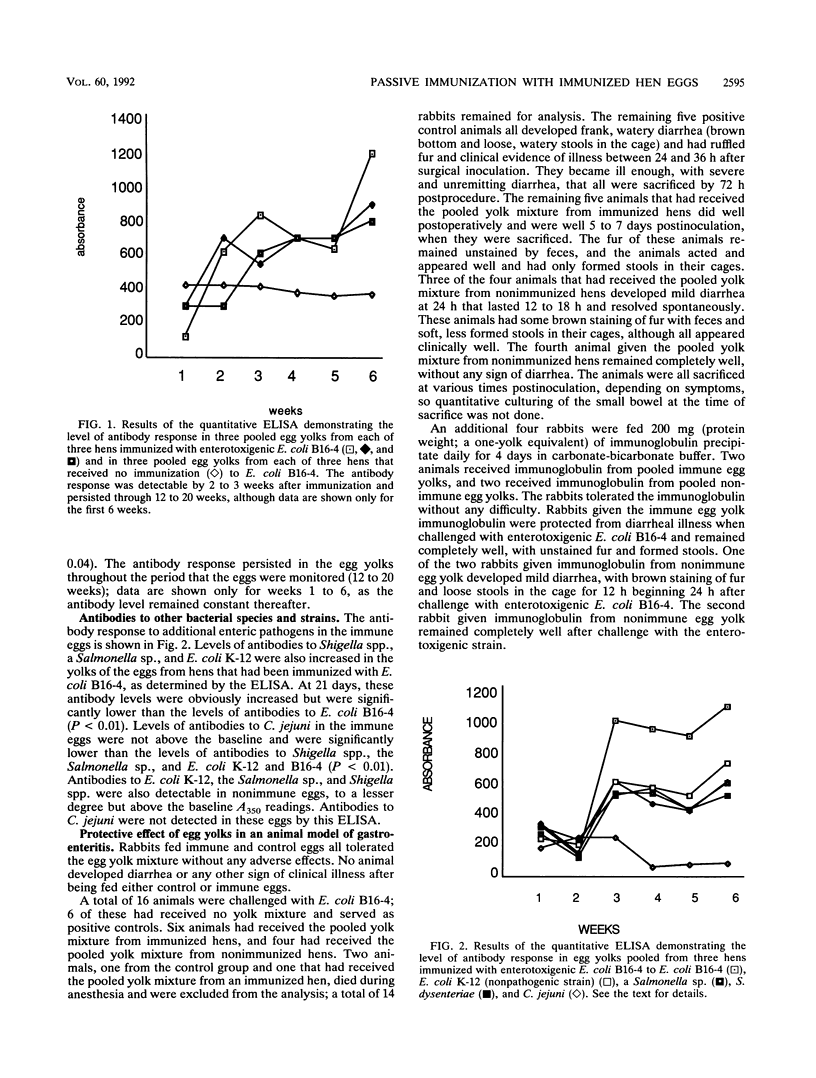
Abstract
White Leghorn hens were immunized with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli B16-4 with heat-labile enterotoxin and colonization factor antigen I in Freund's adjuvant. Specific antibodies were detected by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the serum after 8 days and in eggs after 10 days, with levels reaching peaks at 15 and 20 days after the first immunization, respectively. The protective effects of the egg yolk antibodies were tested in the rabbit reversible ileal tie model of diarrhea. Five control rabbits developed severe diarrhea within 72 h after inoculation with enterotoxigenic E. coli B16-4. Oral ingestion of egg yolks from immunized hens for 4 days prior to inoculation protected five rabbits from diarrhea after challenge with the same strain of E. coli. The rabbits showed no adverse effects from the ingestion of the egg yolks. Four rabbits fed control eggs were also afforded some protection in that three rabbits developed mild diarrhea and one rabbit remained entirely well. In vitro experiments showed that immunoglobulin from egg yolks interfered with the binding of E. coli to purified small bowel mucins; immunoglobulin from immunized hens reduced binding more than immunoglobulin from nonimmunized hens. These findings indicate that eggs from hens immunized with appropriate antigens have potential as a useful source of passive immunity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen T. S., Kett K., Krajci P., Kvale D., Rognum T. O., Scott H., Sollid L. M. Immunobiology and immunopathology of human gut mucosa: humoral immunity and intraepithelial lymphocytes. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1562–1584. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Stollar B. D. Antibodies to calf thymus RNA polymerase II from egg yolks of immunized hens. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):24–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadee K., Petri W. A., Jr, Innes D. J., Ravdin J. I. Rat and human colonic mucins bind to and inhibit adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1245–1254. doi: 10.1172/JCI113199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibl M. M., Wolf H. M., Fürnkranz H., Rosenkranz A. Prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in low-birth-weight infants by IgA-IgG feeding. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 7;319(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807073190101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. I., Svennerholm A. M., Stoll B. J., Khan M. R., Hossain K. M., Huq M. I., Holmgren J. Protection against cholera in breast-fed children by antibodies in breast milk. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 9;308(23):1389–1392. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306093082304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilpert H., Brüssow H., Mietens C., Sidoti J., Lerner L., Werchau H. Use of bovine milk concentrate containing antibody to rotavirus to treat rotavirus gastroenteritis in infants. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):158–166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hädge D., Ambrosius H. Evolution of low molecular weight immunoglobulins--IV. IgY-like immunoglobulins of birds, reptiles and amphibians, precursors of mammalian IgA. Mol Immunol. 1984 Aug;21(8):699–707. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jason J. M., Nieburg P., Marks J. S. Mortality and infectious disease associated with infant-feeding practices in developing countries. Pediatrics. 1984 Oct;74(4 Pt 2):702–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensenius J. C., Andersen I., Hau J., Crone M., Koch C. Eggs: conveniently packaged antibodies. Methods for purification of yolk IgG. