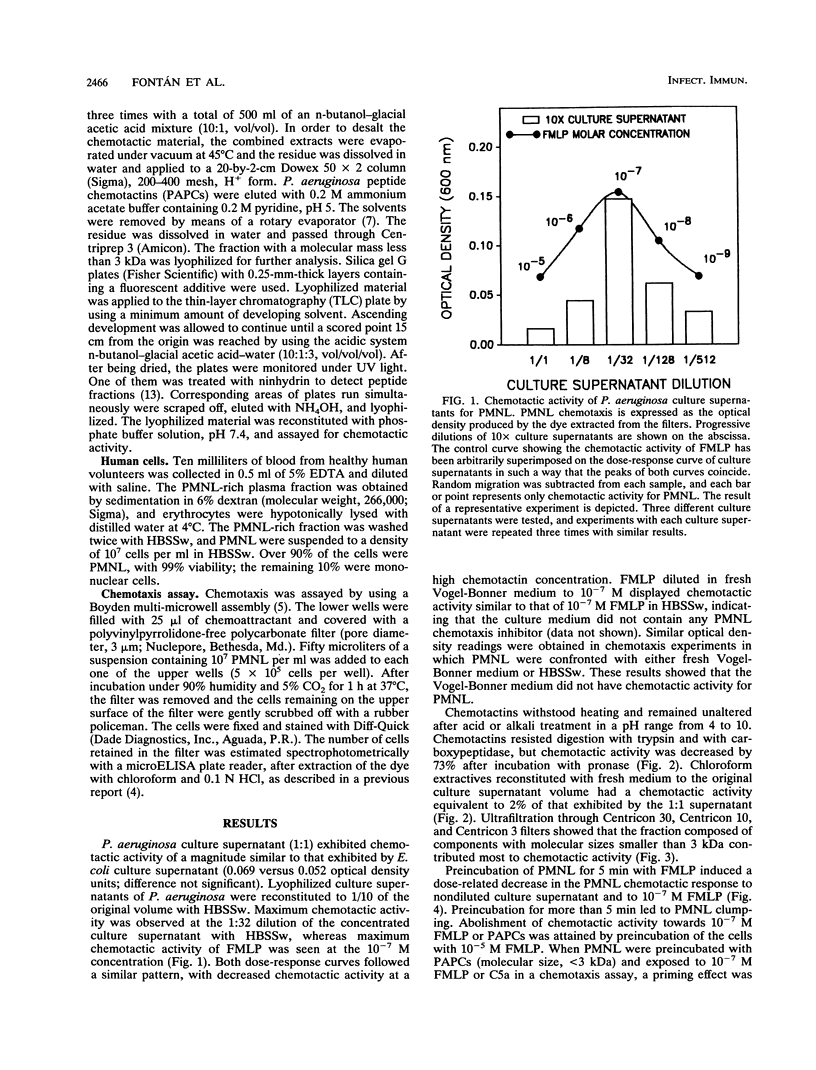
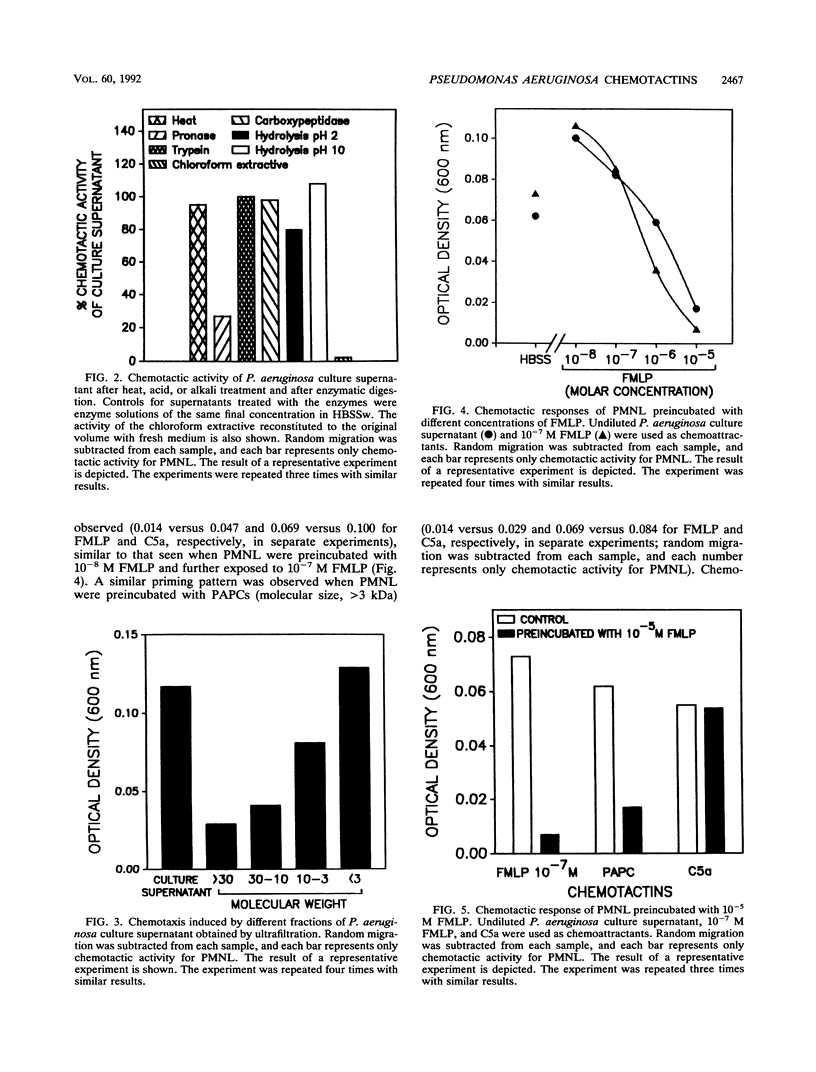
In a previous report, we showed that supernatants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures exhibit chemotactic activity for polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL). In this study, P. aeruginosa chemotactins were isolated, purified, and partially characterized. The organisms were cultured in Vogel-Bonner defined medium, and cultures were stopped in late log phase. Chemotactins withstood heating, remained unaltered after acid or alkali treatment in a pH range from 4 to 10, and resisted digestion by trypsin or carboxypeptidase, but chemotactic activity was decreased by 73% after incubation with pronase. Only 2% of the total chemotactic activity of culture supernatants could be extracted with chloroform. Chemotactins with molecular sizes less than 3 kDa constituted the largest contribution to the chemotactic activity of culture supernatants. Pretreatment of PMNL with 10(-5) M formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) inhibited chemotaxis towards FMLP and P. aeruginosa culture supernatants but not towards complement component C5a. In conclusion, the total chemotactic activity for PMNL of P. aeruginosa culture supernatants was due, almost exclusively, to chemotactins that have properties similar, if not identical, to those exhibited by formylmethionyl peptides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. A., Traynor A. E., Omann G. M., Jesaitis A. J. The chemotactic peptide receptor. A model for future understanding of chemotactic disorders. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Mar;2(1):33–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick V. S., Mellor D. M., Myers D. B., Selden A. C., Keshavarzian A., Broom M. F., Hobson C. H. Production of peptides inducing chemotaxis and lysosomal enzyme release in human neutrophils by intestinal bacteria in vitro and in vivo. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Jan;23(1):121–128. doi: 10.3109/00365528809093861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. M., Dunne M., Kamp D. W. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte- and Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced damage to a human pulmonary epithelial cell line. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):172–177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Falk W., Leonard E. J. Rapid quantitation of neutrophil chemotaxis: use of a polyvinylpyrrolidone-free polycarbonate membrane in a multiwell assembly. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Johnston R. B., Jr Tissue injury in inflammation. Oxidants, proteinases, and cationic proteins. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):669–674. doi: 10.1172/JCI112869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermode J. C., Muthukumaraswamy N., Freer R. J. Characteristics of binding of a potent chemotactic formyl tetrapeptide, formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanyl-phenylalanine, to the receptors on rabbit neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 May;43(5):420–428. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.5.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharazmi A., Fomsgaard A., Conrad R. S., Galanos C., Høiby N. Relationship between chemical composition and biological function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide: effect on human neutrophil chemotaxis and oxidative burst. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jan;49(1):15–20. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt G. C., Gadek J. E., Weiland J. E. Initial recruitment of neutrophils to alveolar structures in acute lung injury. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Apr;70(4):1575–1585. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.70.4.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. C., Wicha M. S., Yoon P., Mayo L., Boxer L. A. Laminin promotes the oxidative burst in human neutrophils via increased chemoattractant receptor expression. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2004–2011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rot A., Henderson L. E., Sowder R., Leonard E. J. Staphylococcus aureus tetrapeptide with high chemotactic potency and efficacy for human leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Feb;45(2):114–120. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.2.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Showell H. V., Corcoran B. A., Ward P. A., Smith E., Becker E. L. The isolation and partial characterization of neutrophil chemotactic factors from Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1831–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordelli D. O., Cerquetti M. C., Morris Hooke A., Bellanti J. A. Effect of chemotactins released by Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa on the murine respiratory tract. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):265–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.265-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordelli D. O., Zeligs B. J., Cerquetti M. C., Morris Hooke A., Bellanti J. A. Inflammatory responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in the murine lung. Eur J Respir Dis. 1985 Jan;66(1):31–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbeck M. J., Roth J. A. Neutrophil activation by recombinant cytokines. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11(4):549–568. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.4.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Test S. T. Effect of tumor necrosis factor on the generation of chlorinated oxidants by adherent human neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Aug;50(2):131–139. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Varani J. Mechanisms of neutrophil-mediated killing of endothelial cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Jul;48(1):97–102. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthen G. S., Haslett C., Rees A. J., Gumbay R. S., Henson J. E., Henson P. M. Neutrophil-mediated pulmonary vascular injury. Synergistic effect of trace amounts of lipopolysaccharide and neutrophil stimuli on vascular permeability and neutrophil sequestration in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jul;136(1):19–28. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G. G., Read P. W., Mandell G. L. Lipopolysaccharide releases a priming substance from platelets that augments the oxidative response of polymorphonuclear neutrophils to chemotactic peptide. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):690–696. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