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90333-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polson A., Coetzer T., Kruger J., von Maltzahn E., van der Merwe K. J. Improvements in the isolation of IgY from the yolks of eggs laid by immunized hens. Immunol Invest. 1985 Aug;14(4):323–327. doi: 10.3109/08820138509022667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Orlans E., Buttress N. Immunoglobulin classes in the hen's egg: their segregation in yolk and white. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jul;4(7):521–523. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Sack R. B., Froehlich J. L. Simple adult rabbit model for Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):739–747. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.739-747.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Serum levels of immune globulins in health and disease: a survey. Pediatrics. 1966 May;37(5):715–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoliar O. A., Pelley R. P., Kaniecki-Green E., Kkaus M. H., Carpenter C. C. Secretory IgA against enterotoxins in breast-milk. Lancet. 1976 Jun 12;1(7972):1258–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91735-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart C. A., Pietrzyk R. A., Furlanetto R. W., Green A. High affinity antibody from hen's eggs directed against the human insulin receptor and the human IGF-I receptor. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):142–150. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Losonsky G., Link H., Hoang Y., Guesry P., Hilpert H., Levine M. M. Protection by milk immunoglobulin concentrate against oral challenge with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 12;318(19):1240–1243. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805123181904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J. G., Oliveria M. A., Russo E. M., Maciel R. M., Pereira A. B. Egg yolk as a source of antibodies for human parathyroid hormone (hPTH) radioimmunoassay. J Immunoassay. 1984;5(1-2):121–129. doi: 10.1080/01971528408063002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke C. A., Cronan S., Goss C., Chadee K., Guerrant R. L. Characterization of binding of Escherichia coli strains which are enteropathogens to small-bowel mucin. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):794–800. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.794-800.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke C. A., Schorling J. B., Barrett L. J., Desouza M. A., Guerrant R. L. Potential role of adherence traits of Escherichia coli in persistent diarrhea in an urban Brazilian slum. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Oct;10(10):746–751. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199110000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J. K., May J. T. Anti-infective properties of breast milk. J Pediatr. 1979 Jan;94(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama H., Peralta R. C., Diaz R., Sendo S., Ikemori Y., Kodama Y. Passive protective effect of chicken egg yolk immunoglobulins against experimental enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection in neonatal piglets. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):998–1007. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.998-1007.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F., Wee S. B., Miskuff R., Vonderfecht S. Antibodies to rotaviruses in chickens' eggs: a potential source of antiviral immunoglobulins suitable for human consumption. Pediatrics. 1988 Feb;81(2):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rham O., Isliker H. Proteolysis of bovine immunoglobulins. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;55(1-6):61–69. doi: 10.1159/000231910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


